bar chart vs column chart
Associated Articles: bar chart vs column chart
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to bar chart vs column chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Bar Charts vs. Column Charts: A Deep Dive into Visible Knowledge Illustration

Bar charts and column charts are basic instruments in information visualization, used to check completely different classes of knowledge. Whereas usually used interchangeably, there are refined but essential distinctions between them, impacting their effectiveness in conveying info and influencing the general interpretation of the offered information. This text delves into the nuances of bar and column charts, exploring their functions, benefits, disadvantages, and greatest practices for efficient information communication.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Bars vs. Columns
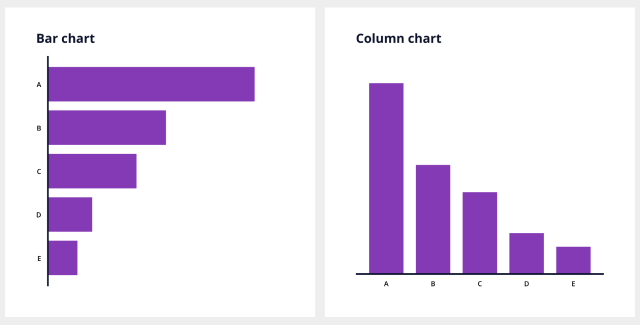
The core distinction between a bar chart and a column chart lies of their orientation:
-
Column charts (often known as vertical bar charts): Current information with rectangular bars extending vertically, with the classes represented alongside the horizontal (x) axis and the values alongside the vertical (y) axis.
-
Bar charts (often known as horizontal bar charts): Current information with rectangular bars extending horizontally, with the classes alongside the vertical (y) axis and the values alongside the horizontal (x) axis.
This seemingly minor distinction considerably influences the chart’s readability and the kind of information it greatest represents. The selection between a bar chart and a column chart just isn’t arbitrary; it must be strategically made based mostly on the precise information and the message you goal to convey.
Selecting the Proper Chart: When to Use Bar Charts and Column Charts
The choice of whether or not to make use of a bar chart or a column chart relies on a number of components:
1. Size of Class Labels:
-
Column charts: Are usually most well-liked when class labels are comparatively brief. Lengthy labels can litter the horizontal axis, making the chart tough to learn.
-
Bar charts: Excel when coping with longer class labels. The horizontal orientation permits for labels to be displayed clearly with out overlapping or requiring important textual content measurement discount. That is particularly helpful when coping with textual information like names of nations, cities, or product descriptions.
2. Knowledge Comparability:
-
Column charts: Are sometimes extra intuitive for evaluating the magnitudes of various classes. The vertical orientation naturally attracts the attention to the peak of the bars, making comparisons simpler. That is notably helpful when showcasing variations in numerical values.
-
Bar charts: Are equally efficient for evaluating magnitudes, however they’re notably advantageous when evaluating the relative rating or order of classes. The horizontal association facilitates simple rating from highest to lowest or vice versa.
3. Knowledge Quantity:
-
Column charts: Are usually extra appropriate for datasets with a reasonable variety of classes. Because the variety of classes will increase, the horizontal axis can change into crowded, impacting readability.
-
Bar charts: Can deal with a bigger variety of classes extra successfully than column charts, notably when mixed with methods like grouping or color-coding to boost visible group.
4. Emphasis on Particular Knowledge Factors:
-
Column charts: Are higher fitted to highlighting particular information factors or emphasizing the magnitude of explicit classes because of the pure concentrate on vertical peak.
-
Bar charts: Can spotlight particular information factors however are more practical at emphasizing the order or rating of classes, because of their horizontal association.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Bar Charts and Column Charts
Column Charts:
Benefits:
- Intuitive for Magnitude Comparability: The vertical orientation makes it simple to check the relative sizes of various classes.
- Appropriate for Quick Labels: Works effectively when class labels are concise.
- Extensively Acknowledged and Understood: A well-known chart kind, simply interpreted by a broad viewers.
Disadvantages:
- Cluttered with Lengthy Labels: Lengthy labels could make the chart tough to learn.
- Much less Efficient for Rating: Rating classes is much less intuitive in comparison with bar charts.
Bar Charts:
Benefits:
- Efficient for Lengthy Labels: Handles lengthy class labels with out sacrificing readability.
- Facilitates Rating: Permits for simple rating of classes based mostly on their horizontal place.
- Helpful for Emphasizing Order: Efficient for presenting information the place the order of classes is essential.
Disadvantages:
- Magnitude Comparability Can Be Much less Intuitive: Whereas nonetheless attainable, evaluating magnitudes would possibly require extra cautious statement than with column charts.
- Can Be Much less House-Environment friendly: Could require extra horizontal area, particularly with many classes.
Greatest Practices for Creating Efficient Bar and Column Charts:
- Select the Proper Chart Kind: Choose the chart kind (bar or column) based mostly on the info and the message you need to talk.
- Clear and Concise Labels: Use clear and concise labels for each axes and information classes.
- Acceptable Scaling: Select a scale that precisely represents the info with out distorting the relationships between classes. Keep away from truncating the y-axis to magnify variations.
- Constant Bar Width: Keep constant bar widths to stop misinterpretations.
- Efficient Shade Palette: Use a colour palette that’s each visually interesting and enhances information readability. Keep away from utilizing too many colours, notably if classes are quite a few.
- Knowledge Annotations: Add information labels or annotations to focus on essential information factors or traits.
- **






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into bar chart vs column chart. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!