C-Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Management Charts for Rely Information
Associated Articles: C-Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Management Charts for Rely Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to C-Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Management Charts for Rely Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
C-Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Management Charts for Rely Information
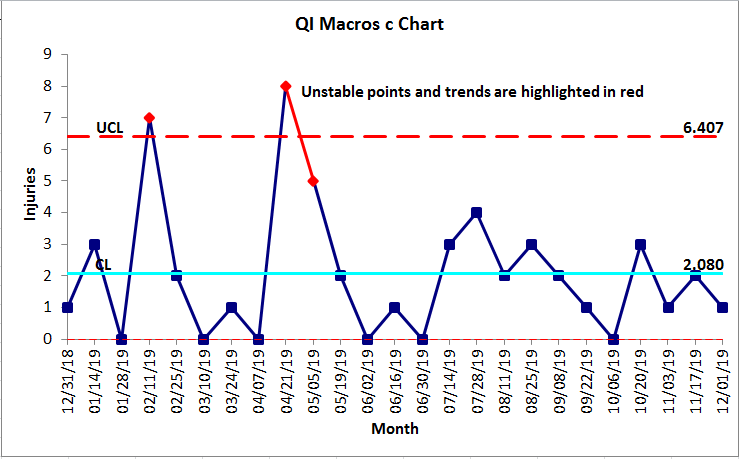
Management charts are important instruments in statistical course of management (SPC) for monitoring the soundness and consistency of a course of. Whereas X-bar and R charts are used for steady information, c-charts are particularly designed for analyzing depend information, representing the variety of defects or nonconformities present in a pattern of fixed measurement. Understanding assemble and interpret c-charts is essential for figuring out assignable causes of variation and enhancing course of efficiency. This text delves into a number of instance issues, illustrating the applying of c-charts and offering detailed options.
Understanding the C-Chart
A c-chart tracks the variety of defects (c) in a constant-sized pattern or unit of manufacturing. In contrast to p-charts (which observe the proportion of defects), c-charts are used when the pattern measurement stays constant. The important thing assumptions for a c-chart are:
- Fixed pattern measurement: The variety of items inspected in every pattern should stay the identical.
- Independence of samples: Defects in a single pattern shouldn’t affect the defects in one other.
- Random prevalence of defects: Defects ought to happen randomly all through the method.
- Poisson distribution: The variety of defects follows a Poisson distribution, which is acceptable for uncommon occasions.
The central line of a c-chart represents the common variety of defects (c̄), calculated as the overall variety of defects divided by the variety of samples. The management limits are calculated utilizing the usual deviation of the Poisson distribution, which is the sq. root of the common variety of defects (√c̄). The higher management restrict (UCL) and decrease management restrict (LCL) are sometimes set at three normal deviations from the central line:
- UCL = c̄ + 3√c̄
- LCL = c̄ – 3√c̄ (Observe: If LCL is damaging, it is set to 0)
Instance Issues and Options
Let’s work by means of a number of examples to solidify our understanding of c-charts.
Instance 1: Manufacturing Defects in Printed Circuit Boards
An organization manufactures printed circuit boards (PCBs). They examine 100 PCBs every day for defects. The variety of defects discovered over 20 days is proven under:
| Day | Defects (c) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12 |
| 2 | 15 |
| 3 | 10 |
| 4 | 11 |
| 5 | 13 |
| 6 | 14 |
| 7 | 9 |
| 8 | 16 |
| 9 | 12 |
| 10 | 11 |
| 11 | 10 |
| 12 | 13 |
| 13 | 15 |
| 14 | 12 |
| 15 | 14 |
| 16 | 9 |
| 17 | 11 |
| 18 | 13 |
| 19 | 10 |
| 20 | 12 |
Answer:
-
Calculate the common variety of defects (c̄):
Sum of defects = 246
Variety of samples (days) = 20
c̄ = 246 / 20 = 12.3 -
Calculate the usual deviation:
σ = √c̄ = √12.3 ≈ 3.51
-
Calculate the management limits:
UCL = c̄ + 3√c̄ = 12.3 + 3 3.51 = 22.83 ≈ 23
LCL = c̄ – 3√c̄ = 12.3 – 3 3.51 = 1.77 ≈ 0 (Since LCL can’t be damaging) -
Assemble the c-chart: Plot the variety of defects for every day, together with the central line (c̄ = 12.3), UCL (23), and LCL (0).
-
Interpretation: Study the chart for factors exterior the management limits or any non-random patterns. If factors fall exterior the boundaries, examine the assignable causes resulting in the elevated defects.
Instance 2: Software program Bugs in a Program
A software program growth group is testing a brand new program. They check 500 traces of code every day and file the variety of bugs discovered. The information for 15 days is:
| Day | Bugs (c) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 25 |
| 2 | 30 |
| 3 | 22 |
| 4 | 28 |
| 5 | 24 |
| 6 | 32 |
| 7 | 20 |
| 8 | 26 |
| 9 | 29 |
| 10 | 23 |
| 11 | 27 |
| 12 | 31 |
| 13 | 21 |
| 14 | 25 |
| 15 | 28 |
Answer: Observe the identical steps as in Instance 1:
-
Calculate c̄: Sum of bugs = 370, Variety of samples = 15, c̄ = 370/15 ≈ 24.67
-
Calculate the usual deviation: σ = √24.67 ≈ 4.97
-
Calculate the management limits:
UCL = 24.67 + 3 4.97 ≈ 40
LCL = 24.67 – 3 4.97 ≈ 9.7 (Spherical to 10 for sensible functions) -
Assemble the c-chart: Plot the info, central line, UCL, and LCL.
-
Interpretation: Analyze the chart for factors exterior the management limits or patterns.
Instance 3: Scratches on Painted Automotive Elements
A automotive producer paints automotive elements. They examine 50 elements every hour and depend the variety of scratches. The information for 10 hours is:
| Hour | Scratches (c) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 5 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 |
| 6 | 3 |
| 7 | 1 |
| 8 | 5 |
| 9 | 4 |
| 10 | 2 |
Answer:
-
Calculate c̄: Sum of scratches = 35, Variety of samples = 10, c̄ = 3.5
-
Calculate the usual deviation: σ = √3.5 ≈ 1.87
-
Calculate the management limits:
UCL = 3.5 + 3 1.87 ≈ 8.51 ≈ 9
LCL = 3.5 – 3 1.87 ≈ -2 (Set to 0) -
Assemble the c-chart: Plot the info, central line, UCL, and LCL.
-
Interpretation: Analyze the chart for out-of-control factors or patterns.
Deciphering the C-Chart and Taking Motion
As soon as the c-chart is constructed, the interpretation includes figuring out factors exterior the management limits or patterns that counsel the method shouldn’t be secure. Factors exterior the management limits point out a major shift within the variety of defects and warrant investigation. Frequent patterns to search for embrace:
- Tendencies: A constant upward or downward development suggests a gradual change within the course of.
- Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low defect counts might point out cyclical influences.
- Stratification: Clusters of factors above or under the central line point out potential subgroups or variations throughout the information.
When out-of-control factors or patterns are recognized, the subsequent step is to analyze the assignable causes. This may contain analyzing adjustments in supplies, tools, personnel, or the method itself. As soon as the foundation trigger is recognized and corrected, the method ought to be monitored once more utilizing a brand new c-chart to make sure stability.
Conclusion
C-charts are a useful software for monitoring processes the place the variety of defects is the important thing metric. By understanding the rules of c-chart development and interpretation, high quality management professionals can successfully establish and deal with sources of variation, resulting in improved course of efficiency and diminished defects. The examples offered on this article illustrate the sensible utility of c-charts and spotlight the significance of cautious information evaluation and investigation to make sure course of stability. Bear in mind to all the time think about the underlying assumptions of the c-chart earlier than making use of it to your information. If these assumptions should not met, different management charting methods could also be extra applicable.

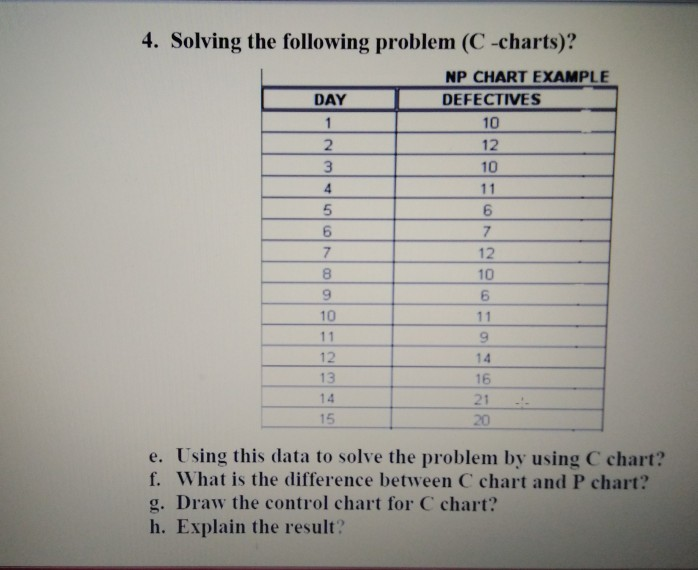

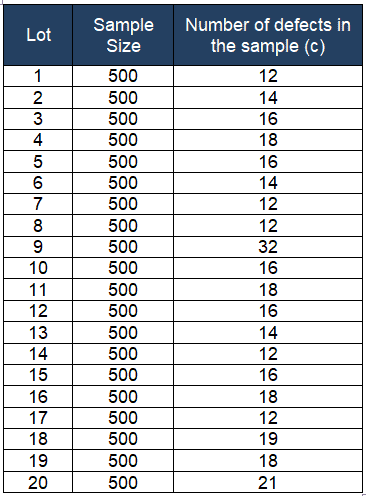
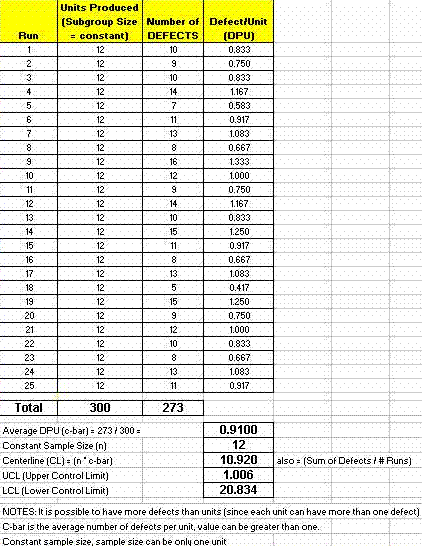


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into C-Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Management Charts for Rely Information. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!