Chart of Accounts in SAP: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Chart of Accounts in SAP: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Chart of Accounts in SAP: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart of Accounts in SAP: A Complete Information

The Chart of Accounts (CoA) in SAP is the spine of its monetary accounting performance. It is a hierarchical construction that organizes an organization’s accounts, enabling correct recording, reporting, and evaluation of monetary transactions. Understanding the CoA is essential for anybody working with SAP’s monetary modules, from configuring the system to decoding monetary statements. This text supplies an in depth overview of the SAP Chart of Accounts, exploring its construction, functionalities, and significance in monetary administration.
Understanding the Construction:
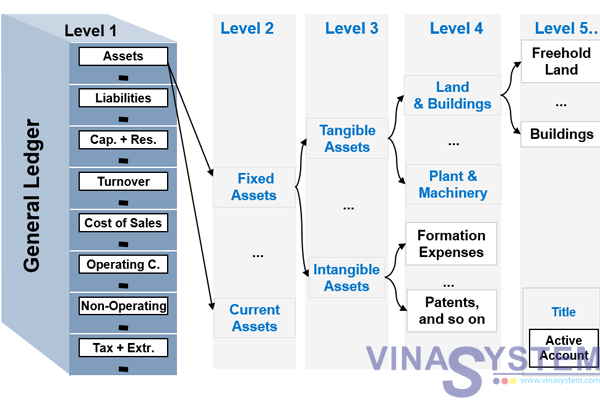
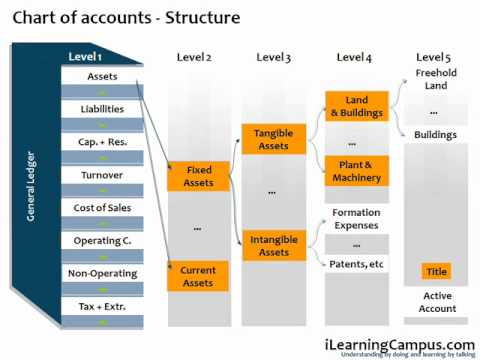
The SAP CoA is not a easy record of accounts; it is a subtle system designed to accommodate the various accounting wants of companies, no matter measurement or complexity. Its hierarchical construction permits for granular element whereas sustaining a transparent overview. Key components embody:
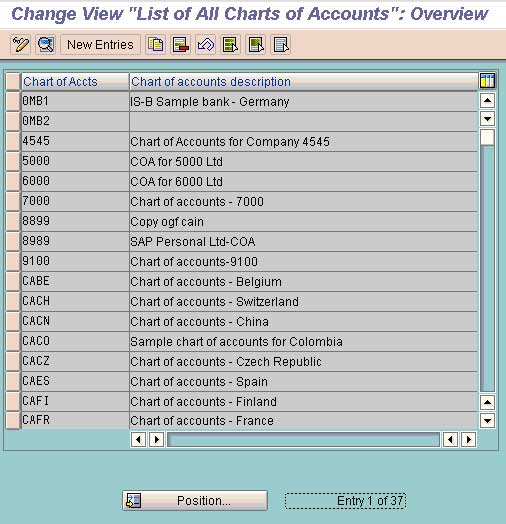
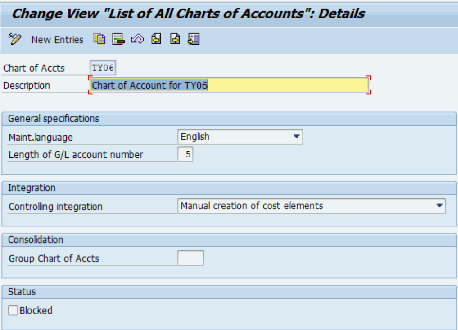
- Chart of Accounts (COA): The best degree, representing the complete accounting framework. An organization can have a number of CoAs, for instance, one for authorized reporting and one other for inside administration reporting.
- Firm Code: A authorized entity throughout the group. Every firm code have to be assigned a selected Chart of Accounts. This enables for unbiased accounting practices and reporting inside completely different authorized entities.
- Account Teams: These group accounts with comparable traits, resembling stability sheet accounts (property, liabilities, fairness), revenue and loss accounts (income, bills), or particular accounts (e.g., clearing accounts). Account teams outline the account’s properties, resembling whether or not it is a debit or credit score stability, and the permitted account sorts.
- G/L Accounts (Normal Ledger Accounts): The person accounts used to file monetary transactions. These are assigned to particular account teams and inherit their properties. The account quantity sometimes follows a structured format, permitting for straightforward identification and categorization (e.g., 100000 for money, 200000 for accounts receivable).
- Account Quantity Ranges: These outline the legitimate vary of numbers for accounts inside a selected account group. This ensures consistency and prevents unintended duplication.
- Subject Standing Variants: These management which fields are obligatory or elective for every account. This enables for flexibility in information entry relying on the account kind.
Sorts of Charts of Accounts:
SAP helps numerous sorts of CoAs to cater to completely different necessities:
- Working Chart of Accounts: That is the first CoA used for day by day enterprise transactions. It accommodates all the required accounts for recording monetary information.
- Group Chart of Accounts: Used for consolidated reporting throughout a number of firm codes. It supplies a summarized view of the monetary efficiency of the complete group.
- Nation-Particular Charts of Accounts: These are pre-configured CoAs designed to adjust to particular native accounting rules and requirements (e.g., US GAAP, IFRS). This ensures that monetary experiences are compliant with authorized necessities.
- Business-Particular Charts of Accounts: Much like country-specific CoAs, these are tailor-made to the wants of particular industries, incorporating accounts related to that sector.
Key Options and Functionalities:
The SAP CoA gives a number of key options that improve monetary administration:
- Account Numbering: The constant and structured numbering system ensures straightforward identification and classification of accounts, simplifying information evaluation and reporting.
- Account Group Task: This function simplifies account upkeep and ensures that accounts adhere to predefined traits.
- Subject Standing Variants: This enables for custom-made information entry screens, lowering errors and enhancing effectivity.
- Account Hierarchy: The hierarchical construction allows drill-down evaluation, permitting customers to look at detailed info whereas sustaining a high-level overview.
- Integration with Different Modules: The CoA is seamlessly built-in with different SAP modules, resembling Supplies Administration (MM), Gross sales and Distribution (SD), and Manufacturing Planning (PP), guaranteeing constant information circulation throughout the complete system.
- Reporting and Evaluation: The CoA supplies the muse for numerous monetary experiences, together with stability sheets, revenue statements, and money circulation statements. Its hierarchical construction facilitates detailed evaluation and pattern identification.
- Auditing and Compliance: The sturdy construction and controls embedded throughout the CoA assist keep information integrity and guarantee compliance with accounting rules.
Creating and Sustaining a Chart of Accounts:
Creating and sustaining a CoA in SAP includes a number of steps:
- Defining Account Teams: That is the preliminary step, the place you outline the properties and traits of various account teams.
- Defining Quantity Ranges: This step includes specifying the legitimate quantity ranges for accounts inside every account group.
- Creating G/L Accounts: This includes assigning accounts to their respective account teams and defining their properties.
- Defining Subject Standing Variants: This lets you customise the info entry screens for various accounts.
- Assigning the CoA to Firm Codes: This hyperlinks the CoA to particular authorized entities throughout the group.
- Common Upkeep: The CoA wants common upkeep to make sure its accuracy and relevance. This consists of including new accounts, modifying present ones, and deleting out of date accounts.
Significance of a Nicely-Outlined Chart of Accounts:
A well-defined and maintained CoA is crucial for a number of causes:
- Correct Monetary Reporting: It ensures the correct recording and reporting of monetary transactions, offering a dependable foundation for decision-making.
- Improved Knowledge Integrity: Its structured strategy minimizes errors and inconsistencies in monetary information.
- Enhanced Compliance: It facilitates compliance with accounting requirements and rules.
- Streamlined Processes: It simplifies monetary processes, lowering handbook effort and enhancing effectivity.
- Higher Resolution Making: The correct and available monetary info offered by a well-defined CoA allows higher knowledgeable enterprise choices.
Challenges and Issues:
Whereas the SAP CoA gives quite a few advantages, sure challenges should be thought-about:
- Complexity: The system’s complexity will be overwhelming for customers unfamiliar with its intricacies.
- Customization: Intensive customization can result in inconsistencies and difficulties in sustaining the system.
- Integration Points: Integration with different methods will be difficult, requiring cautious planning and execution.
- Knowledge Migration: Migrating information from legacy methods to SAP will be complicated and time-consuming.
Conclusion:
The Chart of Accounts in SAP is a elementary part of its monetary accounting performance. Its hierarchical construction, sturdy options, and integration with different modules make it a strong instrument for managing monetary information. By understanding its construction, functionalities, and implications, organizations can leverage its capabilities to enhance monetary reporting, improve information integrity, and make extra knowledgeable enterprise choices. Correct planning, implementation, and ongoing upkeep are essential for maximizing the advantages of the SAP CoA and guaranteeing its long-term effectiveness. Common critiques and updates are important to adapt to evolving enterprise wants and regulatory necessities. Investing in correct coaching for customers can also be important to make sure they will successfully make the most of the system and extract most worth from its capabilities.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Chart of Accounts in SAP: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!