Charting the Eye: A Complete Information to the Anatomy and Physiology of Imaginative and prescient
Associated Articles: Charting the Eye: A Complete Information to the Anatomy and Physiology of Imaginative and prescient
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Charting the Eye: A Complete Information to the Anatomy and Physiology of Imaginative and prescient. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Charting the Eye: A Complete Information to the Anatomy and Physiology of Imaginative and prescient

The human eye, a marvel of organic engineering, is accountable for our notion of the world round us. Its intricate construction, a posh interaction of tissues and fluids, permits us to understand mild, coloration, and depth, finally shaping our expertise of actuality. Understanding the attention’s anatomy is essential to comprehending the mechanisms of imaginative and prescient and the varied circumstances that may have an effect on it. This text serves as a complete information, using a conceptual "chart" method to elucidate the totally different parts and their features.
I. The Outer Layer: Safety and Refraction
Our journey begins with the outermost layer, primarily accountable for safety and the preliminary phases of sunshine refraction.
-
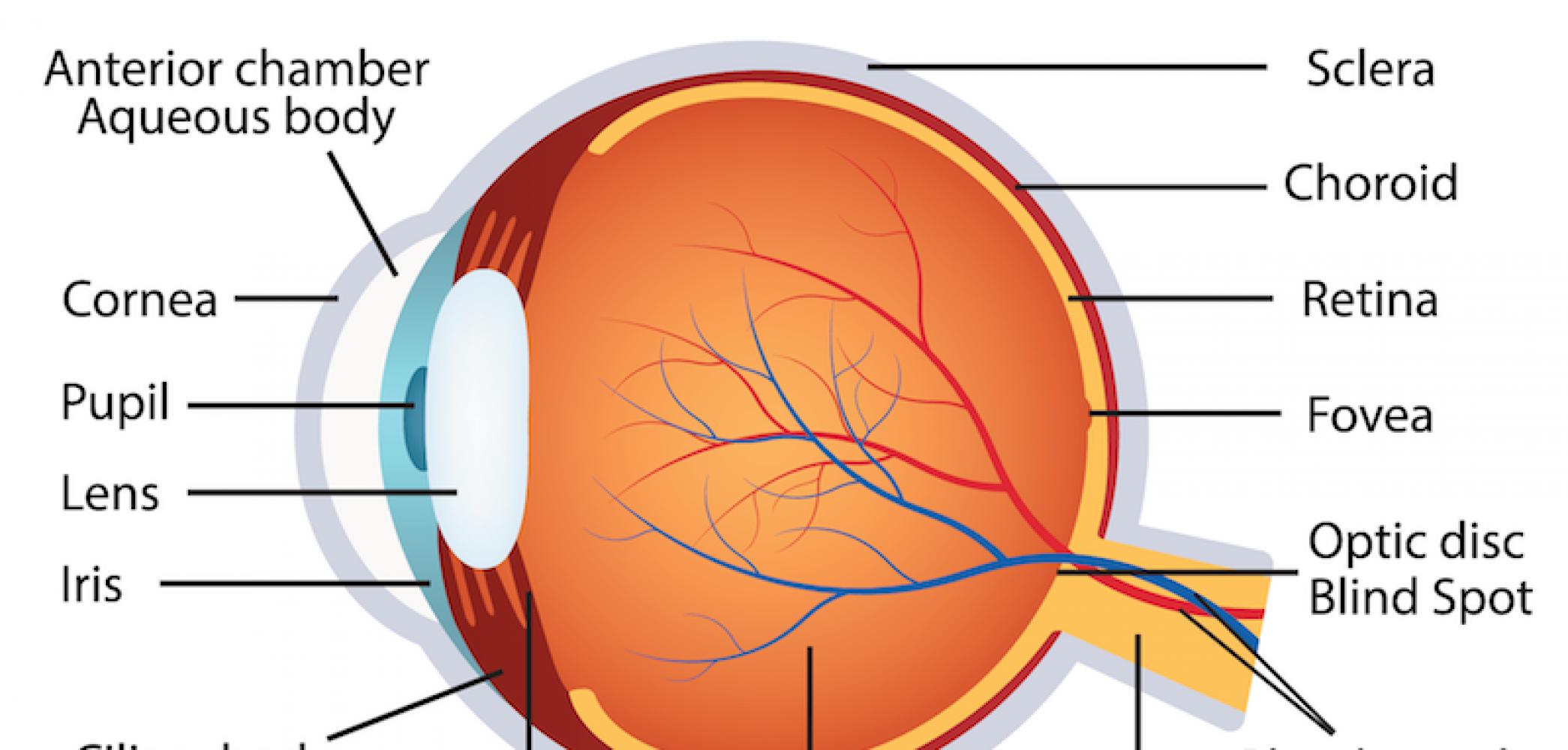
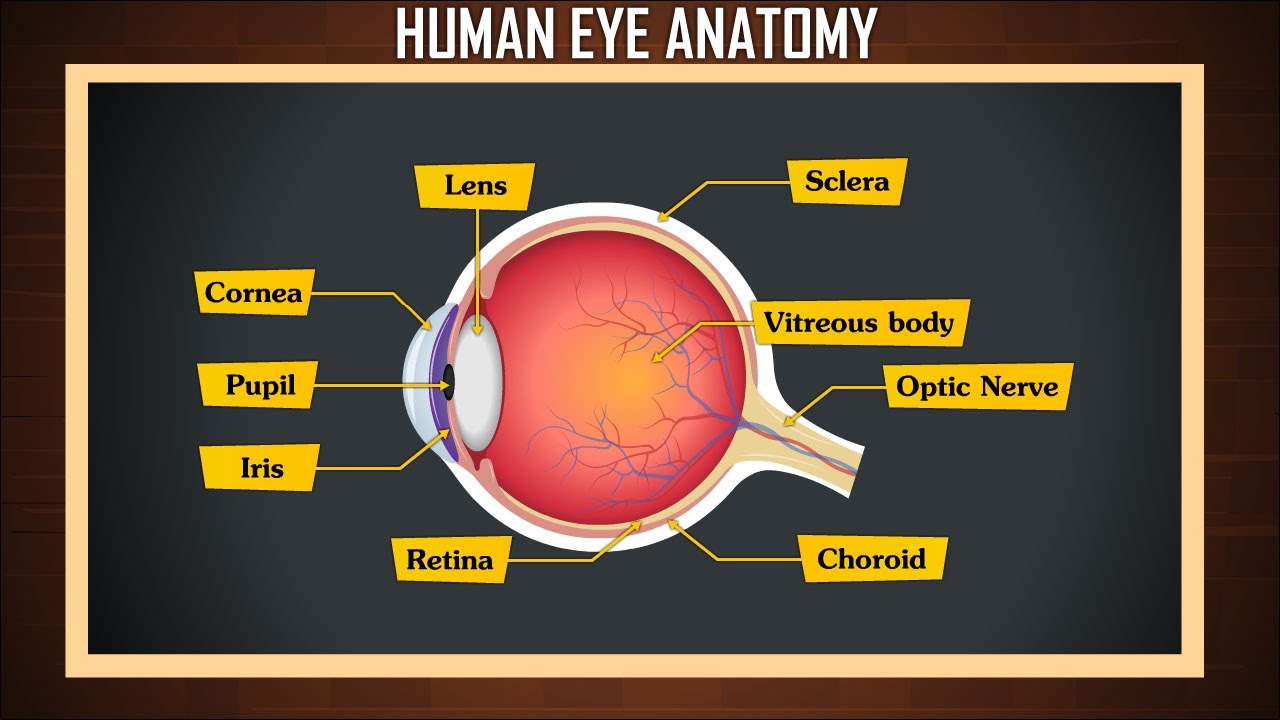
1. Cornea: This clear, dome-shaped construction types the anteriormost a part of the attention. It is extremely avascular (missing blood vessels), receiving its vitamins from the aqueous humor and tear movie. The cornea’s main perform is to refract (bend) incoming mild, contributing considerably to the attention’s focusing energy. Its easy, curved floor is essential for sharp picture formation. Circumstances affecting the cornea, reminiscent of keratitis (irritation) or corneal ulcers, can severely impair imaginative and prescient.
-
2. Sclera: The "white" of the attention, the sclera is a troublesome, fibrous layer that surrounds the cornea and extends posteriorly to kind the majority of the eyeball’s outer coat. It supplies structural assist and safety to the fragile inside constructions. The sclera’s comparatively opaque nature prevents mild scattering, making certain that mild is concentrated exactly onto the retina.
-
3. Conjunctiva: A skinny, clear mucous membrane lining the inside floor of the eyelids and masking the sclera (aside from the cornea). It produces mucus and tears, lubricating the attention and defending it from an infection. Conjunctivitis, generally referred to as pinkeye, is an irritation of the conjunctiva.
II. The Center Layer: Vascular Provide and Lodging
The center layer, or uvea, is richly vascularized, supplying vitamins and oxygen to the attention’s inside constructions. It additionally performs an important function in focusing.
-
4. Choroid: A extremely vascular layer situated between the sclera and the retina. Its wealthy blood provide nourishes the outer layers of the retina. The choroid’s darkish pigmentation absorbs stray mild, stopping inner reflections that might blur imaginative and prescient.
-
5. Ciliary Physique: A hoop-shaped construction situated on the junction of the iris and choroid. It accommodates the ciliary muscular tissues, which management the form of the lens, enabling lodging – the method of adjusting the attention’s focus for close to and much imaginative and prescient. The ciliary physique additionally secretes aqueous humor.
-
6. Iris: The coloured a part of the attention, the iris is a round, muscular diaphragm with a central opening referred to as the pupil. The iris accommodates two units of muscular tissues: the sphincter pupillae (round muscle) constricts the pupil in vivid mild, and the dilator pupillae (radial muscle) dilates the pupil in dim mild. This pupillary reflex regulates the quantity of sunshine coming into the attention, defending the retina from injury and optimizing imaginative and prescient in varied lighting circumstances.
III. The Interior Layer: Photoreception and Sign Transmission
The innermost layer, the retina, is the light-sensitive layer accountable for changing mild into electrical alerts which can be transmitted to the mind.
-
7. Retina: This advanced layer accommodates photoreceptor cells – rods and cones – accountable for detecting mild. Rods are accountable for imaginative and prescient in low mild circumstances and peripheral imaginative and prescient, whereas cones are accountable for coloration imaginative and prescient and visible acuity in vivid mild. The distribution of rods and cones will not be uniform throughout the retina; the fovea, a small despair within the macula, is densely filled with cones and is accountable for our sharpest imaginative and prescient.
-
8. Macula: A small, oval-shaped space within the heart of the retina, containing the fovea. The macula is accountable for central, high-resolution imaginative and prescient. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a typical explanation for imaginative and prescient loss, affecting the macula.
-
9. Optic Disc (Blind Spot): The purpose the place the optic nerve exits the attention. This space lacks photoreceptor cells, leading to a "blind spot" in our visible subject. Our mind compensates for this blind spot by filling within the lacking data from the encircling visible subject.
-
10. Optic Nerve: This nerve carries {the electrical} alerts generated by the photoreceptor cells to the mind for processing. Glaucoma, a situation characterised by elevated intraocular strain, can injury the optic nerve, resulting in imaginative and prescient loss.
IV. The Inside Chambers and Fluids:
The attention accommodates a number of chambers full of fluids that keep its form and supply vitamins.
-
11. Aqueous Humor: A transparent, watery fluid filling the anterior chamber (between the cornea and the lens) and the posterior chamber (between the iris and the lens). It supplies vitamins to the cornea and lens and helps keep intraocular strain. Glaucoma may end up from impaired drainage of aqueous humor.
-
12. Lens: A clear, biconvex construction situated behind the iris. It adjustments form to focus mild onto the retina, a course of referred to as lodging. Cataracts, a clouding of the lens, are a typical explanation for imaginative and prescient loss.
-
13. Vitreous Humor: A transparent, gel-like substance filling the posterior chamber of the attention (between the lens and the retina). It helps keep the form of the eyeball and retains the retina in place. Vitreous detachment, the place the vitreous humor separates from the retina, may cause floaters and, in extreme instances, retinal tears.
V. Accent Constructions:
A number of constructions surrounding the attention play vital roles in its safety and performance.
-
14. Eyelids: These movable folds of pores and skin shield the attention from damage and particles. In addition they assist distribute tears throughout the floor of the attention.
-
15. Eyelashes: These hairs alongside the sides of the eyelids present additional safety from mud and different international particles.
-
16. Eyebrows: These hairs above the eyes assist deflect sweat and different substances away from the eyes.
-
17. Lacrimal Equipment: This method produces and drains tears, which lubricate the attention and shield it from an infection. It contains the lacrimal glands (which produce tears), lacrimal ducts (which drain tears), and the nasolacrimal duct (which drains tears into the nasal cavity).
-
18. Extraocular Muscular tissues: Six muscular tissues surrounding the attention management its motion, permitting us to observe shifting objects and keep binocular imaginative and prescient.
VI. Visible Pathway and Processing:
The visible pathway begins with the photoreceptors within the retina and ends with the visible cortex within the mind.
-
19. Optic Chiasm: The purpose the place the optic nerves from every eye cross. This crossing ensures that data from the left visible subject of each eyes is processed by the precise facet of the mind, and vice versa.
-
20. Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN): A relay station within the thalamus that receives alerts from the optic nerve and transmits them to the visible cortex.
-
21. Visible Cortex: The world within the occipital lobe of the mind accountable for processing visible data. It interprets the alerts obtained from the LGN, permitting us to understand shapes, colours, and motion.
This complete overview, using a chart-like method, supplies an in depth understanding of the attention’s intricate anatomy and physiology. Every part performs an important function within the advanced technique of imaginative and prescient, and disruptions in any half can result in visible impairment. Additional exploration of particular constructions and associated pathologies can result in a deeper appreciation of this outstanding organ and the significance of eye well being.



/GettyImages-1148114654-eb0094c1478547508d71f14b056d4e09.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into Charting the Eye: A Complete Information to the Anatomy and Physiology of Imaginative and prescient. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!