Decoding the Dip: A Complete Information to Urine Dipstick Studying and Interpretation
Associated Articles: Decoding the Dip: A Complete Information to Urine Dipstick Studying and Interpretation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Dip: A Complete Information to Urine Dipstick Studying and Interpretation. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Dip: A Complete Information to Urine Dipstick Studying and Interpretation
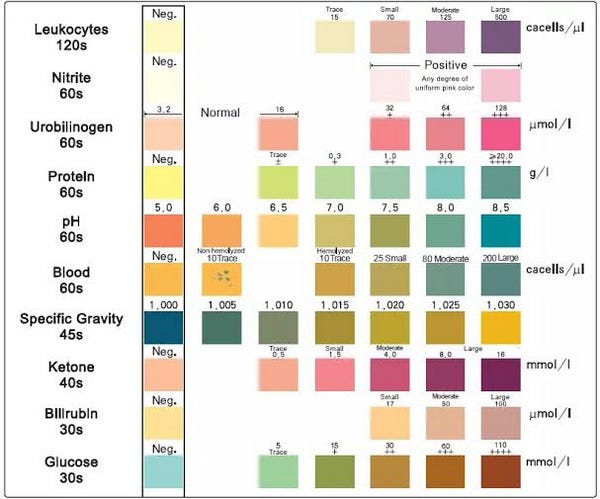
Urine dipsticks, also called urinalysis strips, are cheap and available instruments used for fast screening of assorted elements in urine. These strips comprise a number of reagent pads, every designed to detect a particular analyte, offering a fast overview of urinary well being. Whereas not a alternative for complete laboratory testing, understanding methods to learn and interpret urine dipstick outcomes may be invaluable for healthcare professionals and even people monitoring their very own well being. This text gives a complete information to urine dipstick studying charts, overlaying the assorted analytes examined, interpretation of outcomes, limitations of the check, and scientific significance of irregular findings.
Understanding the Elements of a Urine Dipstick
A typical urine dipstick comprises pads reactive to the next analytes:
-
pH: Measures the acidity or alkalinity of the urine. The traditional vary is usually 4.5 to eight.0. Variations can point out metabolic problems, urinary tract infections (UTIs), or dietary components.
-
Particular Gravity: Signifies the focus of dissolved solids within the urine. Regular values usually vary from 1.005 to 1.030. Deviations can recommend dehydration, kidney illness, or diabetes insipidus.
-
Protein: Detects the presence of protein, primarily albumin, within the urine. Regular urine comprises minimal protein. Important proteinuria can point out kidney injury, glomerulonephritis, or pre-eclampsia.
-
Glucose: Detects the presence of glucose within the urine. Usually, glucose is reabsorbed by the kidneys. Glycosuria can point out hyperglycemia, as seen in diabetes mellitus, or different metabolic problems.
-
Ketones: Detects the presence of ketone our bodies, byproducts of fats metabolism. Ketones seem in urine in periods of hunger, uncontrolled diabetes, or extended vomiting/diarrhea.
-
Blood: Detects the presence of crimson blood cells (RBCs) or hemoglobin within the urine. Hematuria may be indicative of UTIs, kidney stones, glomerulonephritis, or bladder most cancers.
-
Bilirubin: Detects the presence of bilirubin, a breakdown product of hemoglobin. Bilirubinuria suggests liver dysfunction or biliary obstruction.
-
Urobilinogen: Detects the presence of urobilinogen, a breakdown product of bilirubin. Elevated ranges can point out liver illness, hemolysis (destruction of crimson blood cells), or biliary obstruction.
-
Nitrite: Detects the presence of nitrite, a byproduct of bacterial metabolism. A constructive nitrite check typically signifies a UTI attributable to gram-negative micro organism. Nonetheless, a detrimental consequence doesn’t rule out a UTI.
-
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells): Detects the presence of leukocytes, indicating irritation or an infection within the urinary tract. Leukocyturia is commonly related to UTIs.
Studying the Urine Dipstick Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
After dipping the strip right into a well-mixed urine pattern, take away extra urine by gently blotting the sting in opposition to the container. Evaluate the colour adjustments on the reagent pads to the corresponding colour chart offered on the dipstick container or accompanying leaflet. The chart usually makes use of a colour gradient to symbolize completely different ranges of analyte focus. Most charts use a semi-quantitative scale, representing outcomes as detrimental (-), hint (tr), 1+, 2+, 3+, and 4+, with increased numbers indicating better focus. Some exams, like pH and particular gravity, have numerical scales.
Decoding the Outcomes:
The interpretation of outcomes ought to all the time be thought of inside the context of the affected person’s scientific presentation and different laboratory findings. A single irregular consequence doesn’t essentially point out a severe situation. Nonetheless, a mix of irregular findings can present priceless clues for analysis.
-
pH: Important deviations from the traditional vary might warrant additional investigation. Extremely acidic urine may be seen in metabolic acidosis, whereas extremely alkaline urine may be related to urinary tract infections attributable to sure micro organism.
-
Particular Gravity: Excessive particular gravity suggests dehydration or situations like diabetes mellitus. Low particular gravity can point out diabetes insipidus or extreme fluid consumption.
-
Protein: Presence of protein, particularly albumin, warrants additional investigation to evaluate kidney operate. Persistent proteinuria is usually a signal of power kidney illness.
-
Glucose: Presence of glucose normally signifies hyperglycemia, requiring additional evaluation for diabetes mellitus.
-
Ketones: Optimistic ketones recommend metabolic problems like uncontrolled diabetes, hunger, or extended vomiting/diarrhea.
-
Blood: Hematuria requires cautious analysis to find out the trigger, starting from benign situations like strenuous train to severe situations like kidney stones or most cancers. Microscopic hematuria (detected solely via microscopic examination) is commonly extra clinically vital than macroscopic hematuria (seen to the bare eye).
-
Bilirubin: Presence of bilirubin suggests liver dysfunction or biliary obstruction, requiring additional liver operate exams.
-
Urobilinogen: Elevated urobilinogen can point out liver illness, hemolysis, or biliary obstruction.
-
Nitrite: A constructive nitrite check strongly suggests a UTI attributable to gram-negative micro organism. Nonetheless, a detrimental consequence doesn’t rule out a UTI, as some micro organism don’t produce nitrite.
-
Leukocytes: Optimistic leukocytes recommend irritation or an infection within the urinary tract, typically related to UTIs.
Limitations of Urine Dipstick Testing:
Urine dipstick testing is a screening device, not a diagnostic check. It has a number of limitations:
-
Sensitivity and Specificity: Dipsticks might not detect low ranges of sure analytes, resulting in false-negative outcomes. They might additionally produce false-positive outcomes as a result of interference from different substances within the urine.
-
Qualitative vs. Quantitative: Most dipsticks present a semi-quantitative evaluation, indicating the presence and approximate focus of analytes however not the exact quantity. This requires additional quantitative laboratory testing for correct measurement.
-
Interference: Sure drugs, dietary components, and different substances can intrude with the accuracy of the check.
-
Interpretation Requires Scientific Context: Dipstick outcomes ought to all the time be interpreted at the side of the affected person’s scientific presentation, medical historical past, and different laboratory findings. An remoted irregular consequence is probably not clinically vital.
Scientific Significance of Irregular Findings:
Irregular findings on a urine dipstick can point out a variety of situations, together with:
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Indicated by constructive nitrite, leukocytes, and typically blood.
-
Kidney Illness: Indicated by proteinuria, hematuria, and adjustments in particular gravity.
-
Diabetes Mellitus: Indicated by glucosuria and ketonuria.
-
Liver Illness: Indicated by bilirubinuria and elevated urobilinogen.
-
Pre-eclampsia: Indicated by proteinuria and typically hematuria.
-
Bladder Most cancers: Indicated by hematuria.
-
Kidney Stones: Indicated by hematuria and typically adjustments in pH.
-
Dehydration: Indicated by excessive particular gravity.
Conclusion:
Urine dipstick testing is a priceless device for fast screening of urinary abnormalities. Understanding methods to learn and interpret the outcomes, together with appreciating the constraints of the check, is essential for healthcare professionals and people monitoring their well being. Whereas a urine dipstick can present priceless clues, it ought to be thought of a screening device, and additional investigations, together with microscopic examination and extra complete laboratory testing, are sometimes needed to substantiate diagnoses and information applicable administration. At all times seek the advice of with a healthcare skilled for correct interpretation of outcomes and steerage on additional diagnostic steps. Self-diagnosis primarily based solely on urine dipstick outcomes is strongly discouraged.

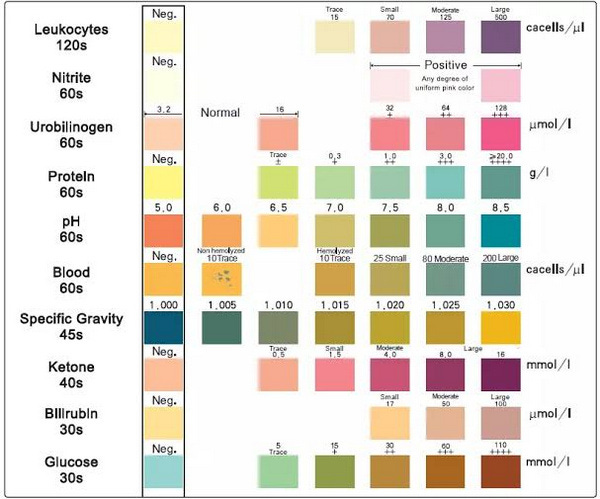

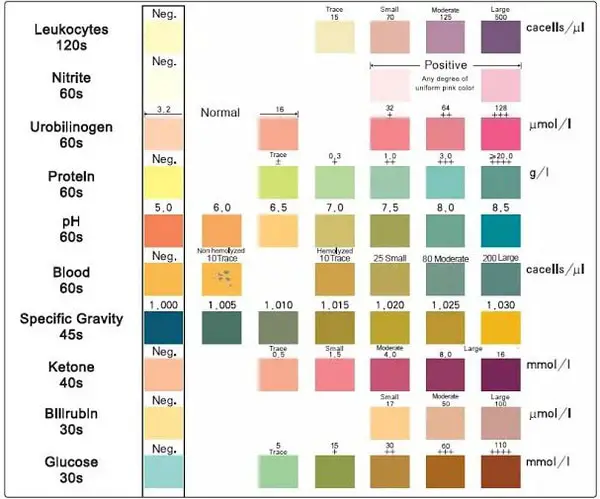




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Decoding the Dip: A Complete Information to Urine Dipstick Studying and Interpretation. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!