Decoding the Dow Jones P/E Ratio: A Historic Chart Evaluation
Associated Articles: Decoding the Dow Jones P/E Ratio: A Historic Chart Evaluation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Dow Jones P/E Ratio: A Historic Chart Evaluation. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Dow Jones P/E Ratio: A Historic Chart Evaluation

The Dow Jones Industrial Common (DJIA) is a extensively adopted barometer of the US inventory market’s well being. Whereas the index itself tracks the value actions of 30 giant, publicly traded corporations, a deeper understanding of its efficiency requires analyzing its Value-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio. The P/E ratio supplies essential context, revealing whether or not the market is overvalued, undervalued, or buying and selling at a good worth relative to its earnings. This text delves into the historic P/E ratio of the Dow Jones, inspecting its fluctuations, key turning factors, and implications for traders.
Understanding the Dow Jones P/E Ratio
The Dow Jones P/E ratio is calculated by dividing the present worth of the Dow Jones Industrial Common by the common earnings per share (EPS) of its constituent corporations. This ratio primarily exhibits how a lot traders are prepared to pay for every greenback of earnings generated by the index. A excessive P/E ratio suggests traders are optimistic about future development and are prepared to pay a premium, whereas a low P/E ratio may point out pessimism or a doubtlessly undervalued market. It is essential to notice that the P/E ratio isn’t a standalone indicator; its interpretation requires contemplating broader financial situations, trade traits, and rates of interest.
Historic Perspective: A Journey By means of the Chart
Analyzing a historic chart of the Dow Jones P/E ratio reveals fascinating traits and patterns. The info reveals vital swings reflecting durations of financial growth and bust, technological innovation, and shifts in investor sentiment. Whereas exact knowledge availability varies, charting the P/E ratio again a number of a long time permits for insightful observations.
Pre-Nineteen Eighties: A Interval of Relative Stability (with caveats)
Previous to the Nineteen Eighties, knowledge on the Dow Jones P/E ratio is much less available and infrequently calculated in a different way, making direct comparisons difficult. Nonetheless, the accessible historic knowledge suggests a comparatively decrease common P/E ratio in comparison with later durations. This may be attributed to a number of components: slower financial development, much less risky markets, and doubtlessly much less refined investor conduct. Nonetheless, it is essential to do not forget that evaluating P/E ratios throughout completely different eras wants cautious consideration of accounting requirements and methodologies.
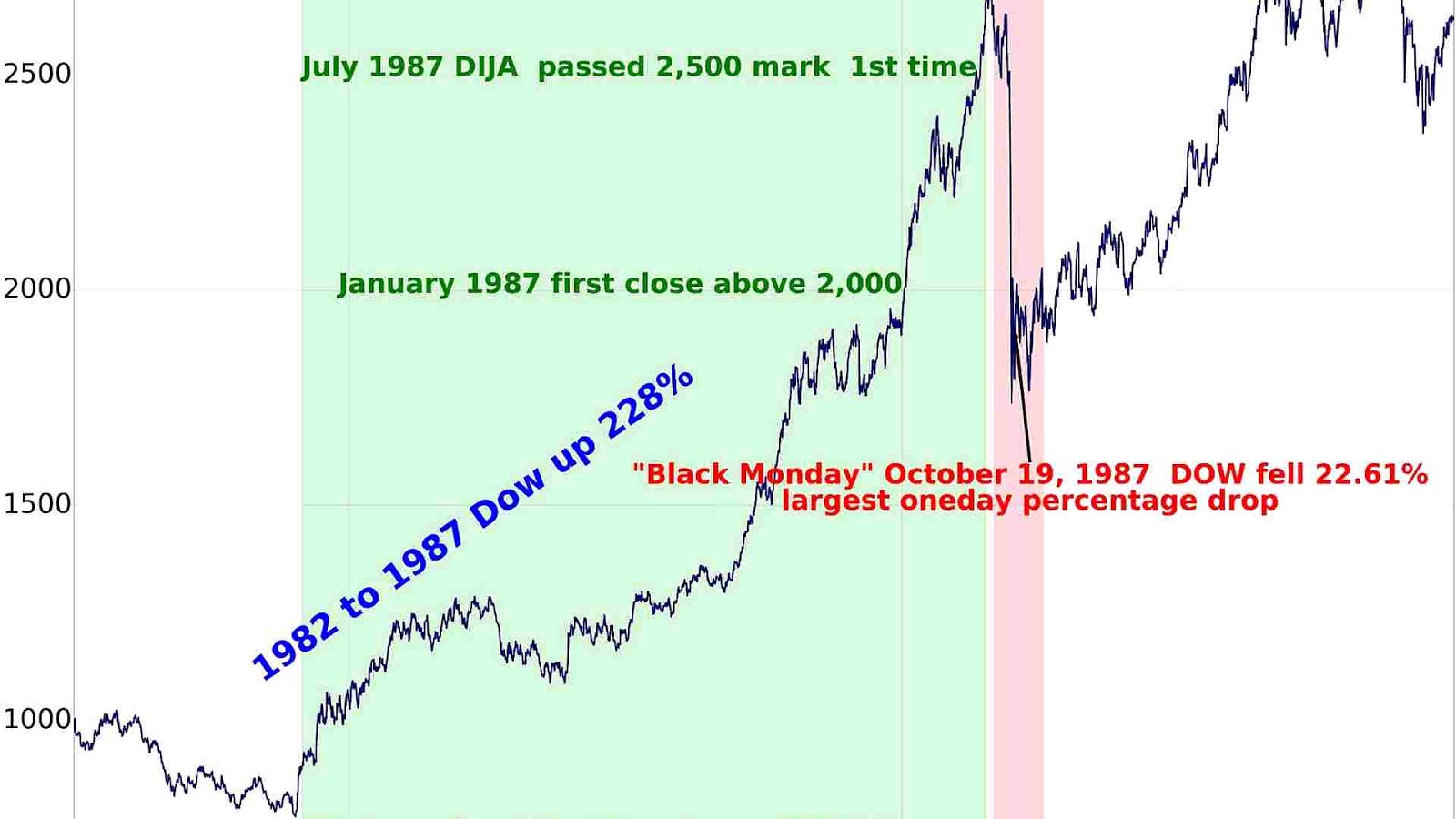
The Nineteen Eighties and Nineteen Nineties: The Bull Market and the Dot-Com Bubble
The Nineteen Eighties and Nineteen Nineties witnessed a dramatic rise within the Dow Jones P/E ratio. The bull market of the Nineteen Eighties, fueled by deregulation and technological developments, pushed the ratio considerably increased. This era noticed elevated investor confidence and a willingness to pay increased multiples for earnings. Nonetheless, essentially the most dramatic surge occurred throughout the late Nineteen Nineties, culminating within the Dot-Com bubble. Fueled by unprecedented technological innovation and exuberantly optimistic investor sentiment, the P/E ratio reached astronomical ranges, far exceeding historic norms. This finally proved unsustainable, resulting in the market crash of 2000-2002.
The 2000s: The Dot-Com Bust and the Monetary Disaster
The burst of the Dot-Com bubble resulted in a pointy decline within the Dow Jones P/E ratio, reflecting the market’s correction and the next bear market. The ratio remained comparatively subdued all through a lot of the early 2000s. Then, the 2008 monetary disaster struck, inflicting one other vital drop within the P/E ratio. The disaster uncovered vulnerabilities within the monetary system and eroded investor confidence, resulting in a pointy market downturn and a decrease valuation of equities.
The 2010s and Past: A Interval of Restoration and Volatility
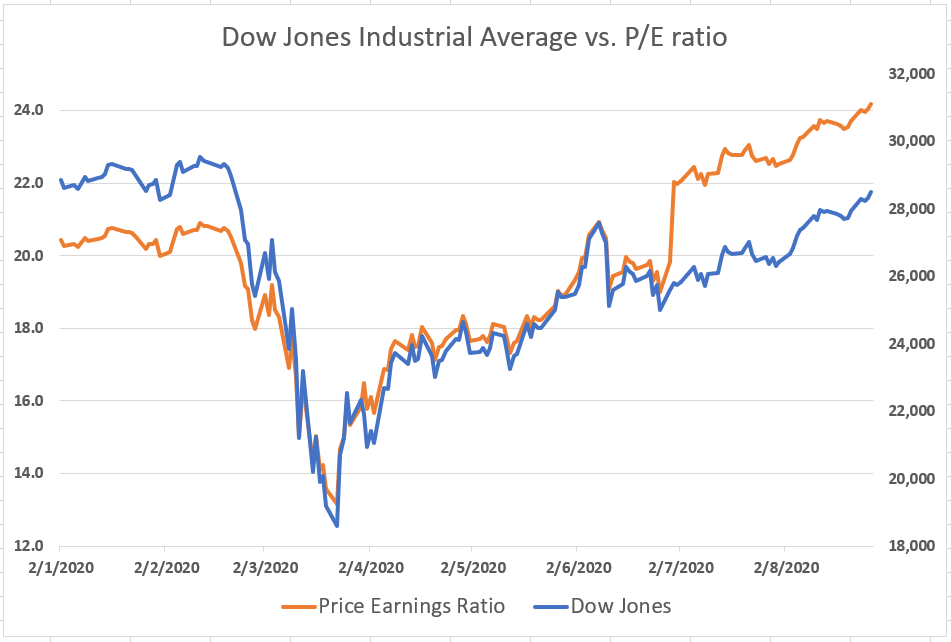
Following the 2008 monetary disaster, the Dow Jones P/E ratio regularly recovered. The interval noticed a protracted bull market, pushed by quantitative easing insurance policies, low rates of interest, and regular financial development. The ratio climbed to ranges akin to pre-crisis highs, albeit with durations of volatility. The rise of expertise corporations and the growing dominance of the FAANG shares (Fb, Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Google) contributed to fluctuations within the total P/E ratio. The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 initially precipitated a pointy drop, however subsequent authorities stimulus and a speedy technological shift led to a swift restoration, pushing the P/E ratio to near-record highs.
Deciphering the Chart: Key Issues
When decoding the historic chart of the Dow Jones P/E ratio, a number of components are essential:
-
Financial Cycles: The P/E ratio tends to correlate with financial cycles. During times of robust financial development, the ratio tends to be increased, reflecting investor optimism and better earnings. Recessions sometimes result in decrease P/E ratios.
-
Curiosity Charges: Rates of interest have a major influence on valuations. Decrease rates of interest typically result in increased P/E ratios, as traders search higher-yielding belongings.
-
Inflation: Excessive inflation erodes the buying energy of earnings, doubtlessly resulting in decrease P/E ratios.
-
Investor Sentiment: Market psychology performs a vital function. Intervals of maximum optimism or pessimism can considerably affect the P/E ratio, resulting in overvaluation or undervaluation.
-
Accounting Practices: Modifications in accounting requirements can have an effect on the reported earnings, influencing the P/E ratio.
The Shiller P/E Ratio: A Smoother Perspective
Whereas the standard Dow Jones P/E ratio makes use of present earnings, the cyclically adjusted price-to-earnings ratio (CAPE ratio), also referred to as the Shiller P/E ratio, makes use of common earnings over the previous 10 years. This smoothing method helps to scale back the influence of short-term earnings fluctuations and supplies a extra secure measure of valuation. Evaluating the standard P/E ratio with the Shiller P/E ratio presents a extra complete understanding of market valuation.
Conclusion: The P/E Ratio as a Instrument, Not a Crystal Ball
The historic chart of the Dow Jones P/E ratio presents useful insights into market valuations over time. Nonetheless, it is essential to do not forget that the P/E ratio is only one software amongst many. It shouldn’t be utilized in isolation to make funding selections. An intensive evaluation requires contemplating different financial indicators, trade traits, and company-specific components. Understanding the historic context, together with the constraints of the P/E ratio, empowers traders to make extra knowledgeable selections and navigate the complexities of the inventory market. The chart serves as a useful information, revealing patterns and traits, nevertheless it’s the investor’s interpretation and understanding of the broader financial panorama that finally decide success.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding the Dow Jones P/E Ratio: A Historic Chart Evaluation. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!