Decoding the Metric Fastener Dimension Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the Metric Fastener Dimension Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Metric Fastener Dimension Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Metric Fastener Dimension Chart: A Complete Information

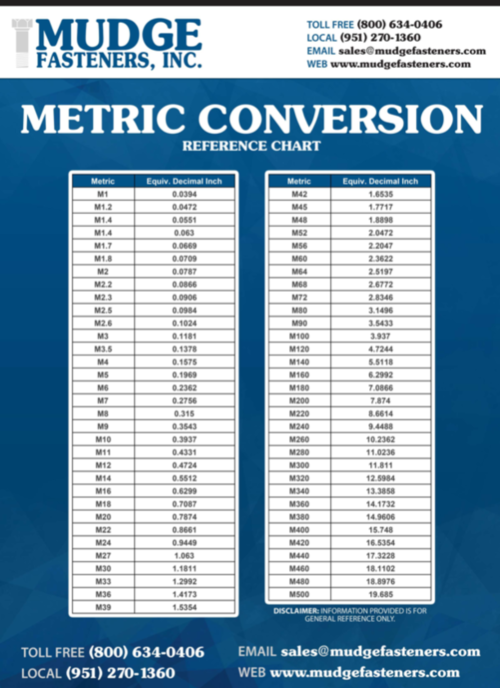
Metric fasteners are the usual in many of the world, providing a standardized system for bolts, screws, nuts, and washers. Understanding the metric fastener dimension chart is essential for anybody working with mechanical assemblies, building, manufacturing, and even easy DIY initiatives. This text supplies a complete overview of the metric system for fasteners, explaining the varied designations, tolerances, and purposes.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Diameter and Pitch
The core of the metric fastener dimension chart revolves round two key parameters: diameter and pitch.
-
Diameter: This refers back to the nominal diameter of the fastener’s shank (the cylindrical half). It is sometimes expressed in millimeters (mm). Frequent diameters vary from very small sizes (e.g., M1.6) utilized in electronics to very giant sizes (e.g., M36) employed in heavy equipment.
-
Pitch: This represents the space between adjoining threads alongside the fastener’s shank. It is also measured in millimeters (mm). A finer pitch (smaller distance between threads) usually means a stronger, extra exact match, whereas a coarser pitch (bigger distance) presents simpler meeting and disassembly. The pitch is commonly indicated immediately after the diameter, separated by a multiplication image (x) or just written as a fraction (e.g., M6 x 1, or M6-1). Some charts might merely use the diameter and indicate a typical pitch for that diameter.
Decoding the Metric Fastener Designation
A typical metric fastener designation follows a particular format:
M[Diameter] [Pitch] [Thread Type] [Material] [Length]
Let’s break down every part:
-
M: This letter denotes that the fastener is metric.
-
Diameter (in mm): As mentioned, that is the nominal diameter of the shank.
-
Pitch (in mm): This means the space between adjoining threads. Frequent pitches for varied diameters are standardized, however variations exist.
-
Thread Sort: This specifies the thread profile. The most typical is the ISO metric coarse (M) and high quality (f) thread profiles. Different specialised thread sorts may embrace:
- ISO Metric Coarse (M): That is the commonest kind, providing a stability between energy and ease of meeting.
- ISO Metric High quality (f): This supplies a finer thread, leading to elevated energy and higher resistance to loosening beneath vibration. Usually utilized in purposes requiring excessive precision or the place house is proscribed.
- ISO Metric Further High quality (ef): Even finer than the high quality thread, providing most energy and precision, sometimes utilized in specialised purposes.
-
Materials: This means the fabric the fastener is comprised of. Frequent supplies embrace metal (varied grades), stainless-steel (varied grades), brass, aluminum, and plastic. The fabric is often implied via context or indicated individually in specs.
-
Size (in mm): This represents the general size of the fastener, from the pinnacle to the top of the shank.
Instance: M8 x 1.25 signifies an 8mm diameter bolt with a 1.25mm pitch. If it had been M8 x 1.25 x 8.8, the 8.8 would point out the fabric grade (excessive tensile metal).
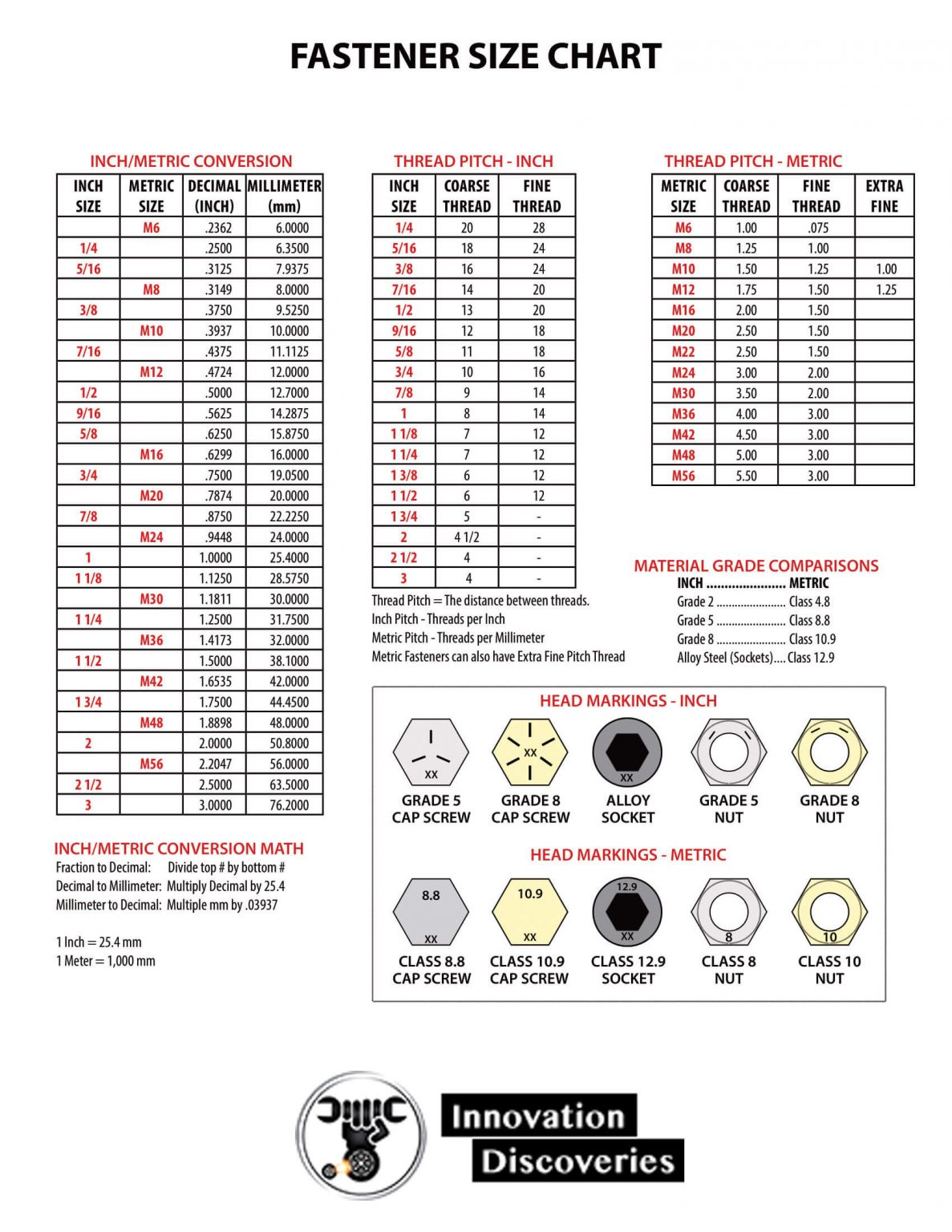
Frequent Metric Fastener Sizes and Their Purposes
The next desk supplies a glimpse into widespread metric fastener sizes and their typical purposes:
| Diameter (mm) | Pitch (mm) | Typical Purposes |
|---|---|---|
| M1.6 | 0.35 | Electronics, small home equipment |
| M2 | 0.4 | Electronics, fashions, small assemblies |
| M3 | 0.5 | Electronics, small equipment elements |
| M4 | 0.7 | Small equipment, furnishings, automotive parts |
| M5 | 0.8 | Common objective, automotive, mild equipment |
| M6 | 1 | Common objective, automotive, furnishings |
| M8 | 1.25 | Common objective, heavy equipment, building |
| M10 | 1.5 | Heavy equipment, building, structural parts |
| M12 | 1.75 | Heavy equipment, building, giant assemblies |
| M16 | 2 | Very heavy equipment, giant constructions |
| M20 | 2.5 | Very heavy equipment, giant constructions |
Past Diameter and Pitch: Different Vital Concerns
Whereas diameter and pitch are elementary, a number of different traits affect fastener choice:
-
Head Sort: Varied head sorts exist, resembling hex head, pan head, button head, countersunk head, and so on., every fitted to particular purposes and aesthetic necessities.
-
Drive Sort: This refers to the kind of instrument used to tighten the fastener. Frequent drive sorts embrace hex (hexagonal), Phillips, Torx, and sq. drive.
-
Thread Class: This defines the tolerances for thread dimensions, impacting the match and energy of the fastener. Totally different courses exist, resembling 6g (coarse) and 6h (high quality), indicating tighter tolerances for the latter.
-
Materials Energy: The fabric energy grade is essential for figuring out the fastener’s load-bearing capability. Larger energy grades (e.g., 8.8, 10.9, 12.9 for metal) point out larger tensile energy.
-
Floor End: Floor remedies like zinc plating, galvanizing, or passivation improve corrosion resistance and sturdiness.
-
Size: The size of the fastener have to be applicable for the appliance, making certain enough thread engagement for safe fastening.
Utilizing a Metric Fastener Dimension Chart Successfully
When utilizing a metric fastener dimension chart, think about the next:
-
Determine the appliance: Decide the required energy, load capability, and environmental circumstances.
-
Choose the suitable diameter: Select a diameter based mostly on the load necessities and the fabric thickness being mounted.
-
Decide the pitch: Choose a rough pitch for ease of meeting or a high quality pitch for elevated energy and vibration resistance.
-
Specify the pinnacle kind and drive kind: Select the pinnacle kind and drive kind which might be suitable with the appliance and out there instruments.
-
Confirm the fabric and energy grade: Make sure the chosen materials and energy grade are appropriate for the appliance.
-
Examine the size: The fastener ought to have enough thread engagement to make sure a safe fastening. Too quick a fastener is not going to present enough grip, whereas too lengthy a fastener may be detrimental.
Conclusion
Understanding the metric fastener dimension chart is important for profitable mechanical meeting. By fastidiously contemplating the diameter, pitch, head kind, drive kind, materials, energy grade, and size, you may choose the suitable fastener for any software. Bear in mind to all the time seek the advice of related requirements and specs to make sure the protection and reliability of your challenge. This text supplies a basis; additional analysis into particular purposes and materials properties is really helpful for superior initiatives. Whereas this information presents a complete overview, the intricacies of fastener choice typically require specialised information and expertise. Consulting with engineers or skilled professionals is all the time really helpful for essential purposes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Decoding the Metric Fastener Dimension Chart: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!