Decoding the pH Chart: A Complete Information to Hydrogen Ion Focus and its Implications
Associated Articles: Decoding the pH Chart: A Complete Information to Hydrogen Ion Focus and its Implications
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the pH Chart: A Complete Information to Hydrogen Ion Focus and its Implications. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the pH Chart: A Complete Information to Hydrogen Ion Focus and its Implications

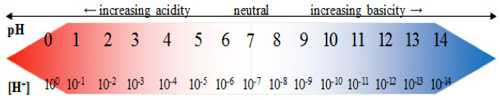
The pH chart, a seemingly easy scale starting from 0 to 14, represents a cornerstone of chemistry and quite a few associated fields. It quantifies the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of an answer by expressing the focus of hydrogen ions (H⁺). Understanding this chart is essential for comprehending a variety of chemical reactions, organic processes, and industrial purposes. This text delves into the intricacies of the pH chart, exploring its derivation, purposes, measurement strategies, and the numerous implications of pH variations throughout various contexts.
The Basis: Defining pH and its Mathematical Illustration
The pH scale is a logarithmic scale, that means that every complete quantity change represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion focus. Mathematically, pH is outlined because the adverse logarithm (base 10) of the hydrogen ion exercise:
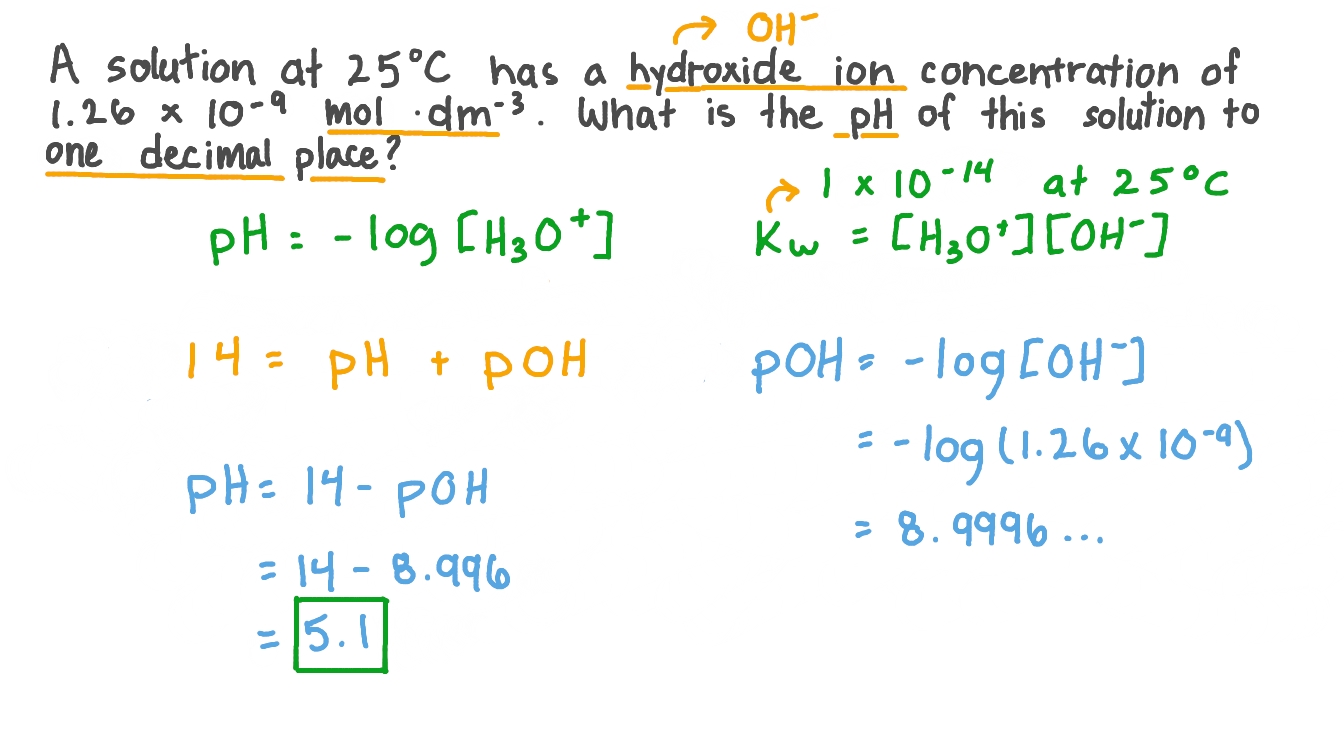
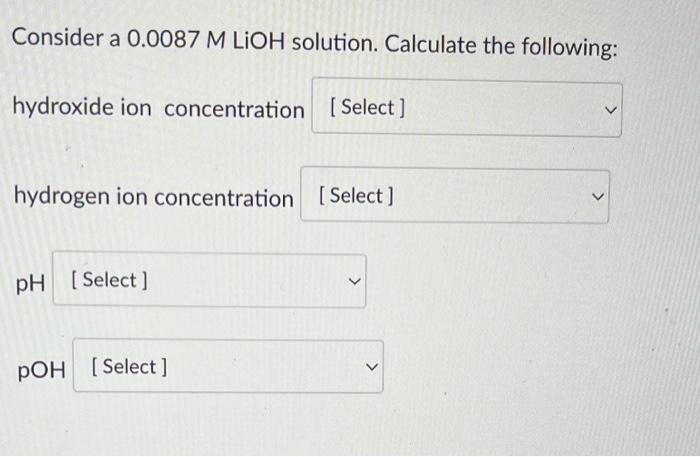
pH = -log₁₀[H⁺]
The place [H⁺] represents the focus of hydrogen ions in moles per liter (mol/L) or molarity (M). The exercise of H⁺ is a thermodynamically corrected focus, accounting for the interactions between ions in resolution. In dilute options, exercise approximates focus, simplifying the calculation.
A pH of seven signifies a impartial resolution, the place the focus of H⁺ ions equals the focus of hydroxide ions (OH⁻). Values beneath 7 point out acidity, with decrease values signifying stronger acids, whereas values above 7 point out basicity (alkalinity), with increased values representing stronger bases. The size shouldn’t be linear; an answer with a pH of three is ten instances extra acidic than an answer with a pH of 4, and 100 instances extra acidic than an answer with a pH of 5.
Derivation and Significance of the pH Scale
The idea of pH was launched by the Danish biochemist Søren Sørensen in 1909. His work centered on the impression of hydrogen ion focus on enzyme exercise, highlighting the significance of exact pH management in organic programs. The size’s logarithmic nature successfully manages the huge vary of hydrogen ion concentrations encountered in varied options, from extremely acidic gastric juices to extremely alkaline drain cleaners.
The importance of the pH chart extends far past its preliminary software in biochemistry. It performs a pivotal position in:
-
Chemical Reactions: Many chemical reactions are extremely delicate to pH. The speed and even the course of a response will be drastically altered by modifications in pH. As an example, the hydrolysis of esters is catalyzed by acids, whereas the saponification of fat requires a primary atmosphere.
-
Environmental Monitoring: pH measurements are essential for assessing water high quality in rivers, lakes, and oceans. Adjustments in pH can point out air pollution, impacting aquatic life and ecosystem well being. Acid rain, a big environmental concern, is characterised by low pH values.
-
Industrial Processes: Quite a few industrial processes require exact pH management. For instance, the manufacturing of prescription drugs, meals processing, and wastewater therapy all depend on sustaining particular pH ranges for optimum effectivity and product high quality.
-
Organic Methods: Sustaining a secure pH is important for the right functioning of organic programs. The pH of blood, as an illustration, is tightly regulated inside a slim vary (roughly 7.35-7.45). Deviations from this vary can result in critical well being penalties, reminiscent of acidosis or alkalosis.
-
Agriculture: Soil pH considerably impacts nutrient availability to crops. Totally different crops thrive beneath completely different pH situations, requiring changes by way of soil amendments to optimize progress.
Measuring pH: Methods and Instrumentation
A number of strategies can be found for measuring pH, starting from easy indicators to classy digital devices.
-
pH Indicators: These are substances that change shade relying on the pH of the answer. Litmus paper, a typical instance, turns purple in acidic options and blue in primary options. Whereas handy for tough estimations, indicators present solely approximate pH values.
-
pH Meters: These digital devices present extra exact pH measurements. They include a pH-sensitive electrode (usually a glass electrode) and a reference electrode. The potential distinction between these electrodes is immediately proportional to the pH of the answer. Trendy pH meters provide excessive accuracy and are extensively utilized in laboratories and industrial settings.
-
Spectrophotometry: This method measures the absorbance or transmission of sunshine by way of an answer containing a pH-sensitive dye. The absorbance is expounded to the pH, permitting for quantitative willpower.
-
Titration: This traditional analytical approach entails regularly including an answer of recognized focus (titrant) to an answer of unknown focus (analyte) till a particular pH is reached. This endpoint signifies the completion of the response and permits for the calculation of the analyte’s focus.
The Influence of pH on Totally different Methods:
The consequences of pH variations are far-reaching and profoundly impression varied programs. Let’s discover some particular examples:
-
Human Physiology: The pH of blood is meticulously regulated by buffer programs, primarily involving carbonic acid and bicarbonate ions. These buffers resist modifications in pH, sustaining a secure inside atmosphere. Disruptions to this delicate steadiness can result in acidosis (low blood pH) or alkalosis (excessive blood pH), each of which will be life-threatening. Digestive processes additionally depend on particular pH ranges in numerous elements of the gastrointestinal tract. The abdomen, for instance, maintains a extremely acidic atmosphere (pH round 2) to assist in digestion.
-
Aquatic Ecosystems: The pH of water our bodies is essential for the survival of aquatic organisms. Adjustments in pH as a result of air pollution can disrupt the fragile steadiness of those ecosystems. Acid rain, brought on by the discharge of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the environment, lowers the pH of lakes and rivers, harming fish and different aquatic life.
-
Soil Chemistry: Soil pH considerably impacts nutrient availability to crops. Totally different crops have completely different optimum pH ranges for nutrient uptake. Acidic soils could lack important vitamins like calcium and magnesium, whereas alkaline soils could have deficiencies in iron and manganese. Soil pH additionally influences the exercise of soil microorganisms, impacting nutrient biking and soil fertility.
-
Meals Science: pH performs a essential position in meals preservation and processing. Many meals preservation strategies depend on controlling pH to inhibit microbial progress. For instance, pickling entails decreasing the pH of meals by way of the addition of acids, stopping spoilage. The pH of meals additionally impacts its style, texture, and shade.
Conclusion:
The pH chart, although seemingly easy, represents a strong device for understanding and controlling chemical and organic processes. Its logarithmic nature effectively captures the huge vary of hydrogen ion concentrations, offering a essential parameter for varied purposes throughout various fields. From environmental monitoring and industrial processes to human physiology and agriculture, the importance of pH can’t be overstated. Understanding the rules behind the pH chart, its measurement strategies, and its far-reaching implications is essential for advancing information and fixing challenges in quite a few scientific and technological domains. Continued analysis and growth in pH measurement and management will undoubtedly result in additional developments in varied fields, reinforcing the enduring significance of this elementary idea in chemistry.
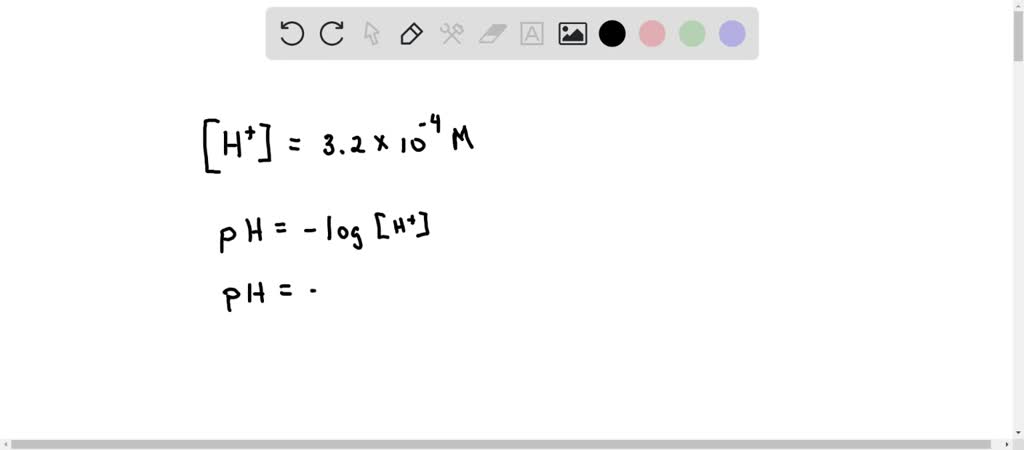
![An unknown substance has the hydrogen ion concentration of [H+] = 3.2](https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/dcb/0b2c9f35fd83bb309b443bbb209f7810.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Decoding the pH Chart: A Complete Information to Hydrogen Ion Focus and its Implications. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!