Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information with Chart
Associated Articles: Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information with Chart
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information with Chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information with Chart

The pH scale, a seemingly easy numerical vary from 0 to 14, represents an unlimited spectrum of chemical properties and performs an important position in numerous pure and industrial processes. Understanding the pH scale is key to varied fields, from chemistry and biology to agriculture and environmental science. This text will delve into the intricacies of the pH scale, exploring its that means, purposes, measurement strategies, and the importance of its numerous ranges. We’ll additionally present an in depth chart illustrating the pH ranges of frequent substances.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What’s pH?
pH stands for "potential of hydrogen," a measure of the focus of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in an answer. A better focus of H⁺ ions signifies a decrease pH, signifying acidity. Conversely, a decrease focus of H⁺ ions signifies a better pH, signifying alkalinity (or basicity). The dimensions is logarithmic, that means every complete quantity change represents a tenfold distinction in H⁺ ion focus. For instance, an answer with a pH of three is ten occasions extra acidic than an answer with a pH of 4, and 100 occasions extra acidic than an answer with a pH of 5.
The pH scale is predicated on the dissociation of water molecules (H₂O) into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻). Pure water, at 25°C, has an equal focus of each ions, leading to a impartial pH of seven. Options with a pH beneath 7 are acidic, whereas options with a pH above 7 are alkaline (or primary).
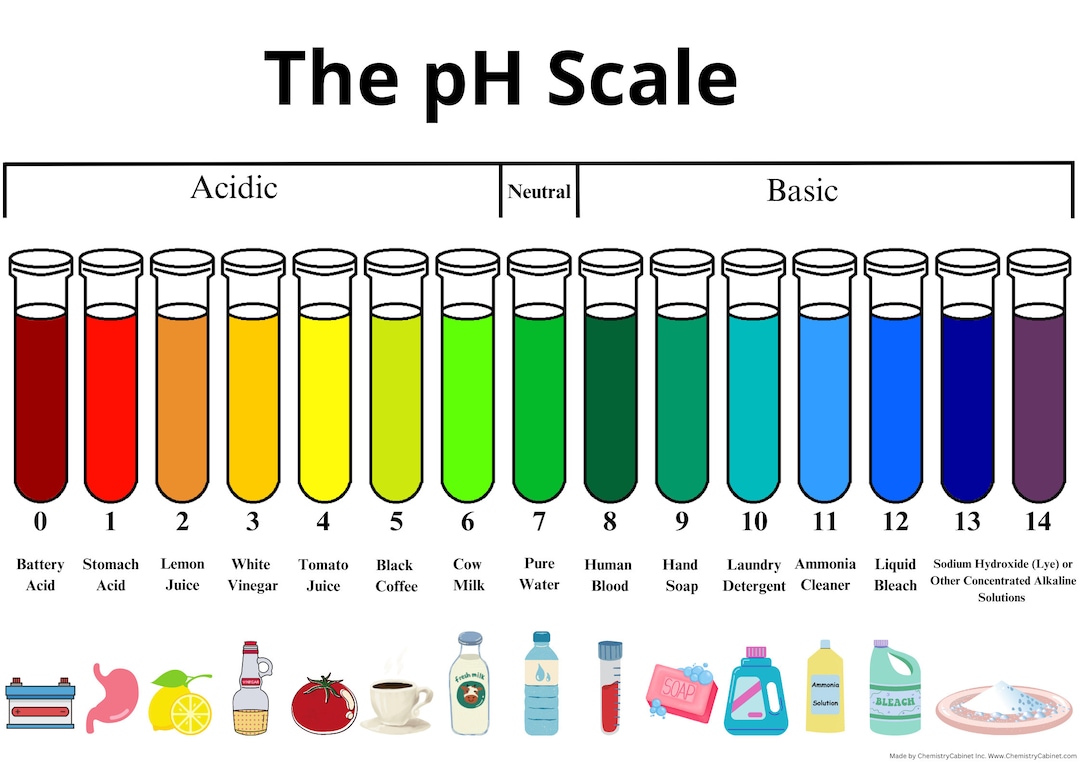
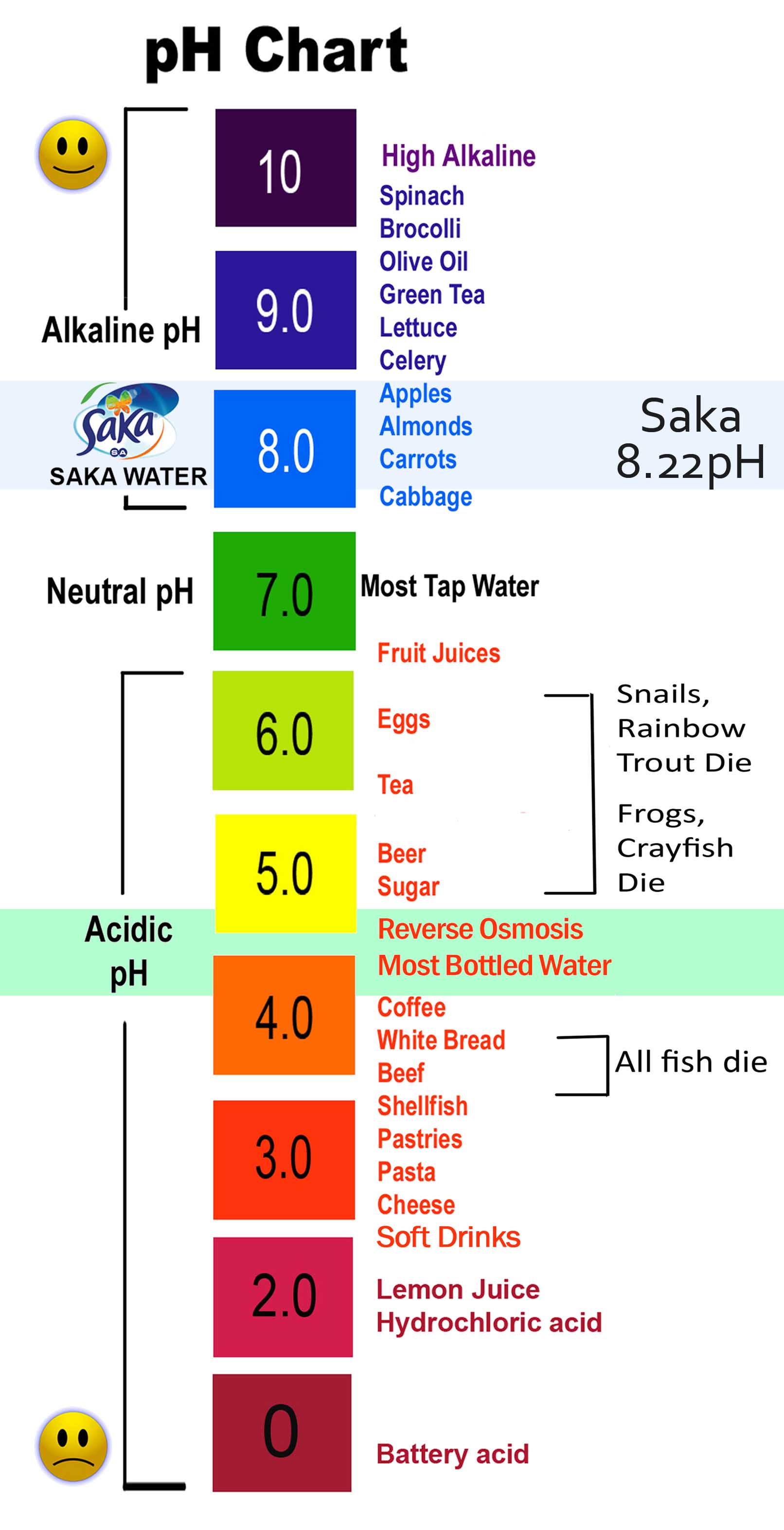
The pH Scale Chart: A Visible Illustration
The next chart offers a visible illustration of the pH scale, categorizing frequent substances in accordance with their pH ranges. It is vital to notice that the precise pH of a substance can differ relying on elements resembling temperature, focus, and purity. This chart provides a basic overview:
| pH Stage | Class | Examples | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-2 | Robust Acid | Battery acid, abdomen acid, hydrochloric acid | Excessive focus of H⁺ ions; extremely corrosive. |
| 2-3 | Acidic | Lemon juice, vinegar, cola | Comprises vital H⁺ ions; could be corrosive relying on focus. |
| 3-4 | Acidic | Grapefruit juice, orange juice, beer | Reasonably acidic. |
| 4-5 | Acidic | Tomato juice, black espresso, rain water | Mildly acidic. |
| 5-6 | Barely Acidic | Urine, milk | Barely acidic. |
| 6-7 | Impartial | Pure water | Equal focus of H⁺ and OH⁻ ions. |
| 7-8 | Barely Alkaline | Seawater, baking soda | Barely alkaline. |
| 8-9 | Alkaline | Toothpaste, egg whites | Reasonably alkaline. |
| 9-10 | Alkaline | Washing soda, borax | Extra alkaline. |
| 10-11 | Alkaline | Milk of magnesia, ammonia answer | Strongly alkaline. |
| 11-12 | Strongly Alkaline | Family bleach, drain cleaner | Extremely alkaline; corrosive. |
| 12-14 | Robust Base | Sodium hydroxide (lye), potassium hydroxide | Very excessive focus of OH⁻ ions; extremely corrosive. |
The Significance of pH in Completely different Fields:
The pH scale’s significance extends throughout quite a few disciplines:
-
Biology: pH performs a vital position in organic techniques. Enzymes, the catalysts of organic reactions, operate optimally inside a slim pH vary. Modifications in pH can denature enzymes, disrupting metabolic processes. The pH of blood, for example, is tightly regulated round 7.4; deviations can have critical well being penalties. The pH of soil additionally considerably impacts plant progress, affecting nutrient availability and microbial exercise.
-
Chemistry: pH is key to quite a few chemical reactions and processes. Titration, a standard analytical method, depends on pH measurements to find out the focus of unknown options. Buffer options, which resist modifications in pH, are essential in sustaining steady circumstances for chemical reactions.
-
Agriculture: Soil pH is a vital consider agriculture. Completely different crops have optimum pH ranges for progress. Testing soil pH permits farmers to regulate soil circumstances via the addition of amendments like lime (to boost pH) or sulfur (to decrease pH), optimizing nutrient uptake and plant well being.
-
Environmental Science: pH measurements are essential in monitoring water high quality. Acid rain, brought on by atmospheric pollution, can drastically decrease the pH of lakes and rivers, harming aquatic life. Monitoring pH ranges in wastewater remedy crops is crucial to make sure efficient remedy and environmental safety.
-
Meals Science and Know-how: pH performs an important position in meals preservation, high quality, and security. The pH of meals impacts microbial progress; acidic environments inhibit the expansion of many dangerous micro organism. pH management is crucial in numerous meals processing methods, resembling fermentation and cheese making.
-
Drugs: pH monitoring is crucial in numerous medical contexts. The pH of blood is an important indicator of well being. Measuring gastric pH helps diagnose and handle gastrointestinal issues. pH-sensitive electrodes are utilized in numerous medical gadgets and diagnostic instruments.
Measuring pH: Strategies and Instruments:
A number of strategies exist for measuring pH:
-
pH Indicators: These are substances that change shade relying on the pH of the answer. Litmus paper, a standard indicator, turns pink in acidic options and blue in alkaline options. Extra subtle indicators present a wider vary of shade modifications for extra exact pH willpower.
-
pH Meters: These digital gadgets use a pH-sensitive electrode to measure the voltage distinction between the electrode and a reference electrode. This voltage distinction is instantly associated to the pH of the answer. pH meters present correct and exact pH measurements.
-
Spectrophotometry: This system makes use of the absorption of sunshine by an answer to find out its pH. Sure substances exhibit modifications of their mild absorption properties with modifications in pH.
The selection of technique is dependent upon the required accuracy, the character of the pattern, and the obtainable assets. For exact measurements, pH meters are most well-liked. For fast estimations or area assessments, pH indicators may suffice.
Conclusion:
The pH scale, although seemingly easy, underpins an unlimited array of chemical and organic processes. Its understanding is essential in quite a few fields, influencing all the pieces from environmental monitoring and agriculture to human well being and industrial processes. By appreciating the logarithmic nature of the size and the implications of various pH ranges, we will higher perceive the complicated world round us and harness the ability of this basic chemical measurement. The accompanying chart serves as a worthwhile reference, providing a glimpse into the varied vary of pH values present in on a regular basis substances, highlighting the pervasive affect of this vital parameter in our world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Decoding the pH Scale: A Complete Information with Chart. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!
