Decoding the Soil pH Chart: Your Information to a Thriving Backyard
Associated Articles: Decoding the Soil pH Chart: Your Information to a Thriving Backyard
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Soil pH Chart: Your Information to a Thriving Backyard. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Soil pH Chart: Your Information to a Thriving Backyard

The well being and productiveness of your backyard hinge on many components, however few are as elementary as soil pH. Understanding and managing your soil’s pH degree is essential for unlocking the complete potential of your crops. This complete information explores the intricacies of the soil pH chart, explaining its significance, the right way to interpret it, and the right way to regulate your soil’s pH for optimum plant progress.
What’s Soil pH?
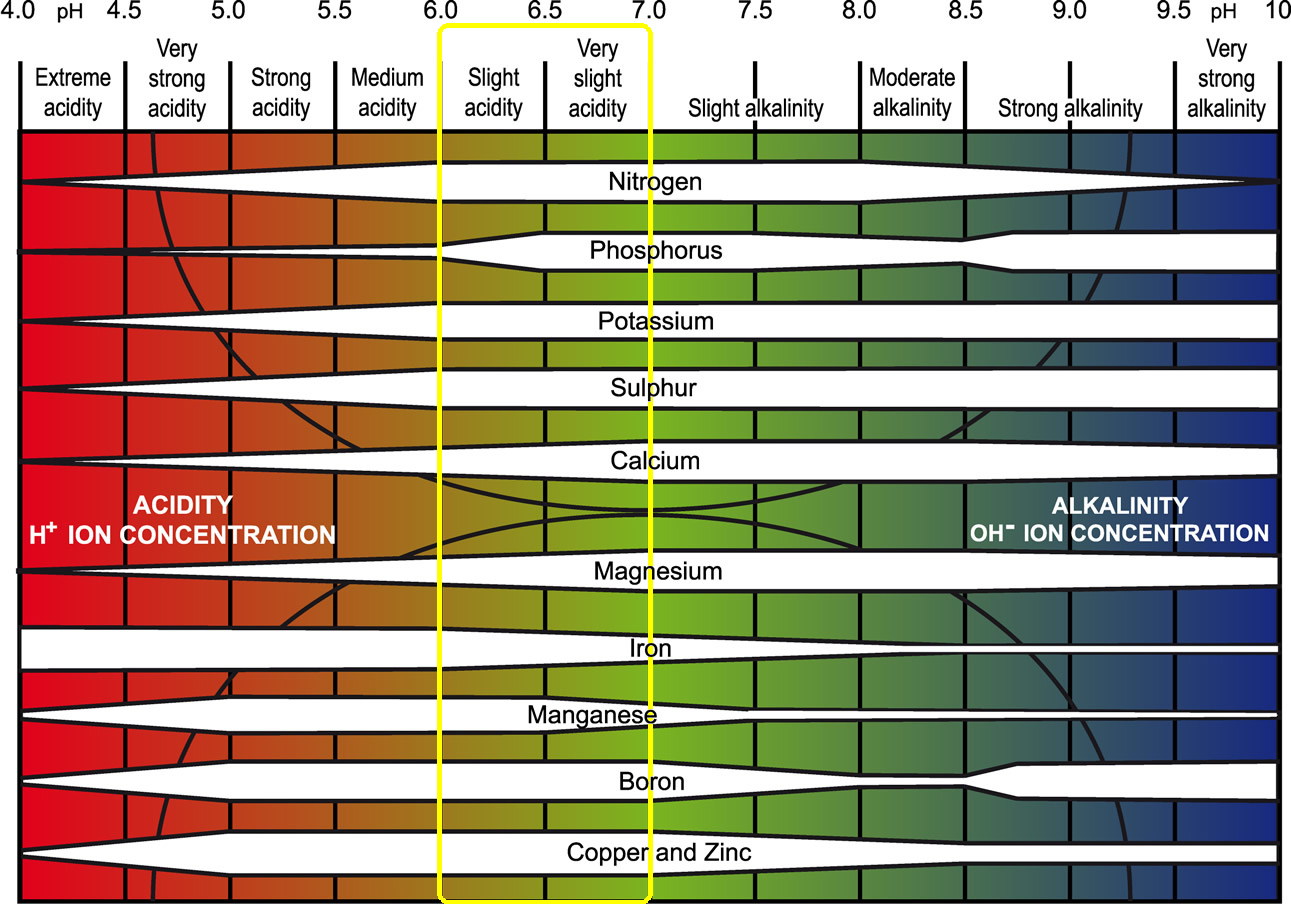
Soil pH measures the acidity or alkalinity of your soil. It is expressed on a scale of 0 to 14, with 7 being impartial. Numbers under 7 point out acidity (rising acidity because the quantity decreases), whereas numbers above 7 point out alkalinity (rising alkalinity because the quantity will increase). The pH degree considerably impacts the provision of important vitamins to your crops.
The Significance of the Soil pH Chart
A soil pH chart is not only a easy quantity; it is a visible illustration of the complicated chemical interactions inside your soil. It acts as a roadmap, guiding you in direction of understanding which vitamins are available to your crops at totally different pH ranges. Totally different crops have totally different pH preferences; some thrive in acidic situations, whereas others choose alkaline situations. A soil pH chart helps you match your crops to the suitable soil setting, maximizing their progress and yield.
Deciphering the Soil pH Chart: A Detailed Breakdown
Whereas a easy chart may simply present the pH scale, a complete understanding requires analyzing the nutrient availability at every pH degree. Let’s break down the standard ranges:
-
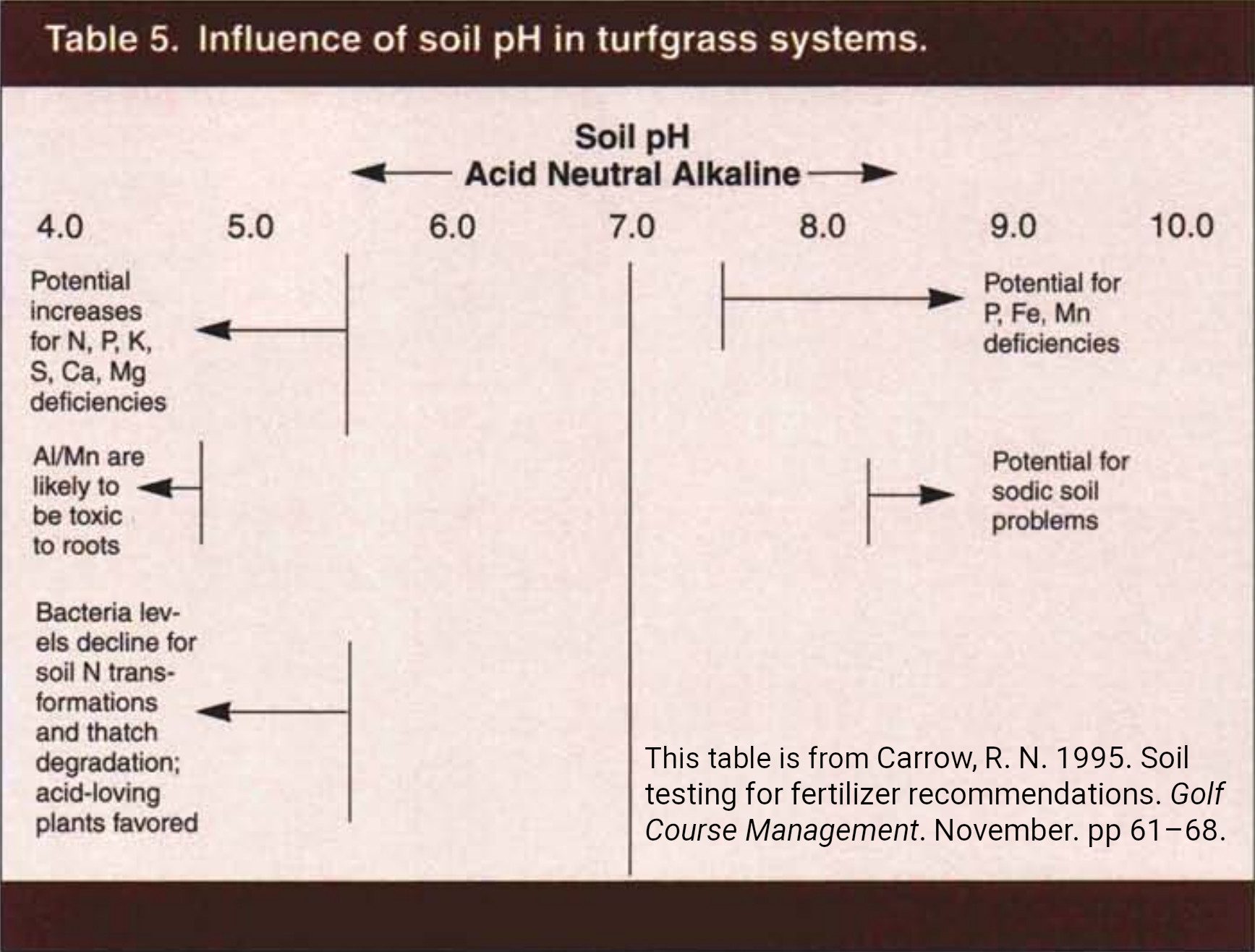
Extremely Acidic (pH 4.0 – 5.5): On this vary, aluminum and manganese change into extremely soluble and may attain poisonous ranges for a lot of crops. The supply of phosphorus, molybdenum, and calcium is considerably diminished. Vegetation tailored to acidic situations, equivalent to blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons, thrive right here.
-
Reasonably Acidic (pH 5.5 – 6.5): That is the best vary for many crops, providing a very good steadiness of nutrient availability. Most greens, flowers, and decorative crops carry out properly inside this vary. Iron, manganese, and zinc are available.
-
Impartial (pH 6.5 – 7.5): A impartial pH gives a comparatively balanced nutrient provide. Nonetheless, some micronutrients is likely to be much less accessible than in barely acidic situations.
-
Reasonably Alkaline (pH 7.5 – 8.5): On this vary, the provision of iron, manganese, zinc, and phosphorus decreases considerably. Many crops present indicators of nutrient deficiencies, exhibiting chlorosis (yellowing of leaves). Vegetation tailored to alkaline situations, equivalent to sure cacti and succulents, can tolerate these situations.
-
Extremely Alkaline (pH 8.5 – 10.0): At this degree, nutrient deficiencies change into extreme, considerably impacting plant progress. Iron deficiency is a standard drawback. Few crops can tolerate such excessive alkalinity.
Elements Influencing Soil pH:
A number of components contribute to the pH of your soil, together with:
-
Dad or mum Materials: The underlying geological materials considerably influences the preliminary pH. Soils derived from limestone are usually alkaline, whereas these derived from granite or sandstone are sometimes acidic.
-
Local weather: Rainfall patterns play an important position. Excessive rainfall can leach away fundamental cations, resulting in extra acidic situations. Arid climates are inclined to favor alkaline soils.
-
Natural Matter: Decomposing natural matter usually lowers the soil pH, making it extra acidic.
-
Fertilizers: Totally different fertilizers can have various results on soil pH. Ammonium-based fertilizers are inclined to acidify the soil, whereas others can enhance alkalinity.
-
Irrigation Water: The pH of your irrigation water may affect the general soil pH over time.
Testing Your Soil pH:
Correct soil pH testing is essential for efficient administration. A number of strategies exist:
-
Soil Testing Kits: Dwelling soil testing kits present a fast and comparatively cheap method to estimate your soil pH. These kits normally contain mixing a soil pattern with a reagent and evaluating the ensuing coloration to a chart. Whereas handy, they provide much less precision than laboratory testing.
-
Laboratory Testing: Sending a soil pattern to an expert laboratory gives probably the most correct outcomes. Laboratories use subtle gear to find out the exact pH and infrequently present a complete evaluation of different soil properties, together with nutrient ranges.
-
Digital Soil Meters: These units present a fast studying of the soil pH by inserting a probe into the soil. Whereas handy, they are often much less correct than laboratory testing and require calibration.
Adjusting Your Soil pH:
As soon as your soil’s pH, you may regulate it to go well with the wants of your crops. The method includes amending the soil with supplies that both enhance or lower its acidity:
-
Decreasing pH (Rising Acidity): To decrease the pH of alkaline soil, you need to use:
- Elemental Sulfur: This can be a slow-acting modification that steadily lowers the pH over time.
- Sulfuric Acid: This can be a faster-acting modification however requires cautious dealing with as a result of its corrosive nature.
- Acidifying Fertilizers: Ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate are examples of fertilizers that may decrease soil pH.
- Natural Matter: Including peat moss, composted pine bark, or leaf mould can steadily enhance soil acidity.
-
Elevating pH (Rising Alkalinity): To boost the pH of acidic soil, you need to use:
- Lime: Floor limestone is the commonest modification used to lift soil pH. It is comparatively cheap and available. Several types of lime have various reactivity charges.
- Wooden Ashes: These comprise calcium and potassium carbonates, which may also help increase the pH. Nonetheless, use them cautiously as they’ll additionally comprise different parts that may not be useful to your crops.
Essential Concerns:
-
Gradual Changes: Keep away from drastic adjustments in soil pH. Make gradual changes over time to permit the soil to equilibrate.
-
Retesting: After making changes, retest your soil pH after a number of weeks or months to observe the effectiveness of your amendments.
-
Plant-Particular Wants: Keep in mind that totally different crops have totally different pH preferences. Analysis the particular wants of your chosen crops earlier than making any changes.
-
Soil Texture: The feel of your soil influences the speed at which pH changes happen. Sandy soils are inclined to require much less modification than clay soils.
Conclusion:
Understanding and managing your soil’s pH is a cornerstone of profitable gardening. Through the use of the soil pH chart as your information, conducting common testing, and making knowledgeable changes, you may create the best setting on your crops to flourish. Keep in mind that endurance and constant monitoring are key to attaining the specified pH degree and cultivating a thriving, productive backyard. The funding in understanding your soil’s pH will yield vital returns within the well being and fantastic thing about your backyard.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Decoding the Soil pH Chart: Your Information to a Thriving Backyard. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!