Decoding the Soundscape: A Deep Dive into the Musical Observe Frequency Chart in Hz
Associated Articles: Decoding the Soundscape: A Deep Dive into the Musical Observe Frequency Chart in Hz
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Soundscape: A Deep Dive into the Musical Observe Frequency Chart in Hz. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Soundscape: A Deep Dive into the Musical Observe Frequency Chart in Hz

Music, a common language understood throughout cultures and generations, is basically constructed upon the exact relationships between frequencies of sound waves. These frequencies, measured in Hertz (Hz), representing cycles per second, decide the pitch of a musical observe. Understanding the frequency chart of musical notes is essential for musicians, composers, sound engineers, and anybody in search of a deeper appreciation of the physics and artistry behind music. This text delves into the intricacies of the musical observe frequency chart, exploring its building, variations, and sensible purposes.
The Basis: A1 and Equal Temperament
The muse of the usual musical observe frequency chart rests upon the frequency assigned to a selected observe, sometimes A4. The Worldwide Group for Standardization (ISO) has standardized the frequency of A4 to 440 Hz. Because of this the observe A above center C vibrates at 440 cycles per second. From this anchor level, the frequencies of all different notes are derived utilizing the rules of equal temperament.
Equal temperament is a tuning system that divides the octave into twelve equal semitones. Every semitone represents a frequency ratio of the twelfth root of two (roughly 1.0595). Because of this to seek out the frequency of a observe a semitone increased, you multiply the frequency of the unique observe by this ratio. Conversely, to seek out the frequency of a observe a semitone decrease, you divide by this ratio.
This systematic strategy ensures that the intervals between notes stay constant all through all the vary of the musical scale. This consistency is essential for creating harmonious melodies and chords, whatever the key or transposition. The ultimate temperament, modulating between keys would end in important discrepancies in intonation, making harmonious music significantly more difficult to create and carry out.
Setting up the Frequency Chart:
Beginning with A4 at 440 Hz, we are able to systematically calculate the frequencies of different notes. Transferring upwards, every semitone will increase the frequency by an element of the twelfth root of two. Transferring downwards, we divide by the identical issue.
Here is a simplified illustration of the method:
- A4: 440 Hz
- A#4 (or Bb4): 440 Hz * 1.0595 ≈ 466.16 Hz
- B4: 466.16 Hz * 1.0595 ≈ 493.88 Hz
- C5: 493.88 Hz * 1.0595 ≈ 523.25 Hz
- And so forth…
This course of continues for all twelve notes inside an octave, after which repeats for subsequent octaves, each increased and decrease. The frequency doubles with every octave. For instance, A5 (the A above A4) might be 880 Hz (440 Hz * 2), and A3 (the A beneath A4) might be 220 Hz (440 Hz / 2).
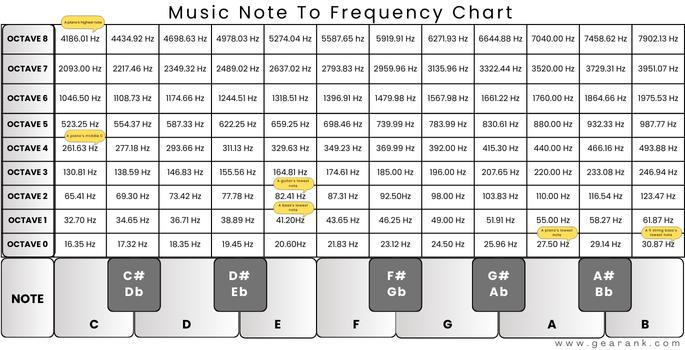
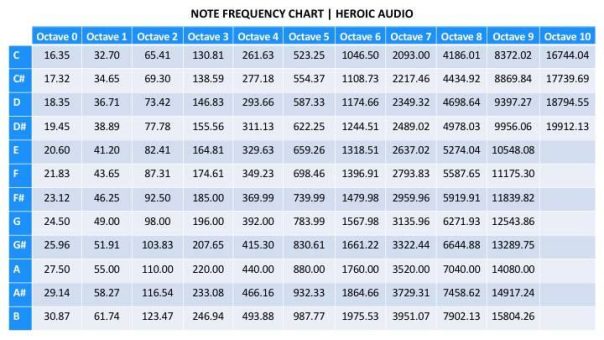
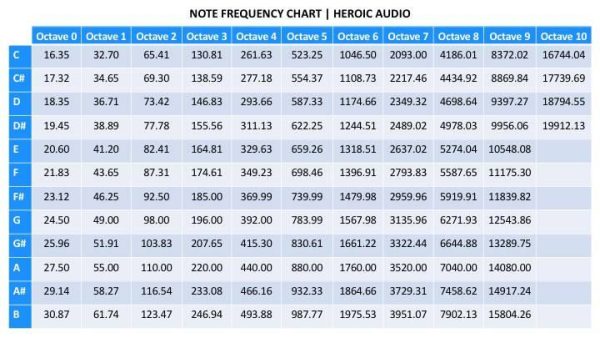
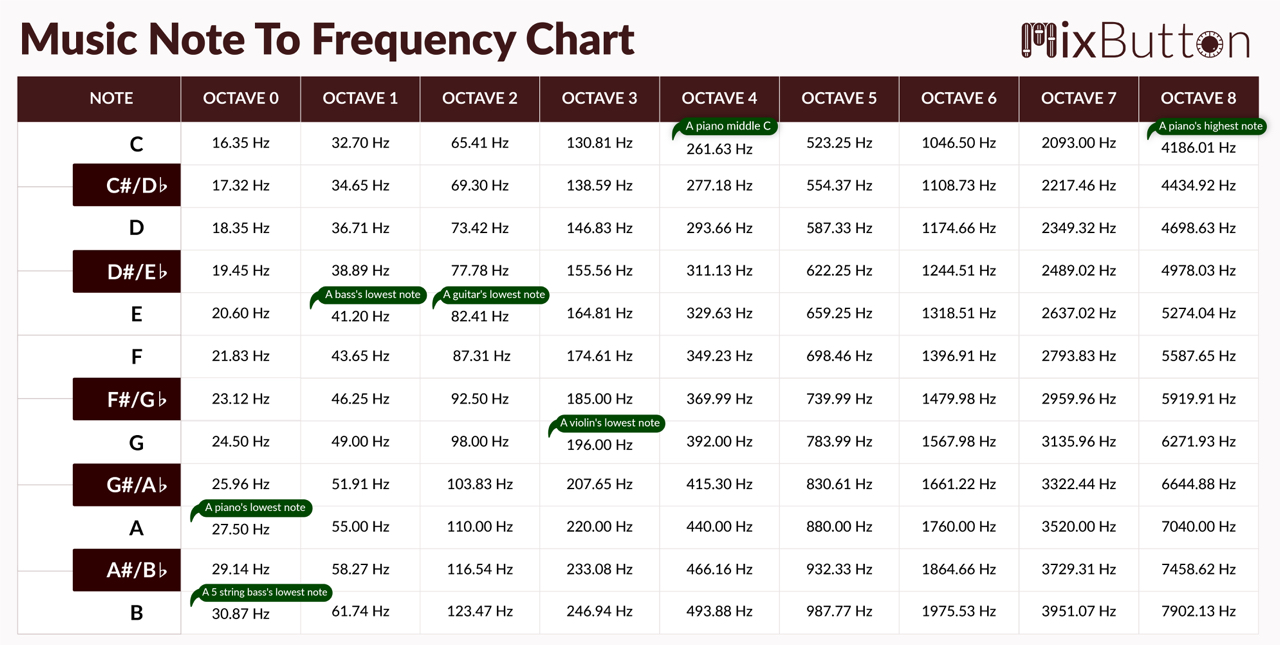
The Full Chart (Partial):
Whereas an entire chart could be intensive, overlaying all the audible vary, a partial chart illustrating just a few octaves supplies a transparent understanding:
| Observe | Frequency (Hz) (approx.) | Octave |
|---|---|---|
| C4 | 261.63 | 4 |
| C#4/Db4 | 277.18 | 4 |
| D4 | 293.66 | 4 |
| D#4/Eb4 | 311.13 | 4 |
| E4 | 329.63 | 4 |
| F4 | 349.23 | 4 |
| F#4/Gb4 | 369.99 | 4 |
| G4 | 392.00 | 4 |
| G#4/Ab4 | 415.30 | 4 |
| A4 | 440.00 | 4 |
| A#4/Bb4 | 466.16 | 4 |
| B4 | 493.88 | 4 |
| C5 | 523.25 | 5 |
| … | … | … |
Variations and Concerns:
Whereas the 440 Hz A4 normal is broadly adopted, it is not universally adhered to. Traditionally, completely different live performance pitches have been used, starting from roughly 415 Hz to 466 Hz. Some orchestras and ensembles should still desire barely completely different tuning requirements, typically based mostly on historic preferences or perceived acoustic advantages. These variations can subtly have an effect on the general timbre and perceived "brightness" of the music.
Moreover, the equal temperament system, whereas handy and broadly used, shouldn’t be the one tuning system. Different programs, akin to simply intonation and Pythagorean tuning, provide completely different interval relationships, typically leading to a richer, extra advanced harmonic expertise, albeit at the price of much less constant intonation throughout completely different keys.
Sensible Functions:
The musical observe frequency chart has quite a few sensible purposes:
- Instrument Tuning: Musicians use tuning forks, digital tuners, or apps based mostly on the frequency chart to precisely tune their devices.
- Sound Design and Synthesis: Composers and sound designers use the chart to create particular tones and timbres utilizing synthesizers and digital audio workstations (DAWs).
- Audio Engineering: Sound engineers use frequency charts to grasp and manipulate the frequency spectrum of audio indicators, using equalization (EQ) to form the sound and take away undesirable frequencies.
- Acoustics: Architects and acousticians use frequency charts to grasp how sound behaves in numerous areas, informing the design of live performance halls, recording studios, and different acoustically delicate environments.
- Music Remedy: Particular frequencies are believed to have therapeutic results, and music therapists could use this data to create calming or stimulating soundscapes.
- Scientific Analysis: The examine of frequency and pitch is essential in understanding human listening to, musical notion, and the neurobiological foundation of musical appreciation.
Past the Chart: The Human Notion of Pitch:
The frequency chart supplies a numerical illustration of pitch, however the human expertise of pitch is much extra nuanced. Our notion of pitch shouldn’t be fully linear; equal intervals in frequency don’t essentially correspond to equal perceived intervals of pitch. This phenomenon, often called the Mel scale, makes an attempt to mannequin the non-linear relationship between frequency and perceived pitch.
Moreover, timbre, the distinctive high quality of a sound that distinguishes it from different sounds of the identical pitch and loudness, can be closely influenced by the harmonic content material of the sound wave – the presence of overtones and different frequencies past the basic frequency. The elemental frequency determines the perceived pitch, however the overtones contribute considerably to the richness and complexity of the general sound.
Conclusion:
The musical observe frequency chart in Hz is a elementary device for understanding the physics and artistry of music. Whereas the 440 Hz A4 normal supplies a typical reference level, variations exist, and the human notion of pitch is much extra advanced than a easy numerical illustration. Understanding the frequency chart, nonetheless, is an important stepping stone to appreciating the intricate relationship between physics, arithmetic, and the deeply human expertise of music. From tuning devices to composing symphonies, the frequency chart performs a significant function in shaping the soundscape that surrounds us and enriches our lives. Additional exploration into the nuances of various tuning programs and the complexities of human auditory notion will solely deepen this appreciation and reveal the huge and interesting world of musical acoustics.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Decoding the Soundscape: A Deep Dive into the Musical Observe Frequency Chart in Hz. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!