distinguish between histogram and bar chart
Associated Articles: distinguish between histogram and bar chart
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to differentiate between histogram and bar chart. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Histograms vs. Bar Charts: Unveiling the Variations in Knowledge Visualization

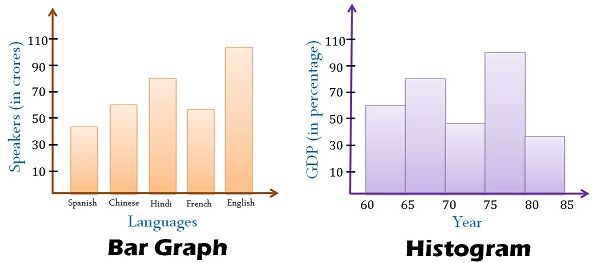
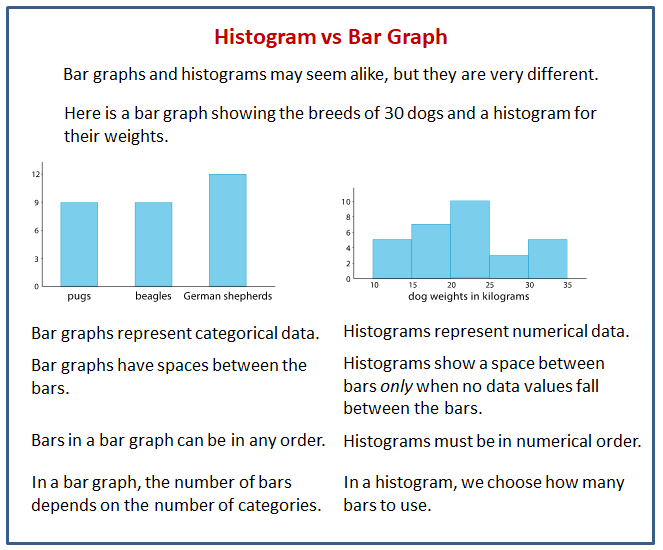
Histograms and bar charts are each standard instruments for visualizing information, usually resulting in confusion as a result of their superficial similarities. Whereas each use rectangular bars to characterize information, their underlying functions and the varieties of information they deal with differ considerably. Understanding these variations is essential for selecting the suitable chart to successfully talk insights out of your information. This text delves into the nuances of histograms and bar charts, highlighting their key distinctions and offering sensible examples to make clear their purposes.
Understanding Bar Charts: Categorical Knowledge Illustration
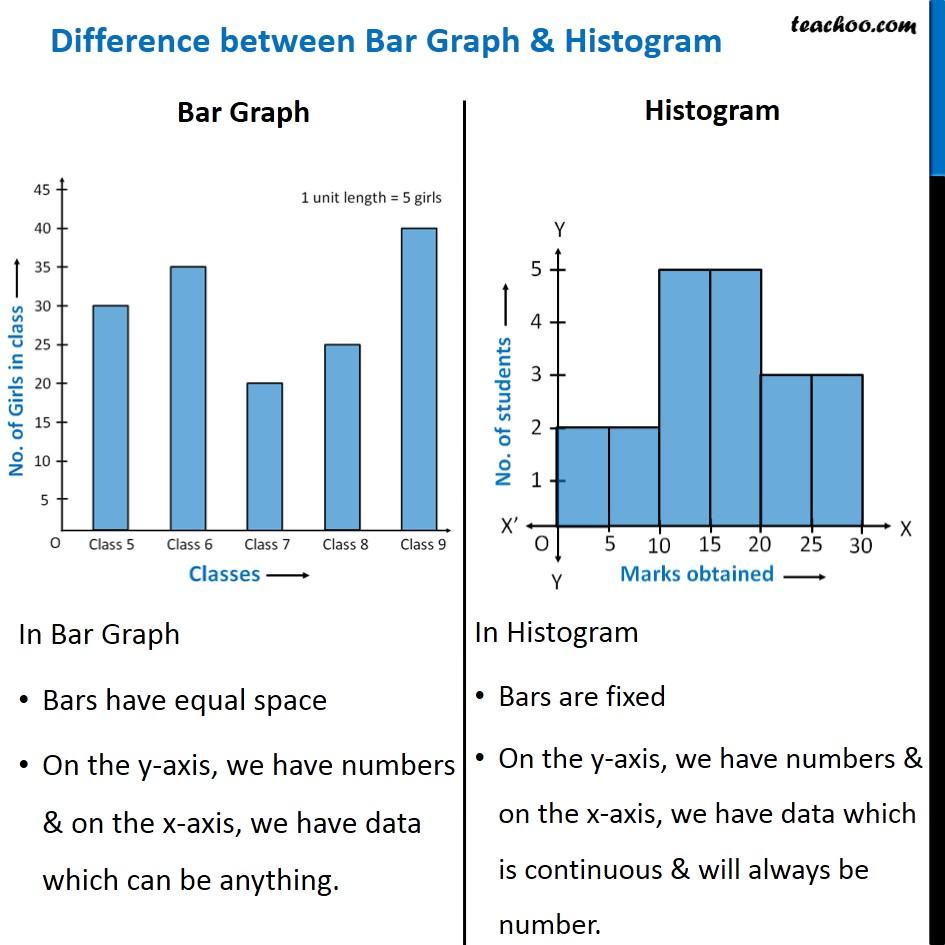
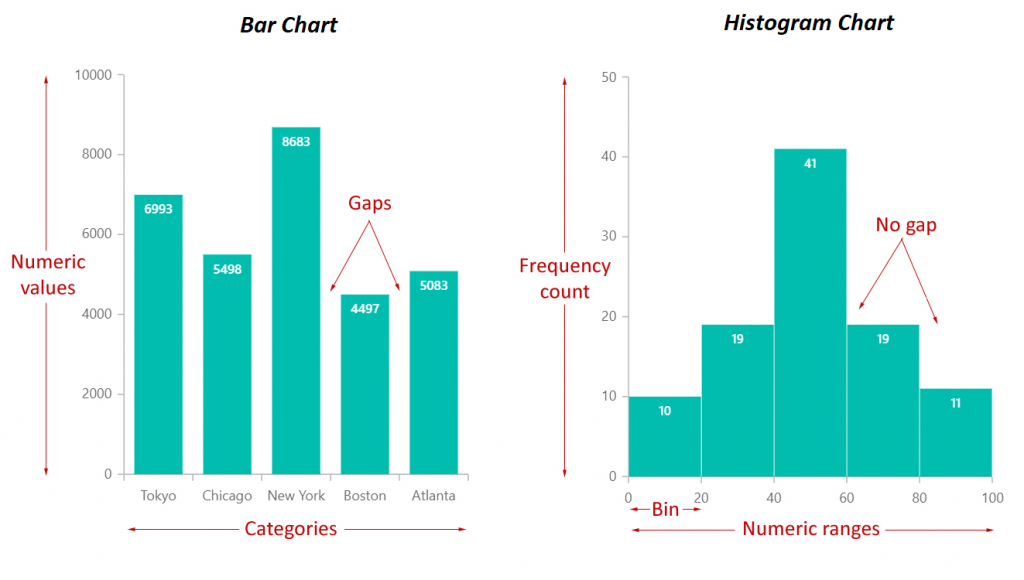
Bar charts are primarily used to characterize categorical information, which includes grouping information into distinct classes or courses. These classes might be qualitative (e.g., colours, varieties of fruits) or quantitative however discrete (e.g., variety of automobiles, scholar grades). The peak or size of every bar corresponds to the frequency or rely of observations inside that particular class. The bars are sometimes separated by gaps, emphasizing the distinct nature of every class.
Key Traits of Bar Charts:
- Categorical Knowledge: Designed for displaying the frequency or rely of observations in distinct classes.
- Discrete Bars: Bars are separated, highlighting the independence of classes.
- Order Issues (Typically): Whereas the order of classes is usually arbitrary, in some circumstances (e.g., time sequence), a selected order conveys significant info.
- A number of Sequence Doable: Bar charts can simply accommodate a number of sequence of knowledge, facilitating comparisons between totally different teams or time intervals (grouped bar charts).
- Straightforward Interpretation: The visible illustration makes it easy to check the frequencies of various classes.
Examples of Bar Chart Purposes:
- Gross sales Efficiency: Evaluating gross sales figures for various product traces over a month.
- Buyer Segmentation: Exhibiting the distribution of consumers throughout totally different age teams.
- Survey Outcomes: Visualizing responses to a multiple-choice query.
- Market Share: Representing the market share of various corporations in a selected trade.
- Election Outcomes: Displaying the variety of votes obtained by totally different candidates.
Understanding Histograms: Steady Knowledge Distribution
Not like bar charts, histograms are used to visualise the distribution of steady information. Steady information can tackle any worth inside a given vary (e.g., top, weight, temperature). A histogram divides this steady information right into a sequence of intervals or bins, and the peak of every bar represents the frequency or variety of information factors falling inside that particular bin. The bars in a histogram are adjoining, implying a steady move of knowledge.
Key Traits of Histograms:
- Steady Knowledge: Designed for displaying the distribution of steady information.
- Adjoining Bars: Bars are contiguous, representing the continual nature of the information.
- Bin Measurement Issues: The selection of bin dimension considerably impacts the looks and interpretation of the histogram. Too few bins can obscure particulars, whereas too many can create a jagged and uninformative visualization.
- Form Reveals Distribution: The general form of the histogram reveals vital details about the information distribution (e.g., regular, skewed, uniform).
- Frequency Density: Histograms might be offered utilizing frequency density on the y-axis, which permits for comparability of distributions with totally different pattern sizes or bin widths.
Examples of Histogram Purposes:
- Examination Scores: Exhibiting the distribution of scholar scores on a steady scale.
- Earnings Distribution: Visualizing the distribution of revenue ranges inside a inhabitants.
- Age Distribution: Displaying the age distribution of a selected group.
- Measurement Errors: Illustrating the distribution of measurement errors in a scientific experiment.
- Picture Processing: Analyzing the depth distribution of pixels in a picture.
Key Variations Summarized:
| Function | Bar Chart | Histogram |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Kind | Categorical (Qualitative or Discrete) | Steady |
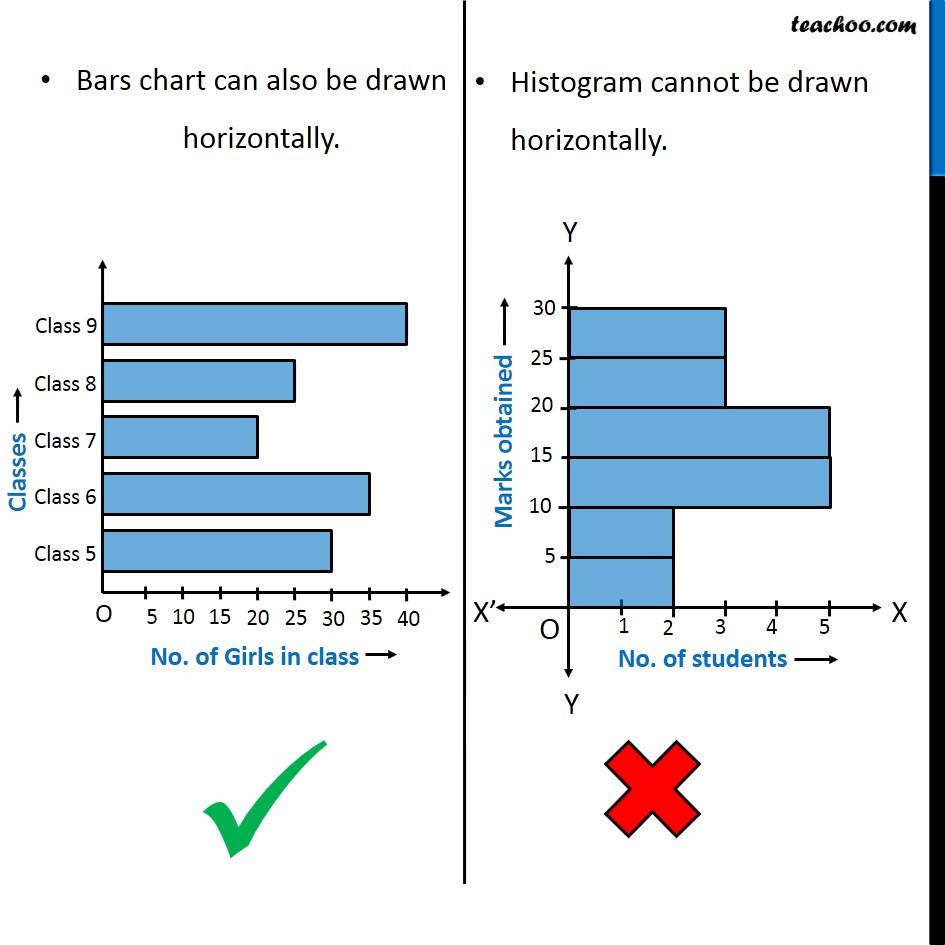
| Bars | Separate, distinct | Adjoining, contiguous |
| X-axis | Classes | Intervals or bins of steady information |
| Y-axis | Frequency or Rely | Frequency or Frequency Density |
| Objective | Examine frequencies throughout classes | Present the distribution of steady information |
| Bin Measurement | Not relevant | Essential for interpretation; impacts look |
| Gaps between bars | Current | Absent |
Selecting Between Bar Charts and Histograms:
The selection between a bar chart and a histogram relies upon fully on the character of your information.
- Use a bar chart when: You might have categorical information and need to examine the frequencies or counts of various classes. The order of classes could or will not be vital.
- Use a histogram when: You might have steady information and need to visualize its distribution. Cautious consideration needs to be given to the selection of bin dimension to successfully characterize the information’s underlying construction.
Superior Issues:
- Overlapping Knowledge: Whereas bar charts can deal with a number of sequence, histograms are much less appropriate for direct comparability of a number of steady datasets. Overlapping histograms might be troublesome to interpret. Contemplate different approaches like kernel density estimation plots for evaluating steady distributions.
- Knowledge Transformation: Remodeling steady information (e.g., utilizing logarithmic scales) can typically enhance the readability of a histogram, particularly when coping with skewed distributions.
- Software program Instruments: Most information visualization software program packages (e.g., Excel, R, Python’s Matplotlib and Seaborn) supply easy-to-use instruments for creating each bar charts and histograms.
Conclusion:
Whereas each bar charts and histograms use bars to characterize information, their purposes and interpretations differ considerably. Bar charts are perfect for visualizing categorical information, showcasing the frequencies of distinct classes. Histograms, alternatively, are designed for steady information, revealing the distribution and underlying patterns of the information. Understanding these variations is important for efficient information communication and correct interpretation of visible representations. By fastidiously contemplating the kind of information and the specified insights, you’ll be able to select essentially the most acceptable chart to successfully convey your findings. Misusing these charts can result in misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions, highlighting the significance of choosing the appropriate visualization software on your particular information evaluation wants.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into distinguish between histogram and bar chart. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!