Forecasting the 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charge: A Deep Dive into the Y-Chart and Past
Associated Articles: Forecasting the 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charge: A Deep Dive into the Y-Chart and Past
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Forecasting the 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charge: A Deep Dive into the Y-Chart and Past. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Forecasting the 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charge: A Deep Dive into the Y-Chart and Past

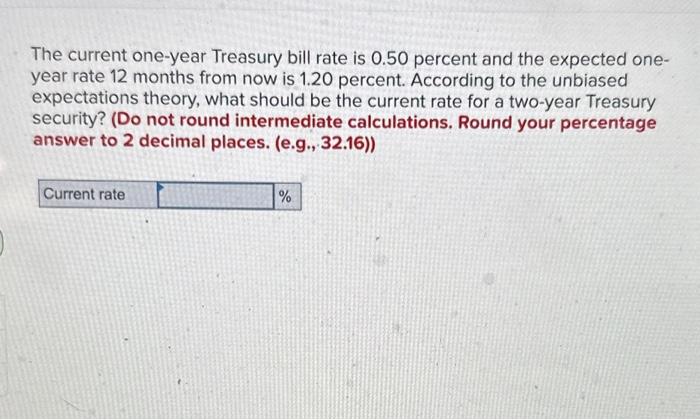
The 1-year Treasury invoice (T-bill) fee serves as an important benchmark for short-term rates of interest in america, impacting all the things from borrowing prices for companies to mortgage charges for owners. Precisely forecasting this fee is a fancy endeavor, requiring a nuanced understanding of macroeconomic elements, financial coverage, and market sentiment. Whereas no forecast is ideal, using instruments just like the Y-chart (a graphical illustration of yield curves) alongside different financial indicators can present beneficial insights into potential future actions. This text delves into the complexities of forecasting the 1-year T-bill fee, specializing in the data gleaned from the Y-chart and incorporating different essential elements for a extra complete evaluation.
The Y-Chart and its Relevance to T-Invoice Charge Forecasting
The Y-chart, also called the yield curve, plots the yields of Treasury securities towards their maturities. It visually represents the connection between the rate of interest (yield) and the time to maturity. By inspecting the slope and form of the yield curve, economists and buyers can infer market expectations about future rates of interest and financial progress.
A steeply upward-sloping yield curve (long-term yields considerably greater than short-term yields) usually suggests expectations of future financial growth and rising rates of interest. Buyers demand greater yields for lending their cash for longer durations, reflecting their perception in greater inflation and stronger financial progress down the road. On this situation, the 1-year T-bill fee is predicted to rise within the coming yr, reflecting the anticipated tightening of financial coverage by the Federal Reserve (Fed).
Conversely, a flat or inverted yield curve (long-term yields decrease than short-term yields) typically indicators issues about future financial slowdown and even recession. Buyers could also be much less prepared to just accept greater dangers related to longer-term bonds, even when the potential return is greater. This situation normally means that the 1-year T-bill fee may both stay secure and even lower, doubtlessly reflecting the Fed’s efforts to stimulate the financial system via decrease rates of interest.
Nonetheless, the Y-chart alone is inadequate for exact forecasting. It supplies beneficial contextual info however lacks the granularity wanted for correct predictions. The form of the yield curve may be influenced by numerous elements past easy financial expectations, together with provide and demand dynamics within the bond market, regulatory modifications, and international financial occasions.
Components Past the Y-Chart: A Holistic Strategy
To develop a extra sturdy forecast for the 1-year T-bill fee, we should take into account a number of different essential elements:
-
Federal Reserve Financial Coverage: The Fed’s actions are paramount. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) units the federal funds fee, the goal fee for in a single day lending between banks. Adjustments within the federal funds fee straight affect different short-term rates of interest, together with the T-bill fee. Analyzing FOMC statements, press conferences, and financial projections supplies essential perception into the Fed’s future coverage path. Ahead steerage, whereas not at all times exact, provides clues in regards to the probably path of rates of interest.
-
Inflation: Inflation is a major driver of rates of interest. Larger inflation erodes the buying energy of cash, prompting the Fed to boost rates of interest to curb inflation. Indicators just like the Shopper Value Index (CPI) and the Producer Value Index (PPI) present beneficial information on inflation tendencies. Market expectations of future inflation, typically mirrored in inflation-indexed bonds (TIPS), additionally play an important position.
-
Financial Development: The tempo of financial progress considerably influences rate of interest actions. Sturdy financial progress normally results in greater inflation and elevated demand for credit score, pushing rates of interest upward. Conversely, weak financial progress can result in decrease rates of interest because the Fed tries to stimulate the financial system. Key financial indicators like GDP progress, employment figures (non-farm payrolls), and client spending present essential information on the well being of the financial system.
-
World Financial Circumstances: The US financial system is intertwined with the worldwide financial system. Occasions in different international locations, resembling geopolitical instability, monetary crises, or important shifts in international commerce, can affect US rates of interest. Monitoring international financial information and geopolitical dangers is important for correct forecasting.
-
Market Sentiment and Hypothesis: Market sentiment and investor expectations play a major position in shaping rate of interest actions. Surprising information or occasions can set off important shifts in market sentiment, resulting in fast modifications in rates of interest. Analyzing market indices, investor confidence surveys, and information sentiment can present insights into market expectations.
Growing a Forecast: A Multi-faceted Strategy
Integrating the data from the Y-chart with these different elements requires a multi-faceted strategy. One widespread technique is to make use of econometric fashions that incorporate numerous macroeconomic variables to foretell future rates of interest. These fashions may be fairly subtle, incorporating lagged variables and interplay phrases to seize complicated relationships between variables.
Nonetheless, econometric fashions are usually not with out limitations. They depend on historic information and should not precisely seize unexpected occasions or shifts in market sentiment. Subsequently, qualitative evaluation, involving knowledgeable judgment and interpretation of present occasions, can also be essential. A balanced strategy that mixes quantitative modeling with qualitative evaluation is usually the simplest technique.
Instance: Hypothetical 1-Yr T-Invoice Charge Forecast
Let’s take into account a hypothetical situation. Suppose the Y-chart exhibits a reasonably upward-sloping curve, suggesting expectations of average financial progress and step by step rising rates of interest. Nonetheless, inflation is presently operating greater than the Fed’s goal, and the Fed has signaled its intention to aggressively fight inflation via additional rate of interest hikes. Moreover, international financial uncertainty is comparatively excessive.
On this situation, an inexpensive forecast may be a gradual enhance within the 1-year T-bill fee over the subsequent yr, maybe from 4% to five%, reflecting the Fed’s tightening coverage and chronic inflationary pressures. The upward-sloping yield curve helps this forecast, however the excessive inflation and international uncertainty add to the upward stress on charges. This forecast would have to be frequently up to date as new financial information and coverage bulletins grow to be accessible.
Conclusion: The Imperfect Artwork of Forecasting
Forecasting the 1-year T-bill fee is a difficult activity, requiring a complete understanding of quite a few interconnected elements. Whereas the Y-chart supplies beneficial insights into market expectations, it’s only one piece of the puzzle. A holistic strategy that integrates the Y-chart with evaluation of financial coverage, inflation, financial progress, international circumstances, and market sentiment is critical for creating a extra correct and sturdy forecast. It’s essential to keep in mind that no forecast is ideal, and sudden occasions can considerably affect rate of interest actions. Common monitoring and adjustment of the forecast primarily based on new info are important for staying knowledgeable and making sound funding selections.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Forecasting the 1-Yr Treasury Invoice Charge: A Deep Dive into the Y-Chart and Past. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!