Japan’s Debt-to-GDP Ratio: A Mountain of Debt or a Managed Problem?
Associated Articles: Japan’s Debt-to-GDP Ratio: A Mountain of Debt or a Managed Problem?
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Japan’s Debt-to-GDP Ratio: A Mountain of Debt or a Managed Problem?. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Japan’s Debt-to-GDP Ratio: A Mountain of Debt or a Managed Problem?

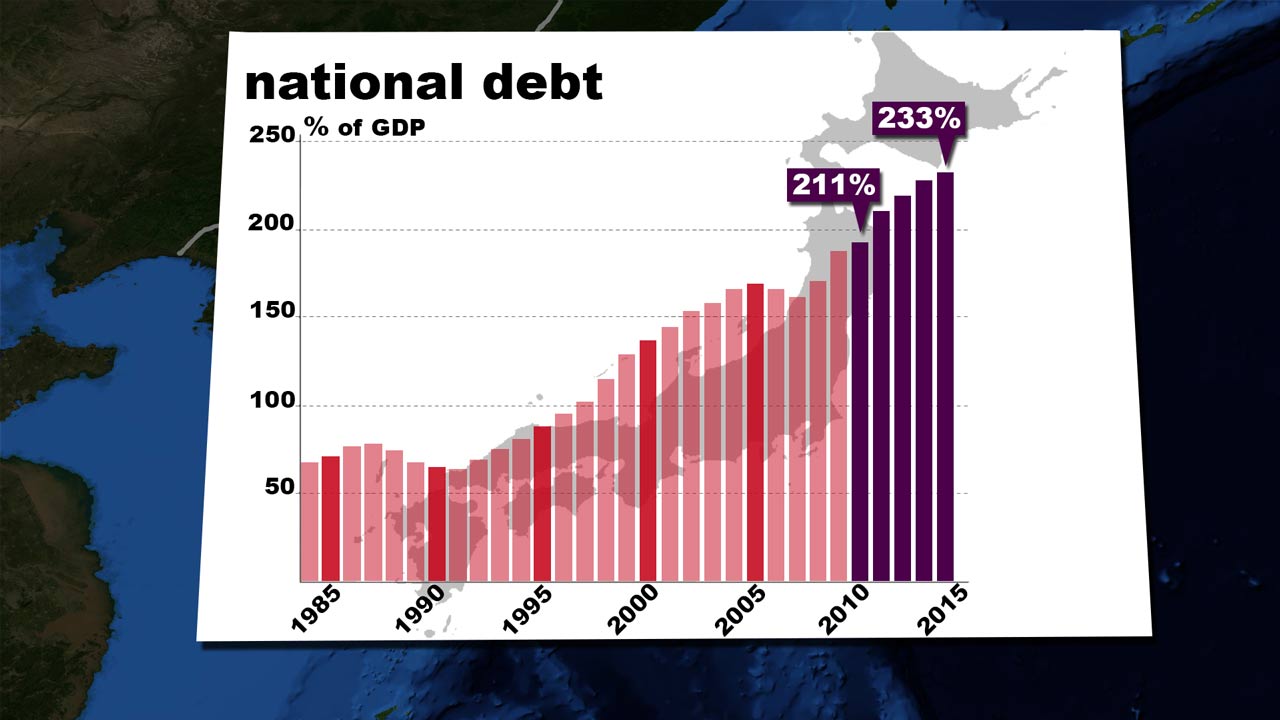
Japan’s staggering authorities debt-to-GDP ratio has lengthy been a supply of worldwide fascination and concern. For many years, it has persistently held the unenviable place of getting the best ratio amongst developed nations, dwarfing even closely indebted international locations like Italy or Greece. Understanding this ratio, its historic context, and the components contributing to its persistence is essential to comprehending Japan’s financial panorama and its potential future. This text will delve into the intricacies of Japan’s debt-to-GDP chart, exploring its evolution, the underlying causes, the implications for the Japanese financial system, and the potential options debated by economists and policymakers.
A Historic Perspective: The Ascent of Japan’s Debt
The chart depicting Japan’s debt-to-GDP ratio reveals a dramatic upward pattern, notably because the bursting of the asset value bubble within the early Nineteen Nineties. Previous to this era, Japan’s debt ranges had been comparatively manageable, reflecting a interval of strong financial progress and financial prudence. Nonetheless, the "Misplaced Decade" (and past) – characterised by deflation, stagnant progress, and a collection of financial crises – essentially altered the trajectory.
The federal government responded to the financial downturn with aggressive fiscal stimulus packages aimed toward boosting demand and stopping a deeper recession. These packages, whereas supposed to be short-term measures, turned a recurring characteristic of Japanese financial coverage. Every stimulus bundle added considerably to the nationwide debt, pushing the debt-to-GDP ratio ever greater. This reliance on fiscal enlargement, coupled with persistent deflation, created a vicious cycle: low progress necessitates extra stimulus, which in flip will increase debt, additional dampening progress prospects.
The chart would visually present a comparatively flat line till the early Nineteen Nineties, adopted by a steep and sustained incline. The years following the 2008 world monetary disaster would present one other vital surge, as Japan carried out additional stimulus measures to counteract the worldwide financial slowdown. The COVID-19 pandemic additionally contributed to an additional improve within the debt-to-GDP ratio, as the federal government carried out large-scale assist packages to mitigate the financial affect of the disaster.
Elements Contributing to the Excessive Debt-to-GDP Ratio:
A number of interconnected components have contributed to the persistently excessive debt-to-GDP ratio in Japan:
-
Demographic Shifts: Japan faces a quickly ageing inhabitants and declining delivery charge, resulting in a shrinking workforce and growing strain on social safety and healthcare programs. These demographic traits necessitate elevated authorities spending, including to the debt burden.
-
Deflationary Pressures: Persistent deflation has hindered financial progress and lowered tax revenues. Deflation makes it harder for the federal government to service its debt, as the true worth of debt will increase over time.
-
Fiscal Stimulus Packages: As beforehand talked about, the repeated reliance on fiscal stimulus packages to fight financial stagnation has been a serious driver of debt accumulation. Whereas these measures could have prevented deeper recessions, they’ve come at the price of a considerably greater nationwide debt.
-
Low Curiosity Charges: Japan has maintained extraordinarily low rates of interest for an prolonged interval, which has helped to maintain the price of servicing the debt comparatively low. Nonetheless, this coverage additionally contributes to deflation and limits the effectiveness of financial coverage.
-
Political Constraints: A fancy political panorama and a reluctance to implement unpopular structural reforms have hindered efforts to handle the debt drawback. There’s usually a political trade-off between short-term financial features and long-term fiscal sustainability.
Implications of the Excessive Debt-to-GDP Ratio:
The excessive debt-to-GDP ratio poses a number of vital challenges for the Japanese financial system:
-
Elevated Vulnerability to Financial Shocks: A excessive debt burden makes Japan extra weak to exterior financial shocks, because it limits the federal government’s fiscal flexibility to reply successfully to crises.
-
Slower Financial Development: The excessive debt stage can crowd out personal funding and hinder financial progress. Traders could also be hesitant to put money into a rustic with such a big debt burden.
-
Potential for a Debt Disaster: Whereas Japan’s debt is essentially held domestically, a sudden lack of confidence within the Japanese financial system may set off a debt disaster, resulting in a pointy improve in rates of interest and a possible sovereign debt default.
-
Elevated Tax Burden: To deal with the debt drawback, the federal government could have to implement vital tax will increase, which may negatively affect shopper spending and financial progress.
Potential Options and Coverage Debates:
Addressing Japan’s debt drawback requires a multi-pronged method that mixes fiscal consolidation, structural reforms, and financial coverage changes. Nonetheless, the optimum technique stays a topic of intense debate amongst economists and policymakers.
-
Fiscal Consolidation: This entails decreasing authorities spending and/or growing tax revenues. Nonetheless, implementing vital fiscal austerity measures may additional dampen financial progress and exacerbate deflationary pressures.
-
Structural Reforms: Bettering productiveness, selling innovation, and growing labor market flexibility are essential to boosting financial progress and producing greater tax revenues. These reforms usually face political resistance resulting from their potential short-term prices.
-
Financial Coverage Changes: Whereas low rates of interest have helped to maintain the price of servicing the debt low, they’ve additionally contributed to deflation. A shift in direction of a extra expansionary financial coverage may stimulate inflation and enhance financial progress, however it additionally carries dangers.
-
Debt Monetization: This entails the central financial institution immediately financing authorities debt by buying authorities bonds. Whereas this might present short-term reduction, it additionally carries the danger of fueling inflation and eroding the central financial institution’s independence.
-
Worldwide Cooperation: Given the worldwide interconnectedness of economies, worldwide cooperation and assist may play a task in managing Japan’s debt drawback.
Conclusion:
Japan’s debt-to-GDP ratio presents a posh and multifaceted problem. The chart’s upward trajectory displays a long time of financial stagnation, demographic shifts, and coverage responses. Whereas the fast danger of a debt disaster could also be low as a result of home nature of the debt and low rates of interest, the long-term sustainability of the present state of affairs stays a critical concern. Addressing this problem requires a complete and punctiliously calibrated method that balances the necessity for fiscal duty with the crucial to stimulate financial progress and enhance dwelling requirements. The success of any technique will rely upon the political will to implement troublesome reforms and the power to navigate the advanced interaction of fiscal, financial, and structural components. The long run trajectory of Japan’s debt-to-GDP ratio might be a vital indicator of its financial well being and its potential to navigate the challenges of the twenty first century.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Japan’s Debt-to-GDP Ratio: A Mountain of Debt or a Managed Problem?. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!