Mastering the p-Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes
Associated Articles: Mastering the p-Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing subject associated to Mastering the p-Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering the p-Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes

Course of management charts are important instruments for monitoring the standard of a course of over time. Whereas many charts concentrate on steady information (like weight or size), many high quality traits are attributes – they’re both current or absent, conforming or non-conforming. The p-chart, a strong management chart inside the Minitab statistical software program bundle, is particularly designed to trace the proportion of non-conforming models in a pattern over time. This text offers a complete information to understanding, creating, deciphering, and using p-charts in Minitab, protecting the whole lot from primary ideas to superior functions.
Understanding the p-Chart’s Basis
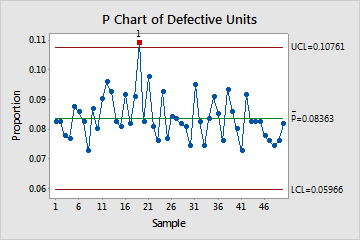
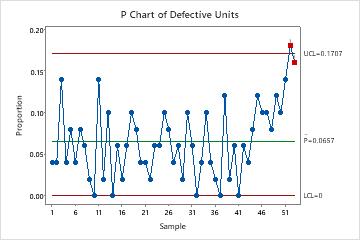
The p-chart plots the proportion (p) of faulty or non-conforming models in a pattern towards the pattern quantity. Every pattern represents a subgroup of models taken from the method at a selected time limit. The chart’s function is to establish whether or not the method is steady (in management) or exhibiting uncommon variation (uncontrolled). Out-of-control indicators point out potential issues inside the course of that require investigation and correction.
The core of the p-chart depends on the binomial distribution, assuming every unit in a pattern has a relentless likelihood of being non-conforming, and the outcomes (conforming/non-conforming) are unbiased. Whereas this assumption isn’t completely met in actuality, the p-chart stays a strong software for sensible course of monitoring.
Key Elements of a p-Chart
A typical p-chart in Minitab shows the next:
- Pattern Proportions (p): The person pattern proportions of non-conforming models plotted on the vertical axis.
- Central Line (p-bar): The common proportion of non-conforming models throughout all samples. This represents the general course of common.
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): The higher boundary past which a pattern proportion suggests the method is uncontrolled. Factors above this restrict sign potential issues.
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): The decrease boundary beneath which a pattern proportion suggests the method is uncontrolled. Factors beneath this restrict additionally point out potential points.
Minitab robotically calculates these limits utilizing established statistical strategies, sometimes based mostly on the usual deviation of the pattern proportions. The formulation used are:
- p-bar: The common of the pattern proportions.
- UCL: p-bar + 3 * √(p-bar(1-p-bar)/n)
- LCL: p-bar – 3 * √(p-bar(1-p-bar)/n)
the place ‘n’ is the pattern dimension. Observe that if the LCL falls beneath zero, it is typically set to zero, as a proportion can’t be adverse.
Making a p-Chart in Minitab
The method of making a p-chart in Minitab is easy:
-
Knowledge Entry: Arrange your information in two columns. The primary column ought to characterize the pattern quantity (or time interval), and the second column ought to include the variety of non-conforming models in every pattern. It is essential to keep up constant pattern sizes all through the info. If pattern sizes fluctuate considerably, Minitab presents choices to account for this, as detailed later.
-
Navigate to Stat > Management Charts > Attributes Charts > P Chart: This opens the p-chart dialog field.
-
Choose Columns: Specify the column containing the variety of non-conforming models because the ‘Variable’ and the column representing the pattern dimension because the ‘Subgroup dimension’. If the pattern dimension is fixed, you’ll be able to merely enter the worth straight.
-
Choices (Optionally available): Discover the ‘Choices’ sub-menu to customise your chart. You may modify the chart title, subtitle, and different visible facets. Extra importantly, you’ll be able to regulate the management limits calculation technique and discover choices for dealing with variable pattern sizes. Minitab offers a number of strategies, together with utilizing a weighted common for p-bar.
-
Create the Chart: Click on ‘OK’ to generate the p-chart. Minitab will show the chart, together with the pattern proportions, central line, UCL, and LCL.
Decoding the p-Chart
Decoding the p-chart includes in search of indicators that the method is uncontrolled. These indicators sometimes embody:
-
Factors outdoors the management limits: Any level above the UCL or beneath the LCL signifies a statistically vital deviation from the anticipated course of habits. These factors warrant rapid investigation to establish the basis reason for the variation.
-
Runs: A sequence of consecutive factors above or beneath the central line, even when they do not exceed the management limits, would possibly point out a shift within the course of imply. Minitab typically highlights potential runs on the chart.
-
Traits: A constant upward or downward development within the plotted factors suggests a gradual change within the course of over time.
-
Uncommon patterns: Any uncommon or non-random patterns within the information, akin to cyclical variations, warrant investigation.
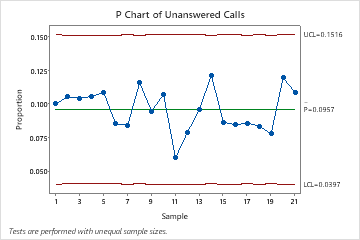
Dealing with Variable Pattern Sizes in Minitab
When pattern sizes fluctuate throughout subgroups, the usual p-chart formulation want modification. Minitab presents a number of approaches to deal with this:
-
Utilizing a weighted common for p-bar: This technique calculates the common proportion, weighting every pattern proportion by its corresponding pattern dimension. This offers a extra correct illustration of the general course of common.
-
Utilizing the common pattern dimension: This simplifies the calculation through the use of the common pattern dimension throughout all subgroups within the management restrict formulation. Whereas much less exact than the weighted common, it is a easier strategy if the variation in pattern sizes just isn’t substantial.
Minitab’s p-chart dialog field means that you can choose the suitable technique for dealing with variable pattern sizes.
Superior Purposes and Concerns
The p-chart’s functions prolong past primary course of monitoring:
-
Course of Functionality Evaluation: By analyzing the management chart information, you’ll be able to assess the method functionality to satisfy specified high quality necessities.
-
Figuring out assignable causes: Factors outdoors the management limits present clues to establish and tackle assignable causes of variation, resulting in course of enchancment.
-
Predictive modeling: The p-chart information can be utilized to develop predictive fashions for forecasting future course of efficiency.
-
Integration with different Minitab instruments: The p-chart will be built-in with different Minitab instruments, akin to functionality evaluation and speculation testing, for a extra complete evaluation.
Limitations of the p-Chart
Whereas a priceless software, the p-chart has limitations:
-
Assumption of fixed likelihood: The belief of a relentless likelihood of non-conformance won’t all the time maintain true in real-world situations.
-
Sensitivity to pattern dimension: The effectiveness of the p-chart depends upon the pattern dimension. Small pattern sizes can result in wider management limits and diminished sensitivity to course of shifts.
-
Interpretation requires judgment: Whereas statistical indicators point out potential issues, deciphering these indicators requires skilled judgment and consideration of the particular context of the method.
Conclusion
The p-chart in Minitab is a strong software for monitoring and bettering processes the place the standard attribute is an attribute. By understanding its ideas, successfully utilizing Minitab’s capabilities, and thoroughly deciphering the outcomes, you’ll be able to considerably improve your skill to regulate and optimize your processes, resulting in improved high quality and diminished variability. Keep in mind to all the time contemplate the restrictions of the p-chart and mix its insights with different high quality administration methods for a complete strategy to course of enchancment. The flexibility to precisely interpret and react to the indicators supplied by the p-chart is vital to using this highly effective software to its full potential.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied priceless insights into Mastering the p-Chart in Minitab: A Complete Information to Course of Management for Attributes. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!