Navigating the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowcharts
Associated Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowcharts
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Navigating the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowcharts. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowcharts

Stable waste administration (SWM) is a essential side of public well being and environmental safety. Environment friendly and efficient SWM methods are important for stopping air pollution, defending human well being, and conserving sources. A key device for understanding and optimizing these methods is the method flowchart. This text delves into the intricacies of making and deciphering stable waste administration course of flowcharts, exploring the assorted levels concerned and the particular concerns for various waste streams.
Understanding the Objective of a Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowchart:
A course of flowchart visually represents the sequential steps concerned in managing stable waste, from its era to its ultimate disposal. These charts are invaluable instruments for:
- System Evaluation: Figuring out bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for enchancment inside the current SWM system.
- Planning and Design: Guiding the event of recent or improved SWM infrastructure and techniques.
- Coaching and Schooling: Offering a transparent and concise illustration of the SWM course of for stakeholders, together with waste turbines, collectors, and processors.
- Monitoring and Analysis: Monitoring the efficiency of the SWM system and assessing its effectiveness in attaining its targets.
- Communication and Collaboration: Facilitating communication and collaboration amongst completely different stakeholders concerned in SWM.
Parts of a Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowchart:
A typical SWM flowchart makes use of commonplace flowchart symbols to characterize completely different levels and actions. These embody:
- Rectangles: Characterize processes or actions.
- Diamonds: Characterize determination factors or branching paths.
- Parallelograms: Characterize enter or output.
- Arrows: Point out the stream of supplies or data.
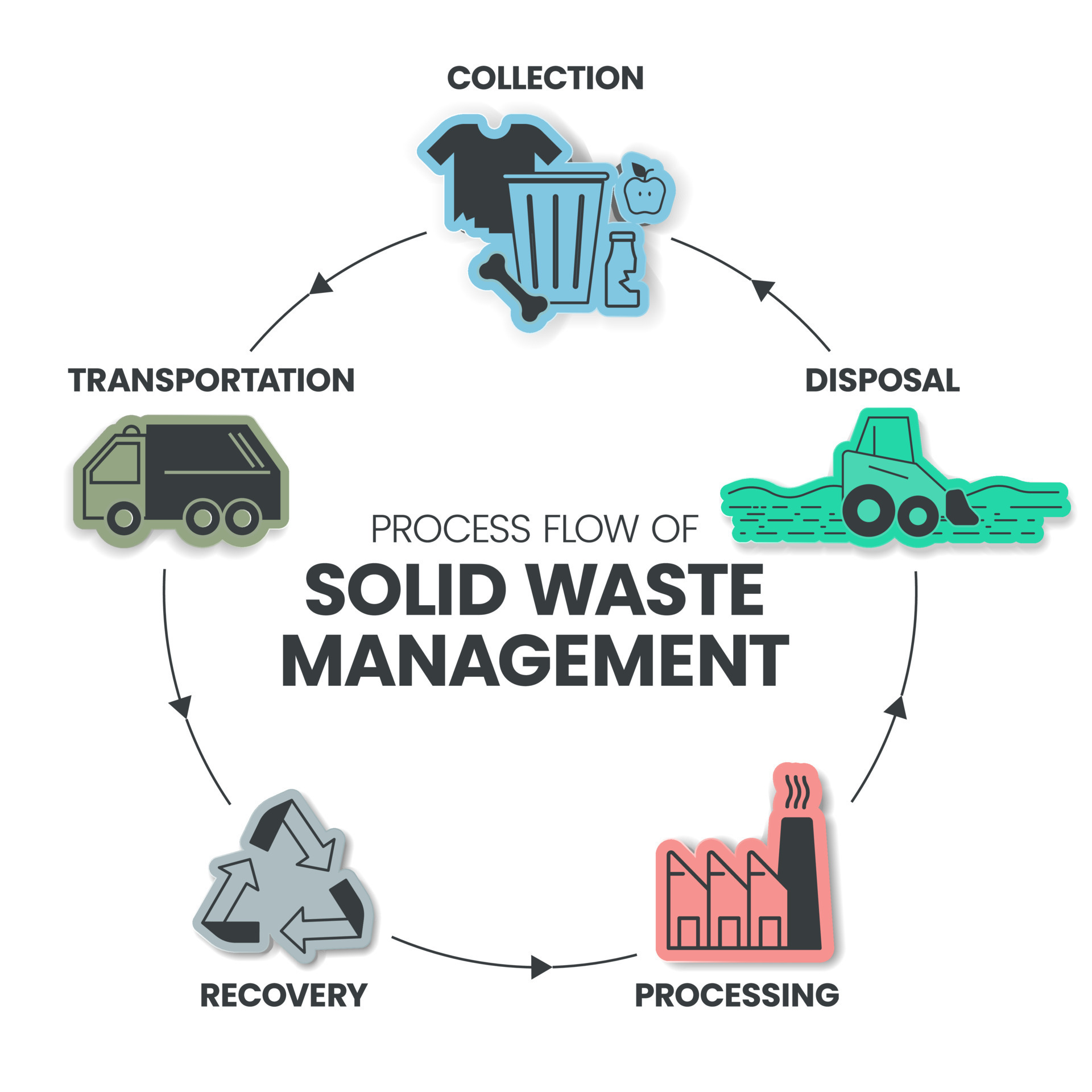
A Generic Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowchart:
Whereas particular flowcharts will range relying on the context (e.g., residential, business, industrial), a generic flowchart usually contains the next levels:
-
Waste Technology: That is the place to begin, representing the era of stable waste from numerous sources (residential, business, industrial, institutional). The flowchart may additional categorize waste based mostly on its kind (natural, recyclable, hazardous, and so forth.).
-
Waste Assortment: This stage depicts the strategies used to gather waste from era factors. This might contain curbside assortment, communal bins, or specialised assortment for hazardous waste. The flowchart ought to specify the gathering frequency and the sorts of automobiles used.
-
Waste Transportation: This stage reveals the transportation of collected waste to switch stations, processing services, or landfills. The flowchart ought to point out the routes, transportation strategies (vehicles, trains), and distances concerned.
-
Waste Switch (Elective): Switch stations are sometimes used to consolidate waste from a number of assortment factors earlier than transporting it to the ultimate disposal or processing facility. This stage is non-obligatory however frequent in bigger methods.
-
Waste Processing: It is a essential stage that entails numerous strategies relying on the kind of waste. This might embody:
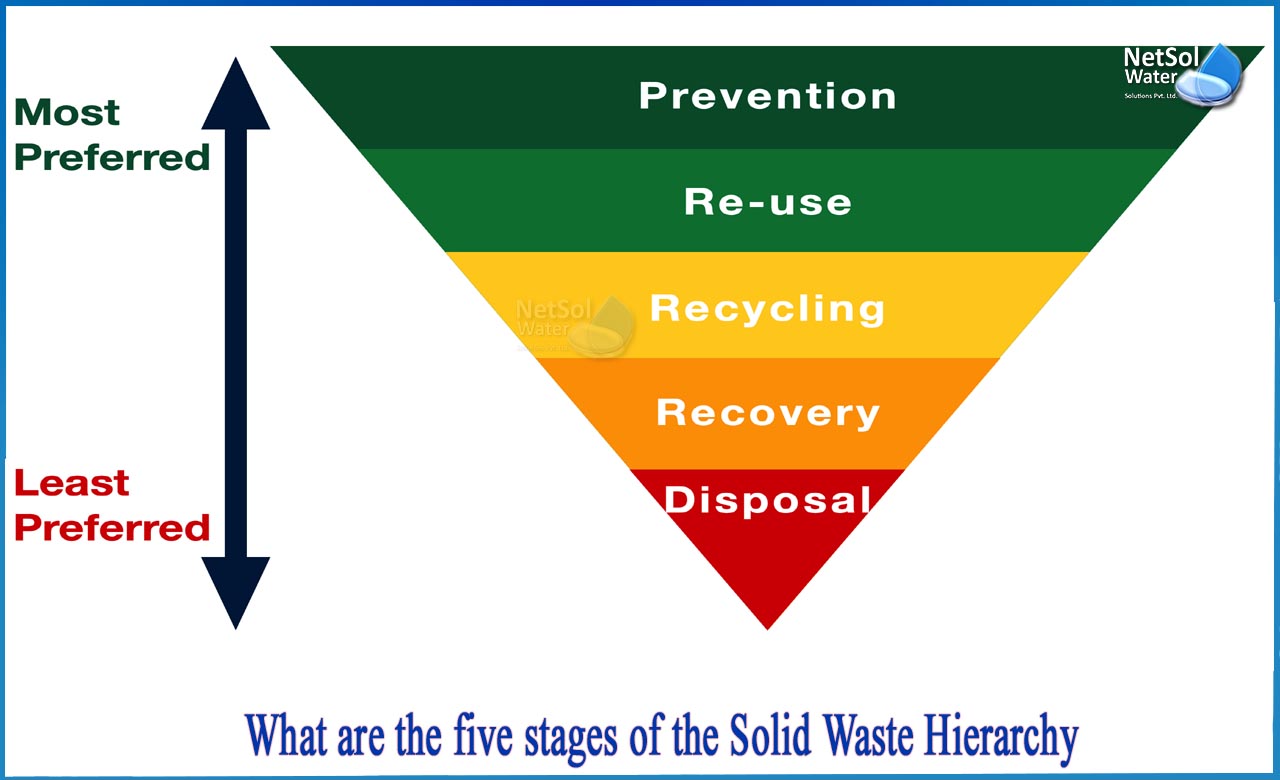
- Recycling: Separating and processing recyclable supplies for reuse.
- Composting: Processing natural waste to supply compost.
- Incineration: Burning waste to cut back quantity and generate vitality (with applicable emission controls).
- Waste-to-Vitality: Using waste as a gasoline supply for vitality era.
-
Waste Disposal: That is the ultimate stage, the place processed or unprocessed waste is disposed of. Choices embody:
- Landfilling: Burying waste in designated landfills, typically with measures to stop environmental contamination.
- Incineration with ash disposal: The ash residue from incineration requires correct disposal.
- Deep effectively injection (for particular liquid waste): Injecting liquid waste deep underground.
Determination Factors within the Flowchart:
The flowchart ought to incorporate determination factors to account for the variability in waste streams and processing choices. Examples embody:
- Waste Sorting: A call level to find out whether or not waste is recyclable, compostable, or destined for landfill.
- Materials Restoration Facility (MRF) Processing: A call level to find out the suitable processing methodology for various recyclable supplies.
- Hazardous Waste Dealing with: A call level to segregate and deal with hazardous waste based on laws.
- Landfill Capability: A call level to find out if landfill capability is ample or if various disposal strategies are wanted.
Particular Concerns for Totally different Waste Streams:
The flowchart needs to be tailor-made to the particular waste streams being managed. For example:
-
Hazardous Waste Administration: Requires a extra detailed flowchart that addresses particular dealing with, storage, transportation, and disposal necessities for hazardous supplies. This contains detailed labeling, security precautions, and compliance with laws.
-
Medical Waste Administration: Requires strict protocols for dealing with infectious and probably hazardous medical waste, together with sterilization, incineration, and protected disposal practices.
-
E-waste Administration: Focuses on the right dismantling, recycling, and disposal of digital waste, contemplating the environmental influence of heavy metals and different hazardous elements.
-
Building and Demolition Waste Administration: Addresses the particular challenges of managing giant volumes of development particles, specializing in recycling, reuse, and minimizing landfill disposal.
Superior Options in Stable Waste Administration Flowcharts:
Extra superior flowcharts can incorporate:
- Knowledge Integration: Linking the flowchart to databases that observe waste era, assortment, processing, and disposal information.
- Efficiency Indicators: Together with key efficiency indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectivity and effectiveness of the SWM system.
- Danger Evaluation: Figuring out potential dangers and hazards related to every stage of the SWM course of.
- Environmental Affect Evaluation: Incorporating data on the environmental influence of various SWM choices.
Conclusion:
Stable waste administration course of flowcharts are indispensable instruments for understanding, optimizing, and speaking the complexities of SWM methods. By visually representing the sequential steps concerned, these charts present a transparent and concise overview of the complete course of, facilitating environment friendly administration, improved decision-making, and enhanced environmental safety. Tailoring the flowchart to particular waste streams and incorporating superior options ensures a complete and efficient illustration of the SWM course of, contributing to a extra sustainable and more healthy atmosphere. The continual refinement and updating of those flowcharts based mostly on efficiency information and rising applied sciences are essential for sustaining environment friendly and environmentally sound stable waste administration practices.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Navigating the Labyrinth: A Complete Information to Stable Waste Administration Course of Flowcharts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!