Navigating the Tableau Panorama: A Complete Information to Chart Varieties
Associated Articles: Navigating the Tableau Panorama: A Complete Information to Chart Varieties
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Navigating the Tableau Panorama: A Complete Information to Chart Varieties. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Tableau Panorama: A Complete Information to Chart Varieties
Tableau, a robust knowledge visualization instrument, gives an enormous array of chart varieties, every designed to successfully talk particular insights out of your knowledge. Choosing the proper chart is essential for clear and impactful storytelling. A poorly chosen chart can obfuscate knowledge, resulting in misinterpretations and flawed conclusions. This text delves into the assorted chart varieties out there in Tableau, explaining their strengths, weaknesses, and perfect functions. We’ll discover each the elemental charts and a few of the extra specialised choices, offering a complete information that can assist you choose the perfect visualization on your knowledge.
I. Fundamental Chart Varieties: The Basis of Knowledge Visualization
These charts kind the bedrock of information visualization in Tableau, providing a strong place to begin for exploring and understanding your knowledge.
A. Bar Charts: Arguably essentially the most versatile chart kind, bar charts excel at evaluating categorical knowledge throughout totally different teams. They are perfect for exhibiting the relative sizes of various classes, making it straightforward to establish the biggest and smallest values.
- Strengths: Easy to grasp, efficient for comparisons, simply accommodates a number of classes.
- Weaknesses: Can turn into cluttered with too many classes, much less efficient for exhibiting tendencies over time.
- Perfect Purposes: Evaluating gross sales throughout totally different areas, exhibiting the distribution of buyer demographics, illustrating the frequency of various occasions. Horizontal bar charts are significantly helpful when class labels are lengthy.
B. Line Charts: Line charts are excellent for visualizing tendencies and patterns over time or throughout steady variables. They successfully showcase adjustments and fluctuations in knowledge, highlighting progress, decline, or cyclical patterns.
- Strengths: Wonderful for exhibiting tendencies, simply identifies peaks and troughs, permits for comparability of a number of tendencies.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with too many strains, much less efficient for evaluating discrete classes.
- Perfect Purposes: Monitoring gross sales over time, monitoring web site site visitors, visualizing inventory costs, exhibiting the development of a course of.
C. Pie Charts: Pie charts symbolize the proportion of every class inside an entire. They’re efficient at exhibiting the relative contribution of various elements to a complete.
- Strengths: Easy to grasp, visually interesting, successfully reveals proportions.
- Weaknesses: Tough to check small segments precisely, turns into cluttered with many classes, would not present tendencies properly.
- Perfect Purposes: Exhibiting market share, illustrating the composition of a price range, representing the distribution of buyer segments. Keep away from utilizing pie charts with many segments, as they turn into tough to interpret.
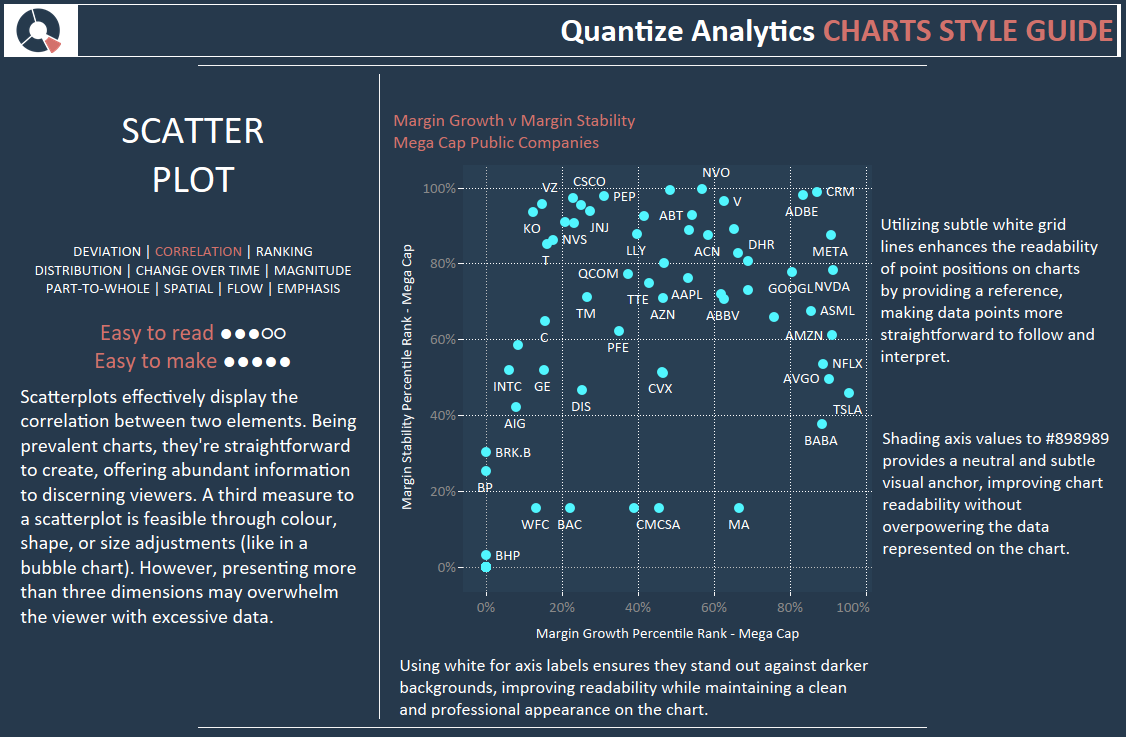
D. Scatter Plots: Scatter plots are used to point out the connection between two steady variables. They assist establish correlations, clusters, and outliers within the knowledge.
- Strengths: Reveals relationships between variables, identifies correlations, highlights outliers.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with giant datasets, would not instantly present causality.
- Perfect Purposes: Exploring the connection between promoting spend and gross sales, analyzing the correlation between temperature and ice cream gross sales, figuring out outliers in a dataset. Including a development line can additional improve interpretation.
II. Superior Chart Varieties: Unveiling Deeper Insights
Tableau gives a spread of extra superior chart varieties that permit for deeper exploration and extra nuanced knowledge storytelling.
A. Space Charts: Just like line charts, space charts emphasize the magnitude of change over time. The world underneath the road represents the cumulative worth, making them helpful for visualizing totals or aggregates.
- Strengths: Exhibits tendencies and cumulative values, visually interesting, efficient for highlighting adjustments over time.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to check a number of areas, much less efficient for detailed comparisons.
- Perfect Purposes: Visualizing web site site visitors over time, exhibiting the cumulative gross sales over a interval, representing the expansion of an organization’s income.
B. Heatmaps: Heatmaps use colour depth to symbolize the magnitude of information values throughout two categorical variables. They’re glorious for figuring out patterns and tendencies throughout a number of dimensions.
- Strengths: Successfully highlights patterns and tendencies, straightforward to establish excessive and low values, good for big datasets.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with too many classes, much less efficient for exhibiting exact values.
- Perfect Purposes: Analyzing gross sales efficiency throughout totally different areas and product classes, visualizing buyer churn charges throughout demographics, illustrating correlation matrices.
C. Treemaps: Treemaps symbolize hierarchical knowledge utilizing nested rectangles. The scale of every rectangle corresponds to the worth it represents, permitting for fast visible comparability of various ranges within the hierarchy.
- Strengths: Successfully visualizes hierarchical knowledge, permits for simple comparability of various ranges, good for exhibiting proportions.
- Weaknesses: Will be tough to interpret with many ranges, much less efficient for exhibiting exact values.
- Perfect Purposes: Exhibiting market share throughout totally different product classes, visualizing the distribution of gross sales throughout totally different areas and departments, representing the construction of an organization’s group.
D. Field Plots: Field plots summarize the distribution of a steady variable, exhibiting the median, quartiles, and outliers. They’re glorious for evaluating the distributions of a number of teams.
- Strengths: Successfully compares distributions, identifies outliers, reveals central tendency and unfold.
- Weaknesses: Will be much less intuitive than different chart varieties, much less efficient for exhibiting detailed tendencies.
- Perfect Purposes: Evaluating the distribution of salaries throughout totally different departments, analyzing the efficiency of various funding methods, figuring out outliers in a dataset.
E. Twin Axis Charts: Twin axis charts mix two totally different measures on a single chart, utilizing a shared x-axis. This permits for the comparability of two associated metrics, revealing correlations and tendencies.
- Strengths: Permits comparability of two totally different measures, reveals relationships between variables, enhances knowledge storytelling.
- Weaknesses: Will be advanced to interpret, requires cautious consideration of axis scales.
- Perfect Purposes: Exhibiting gross sales and revenue margins over time, evaluating web site site visitors and conversion charges, visualizing the connection between buyer satisfaction and buyer lifetime worth.
III. Selecting the Proper Chart: A Strategic Strategy
Deciding on the suitable chart kind relies on a number of components:
- Sort of information: Categorical, steady, or a mixture of each.
- Variety of variables: One, two, or extra.
- Goal: Evaluating values, exhibiting tendencies, figuring out correlations, or highlighting distributions.
- Viewers: The extent of technical experience of your viewers will affect your chart alternative.
Earlier than making a visualization, clearly outline your goal and think about the kind of knowledge you are working with. Experiment with totally different chart varieties to seek out the one which greatest communicates your insights. At all times prioritize readability and ease – a well-designed chart ought to inform a compelling story with out overwhelming the viewer.
IV. Past the Fundamentals: Leveraging Tableau’s Superior Options
Tableau gives many options that may improve your visualizations:
- Filters: Enable customers to work together with the info and discover totally different subsets.
- Tooltips: Present detailed details about particular person knowledge factors on hover.
- Annotations: Add context and explanations to the chart.
- Dashboards: Mix a number of charts right into a single, cohesive view.
- Story Factors: Create interactive narratives that information the person via your knowledge.
By mastering these options, you possibly can create dynamic and informative visualizations that successfully talk advanced insights to your viewers. Keep in mind that knowledge visualization is an iterative course of; do not hesitate to experiment and refine your charts till they successfully convey your message.
In conclusion, Tableau’s numerous vary of chart varieties gives highly effective instruments for knowledge exploration and storytelling. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of every chart kind and leveraging Tableau’s superior options, you possibly can create impactful visualizations that drive knowledgeable decision-making. The bottom line is to decide on the chart that most closely fits your knowledge and your goal, guaranteeing readability, accuracy, and efficient communication of your insights.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Navigating the Tableau Panorama: A Complete Information to Chart Varieties. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!