NP and P Charts: Unveiling the Nuances of Statistical Course of Management for Attributes
Associated Articles: NP and P Charts: Unveiling the Nuances of Statistical Course of Management for Attributes
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to NP and P Charts: Unveiling the Nuances of Statistical Course of Management for Attributes. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
NP and P Charts: Unveiling the Nuances of Statistical Course of Management for Attributes

Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a strong instrument utilized in numerous industries to observe and enhance the standard of processes. When coping with knowledge representing the variety of defects or nonconforming models, two generally employed management charts are the NP chart and the P chart. Whereas each goal to detect shifts within the course of common, they differ considerably of their software and interpretation. Understanding these variations is essential for efficient high quality administration. This text delves deep into the distinctions between NP and P charts, clarifying their utilization, benefits, and limitations.
Understanding Attributes Knowledge:
Earlier than diving into the specifics of NP and P charts, it is important to know the character of attributes knowledge. Not like variables knowledge (e.g., weight, size, temperature), attributes knowledge classifies objects as both conforming or nonconforming based mostly on a predefined criterion. This classification may be binary (conforming/nonconforming) or contain a number of classes of defects. The info collected for attributes management charts focuses on the rely of nonconforming models or the variety of defects discovered inside a pattern. This contrasts with variables knowledge, which supplies steady measurements.
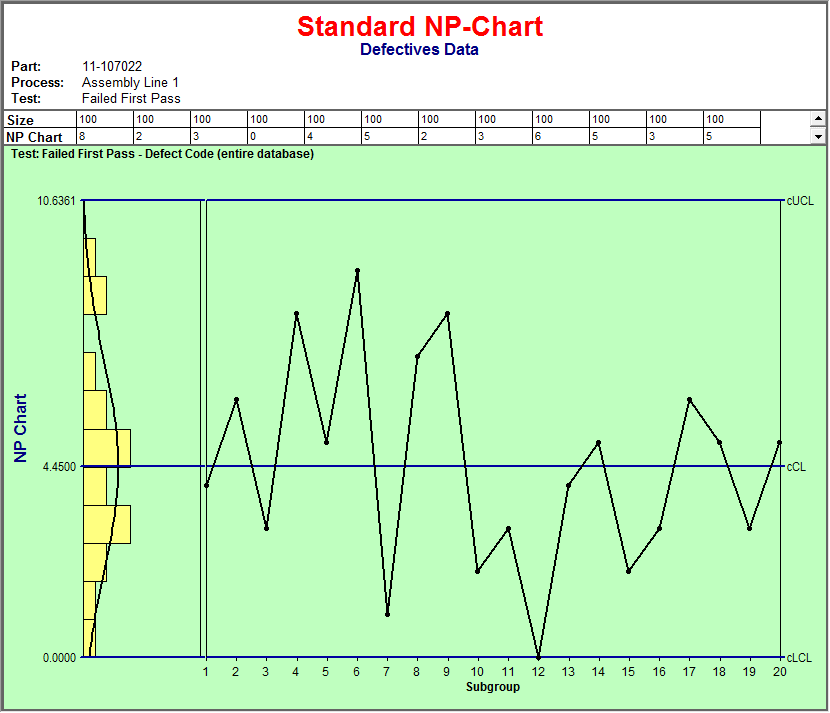
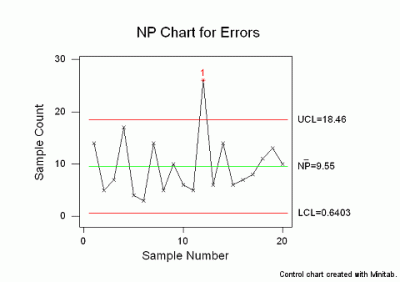
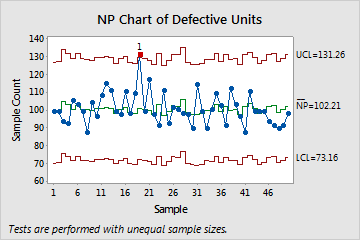
The NP Chart: Counting Defects in Fixed Pattern Measurement
The NP chart, or "nonconforming models" chart, is designed for conditions the place the pattern measurement (n) stays fixed throughout all subgroups. It displays the variety of nonconforming models (NP) in every pattern. The chart tracks the uncooked rely of defects, making it simple to know and interpret.
-
Knowledge Necessities: The NP chart requires a continuing pattern measurement (n) for every subgroup and the variety of nonconforming models (Np) noticed in every pattern.
-
Heart Line (CL): The middle line represents the typical variety of nonconforming models. It is calculated as:
CL = n * p-bar, the placep-baris the typical proportion of nonconforming models throughout all subgroups. -
Management Limits (UCL and LCL): The higher management restrict (UCL) and decrease management restrict (LCL) outline the appropriate vary of variation across the middle line. These limits are calculated utilizing the next formulation:
UCL = n * p-bar + 3 * sqrt(n * p-bar * (1 - p-bar))LCL = n * p-bar - 3 * sqrt(n * p-bar * (1 - p-bar))
Word that if the calculated LCL is detrimental, it’s sometimes set to zero, as you can’t have a detrimental variety of nonconforming models.
-
Interpretation: Factors plotting exterior the management limits point out a possible shift within the course of common, signaling the necessity for investigation and corrective motion. Patterns throughout the management limits (e.g., developments, runs) also can recommend underlying course of instability, even when no factors fall exterior the bounds.
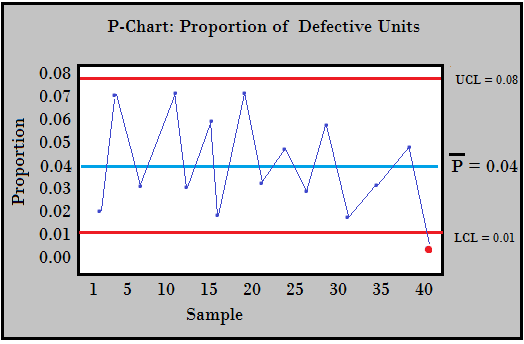
The P Chart: Monitoring Proportion of Defects with Variable Pattern Measurement
The P chart, or "proportion nonconforming" chart, is used when the pattern measurement (n) varies from subgroup to subgroup. As a substitute of monitoring the uncooked variety of nonconforming models, it displays the proportion (p) of nonconforming models in every pattern. This enables for a constant comparability throughout samples of various sizes.
-
Knowledge Necessities: The P chart requires the pattern measurement (n) and the variety of nonconforming models (Np) for every subgroup. The proportion of nonconforming models (p) for every subgroup is calculated as:
p = Np / n. -
Heart Line (CL): The middle line represents the typical proportion of nonconforming models. It is calculated as:
CL = p-bar, the placep-baris the typical proportion of nonconforming models throughout all subgroups. -
Management Limits (UCL and LCL): The higher and decrease management limits are calculated as follows:
UCL = p-bar + 3 * sqrt(p-bar * (1 - p-bar) / n)LCL = p-bar - 3 * sqrt(p-bar * (1 - p-bar) / n)
Just like the NP chart, a detrimental LCL is usually set to zero. Word that the pattern measurement (n) is integrated into the management restrict calculations, accounting for the variability in pattern sizes.
-
Interpretation: Factors exterior the management limits recommend a course of shift, whereas patterns throughout the limits might point out underlying instability.
Key Variations Summarized:
| Characteristic | NP Chart | P Chart |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern Measurement | Fixed | Variable |
| Knowledge Plotted | Variety of nonconforming models (Np) | Proportion of nonconforming models (p) |
| Heart Line (CL) | n * p-bar |
p-bar |
| Management Limits | Primarily based on n, p-bar
|
Primarily based on n, p-bar for every subgroup |
| Software | Fixed pattern measurement conditions | Variable pattern measurement conditions |
| Interpretation | Variety of defects exceeding limits | Proportion of defects exceeding limits |
Selecting Between NP and P Charts:
The selection between an NP chart and a P chart relies upon totally on the consistency of the pattern measurement. If the pattern measurement stays fixed throughout all subgroups, the NP chart is extra applicable. Its simplicity and direct interpretation of the variety of defects make it simpler to know and talk. Nonetheless, if the pattern measurement varies, the P chart is critical to account for this variability and guarantee correct interpretation. Utilizing an NP chart with variable pattern sizes will result in deceptive management limits and inaccurate conclusions.
Benefits and Limitations:
NP Chart Benefits:
- Simplicity: Straightforward to know and interpret, particularly for these much less conversant in statistical ideas.
- Direct Depend: Immediately shows the variety of nonconforming models, offering a transparent image of the defect rely.
- Appropriate for Fixed Pattern Sizes: Environment friendly and correct when pattern sizes are constant.
NP Chart Limitations:
- Restricted to Fixed Pattern Sizes: Can’t be used successfully with various pattern sizes.
- Might Obscure Developments with Various Pattern Sizes: If used with variable pattern sizes, developments is perhaps masked because of the various scales.
P Chart Benefits:
- Handles Variable Pattern Sizes: Permits for comparability throughout subgroups with totally different pattern sizes.
- Proportion-Primarily based Evaluation: Offers a standardized measure of nonconformity, no matter pattern measurement.
- Versatile: Relevant to a wider vary of conditions than the NP chart.
P Chart Limitations:
- Extra Advanced Calculation: Management restrict calculations are barely extra concerned than these for the NP chart.
- Might Be Much less Intuitive: The interpretation focuses on proportions somewhat than uncooked counts, which may be much less intuitive for some.
- Requires Enough Pattern Sizes: For correct outcomes, adequate pattern sizes are wanted, notably when the proportion of nonconforming models is low.
Conclusion:
Each NP and P charts are beneficial instruments for monitoring attributes knowledge in SPC. The selection between them hinges on the consistency of the pattern measurement. The NP chart presents simplicity and direct interpretation for fixed pattern sizes, whereas the P chart supplies flexibility and standardized evaluation for variable pattern sizes. Understanding the nuances of every chart and selecting the suitable one is essential for efficient course of monitoring and enchancment. Correct software and interpretation of those charts, together with a complete understanding of the method being monitored, are key to profitable high quality administration. Keep in mind that management charts are just one element of a broader high quality administration system and must be used along side different instruments and strategies for complete course of enchancment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into NP and P Charts: Unveiling the Nuances of Statistical Course of Management for Attributes. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!