pareto chart vs pie chart
Associated Articles: pareto chart vs pie chart
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing subject associated to pareto chart vs pie chart. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Pareto Chart vs. Pie Chart: Unveiling the Finest Instrument for Information Visualization
Information visualization is essential for efficient communication and decision-making. Choosing the proper chart kind is paramount to precisely signify knowledge and convey insights clearly. Two standard decisions, the Pareto chart and the pie chart, are sometimes in contrast, typically mistakenly used interchangeably. Whereas each purpose to point out proportions of various classes inside a complete, their strengths lie in several purposes and the kind of data they successfully talk. This text delves into the nuances of every chart, evaluating their strengths and weaknesses to information you in choosing the optimum instrument on your knowledge evaluation wants.
Understanding the Pie Chart:
The pie chart, a well-recognized round chart divided into slices, represents the proportion of every class relative to the full. Every slice’s measurement corresponds on to its share of the entire. Its simplicity makes it simply comprehensible, even for people with restricted statistical information. Pie charts are efficient at rapidly displaying the relative sizes of various classes, offering a visible illustration of the general distribution.
Strengths of Pie Charts:
- Simplicity and Intuitiveness: Pie charts are visually interesting and simple to interpret, requiring minimal clarification. The proportional illustration of classes is straight away obvious.
- Straightforward to Create: Most spreadsheet software program and knowledge visualization instruments readily generate pie charts with minimal effort.
- Efficient for Small Variety of Classes: When coping with a restricted variety of classes (sometimes lower than 6), pie charts successfully spotlight the relative contributions of every.
- Good for Excessive-Degree Overview: They provide a fast overview of the information distribution, appropriate for displays and stories the place an in depth evaluation is not the first focus.
Weaknesses of Pie Charts:
- Issue in Evaluating Slices: Exact comparisons between slices, notably these with comparable sizes, may be difficult. Small variations are exhausting to discern visually.
- Restricted to a Few Classes: Because the variety of classes will increase, the pie chart turns into cluttered and tough to interpret. Overlapping labels and tiny slices obscure the information’s that means.
- Lack of ability to Present Traits or Relationships: Pie charts solely signify proportions; they do not reveal tendencies, patterns, or relationships between variables.
- Issue in Representing Percentages Precisely: Exact share values typically have to be added as labels, growing chart complexity and doubtlessly lowering readability.
- Susceptibility to Misinterpretation: Visible notion may be misleading. The world of a slice, not simply its angle, determines its perceived measurement, resulting in potential misinterpretations.
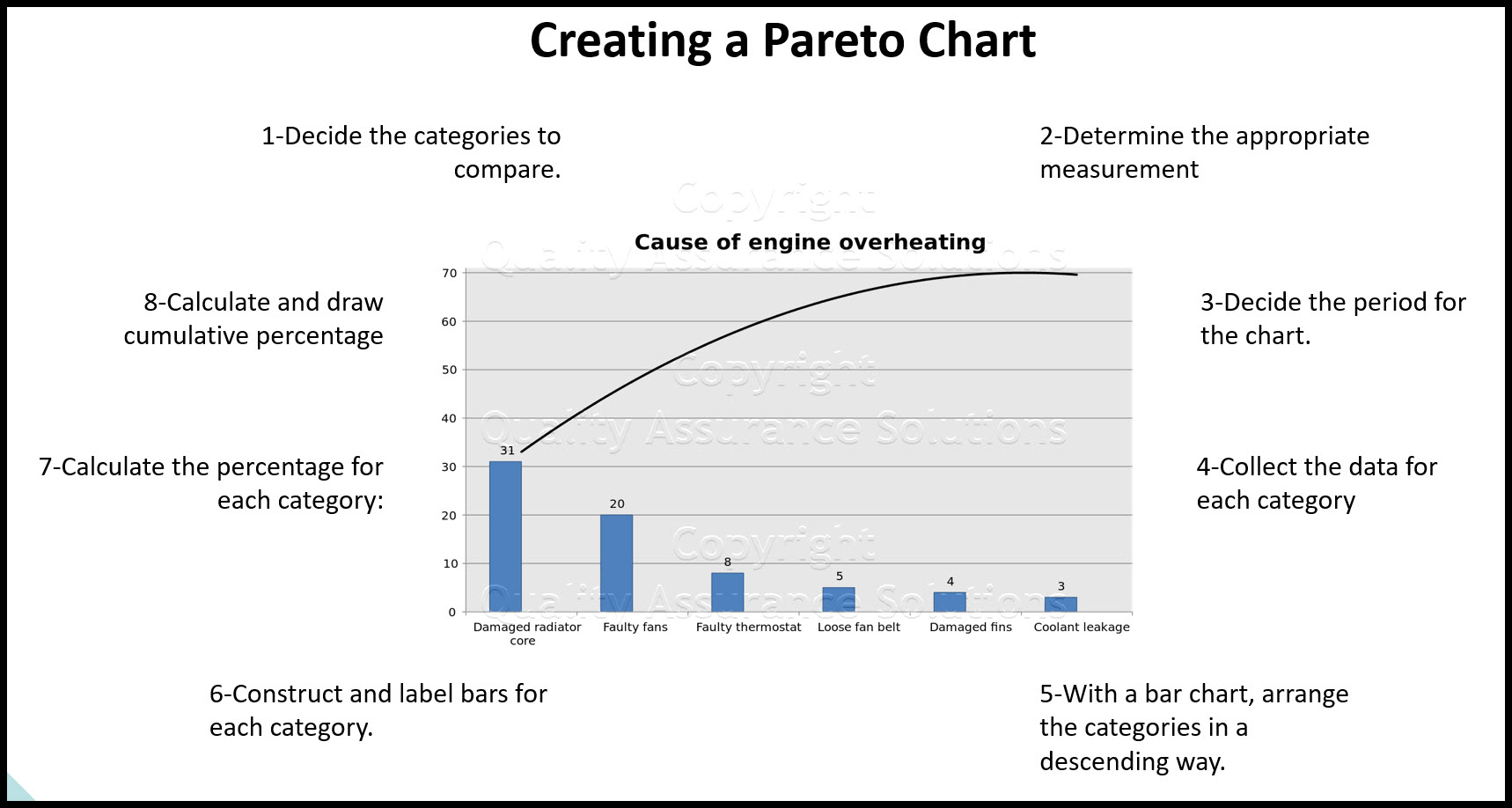
Understanding the Pareto Chart:
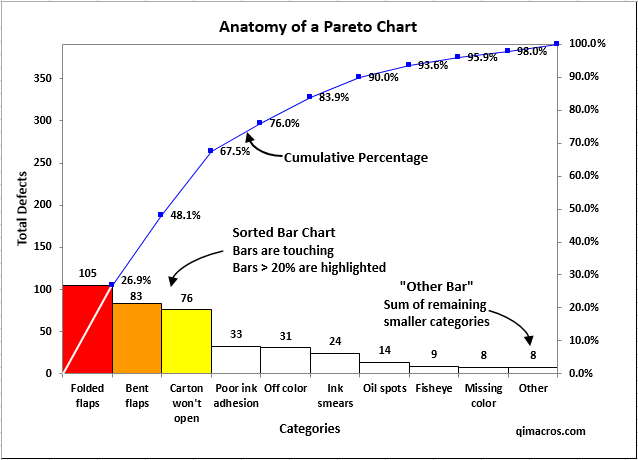
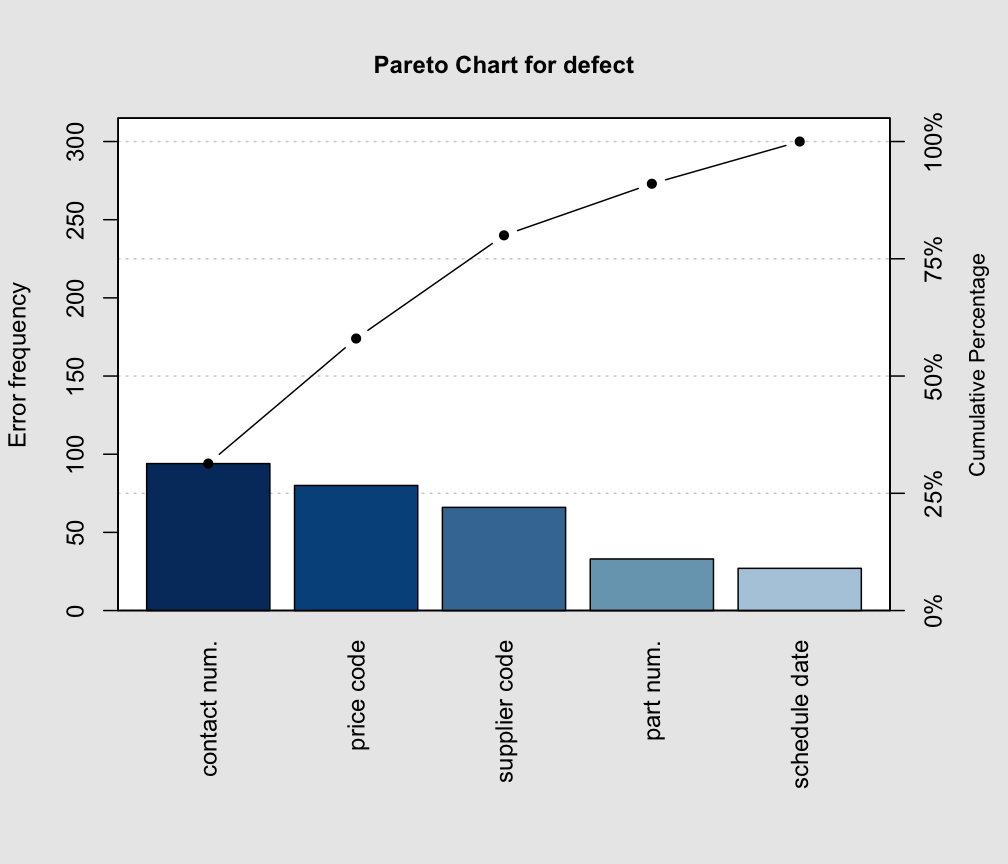
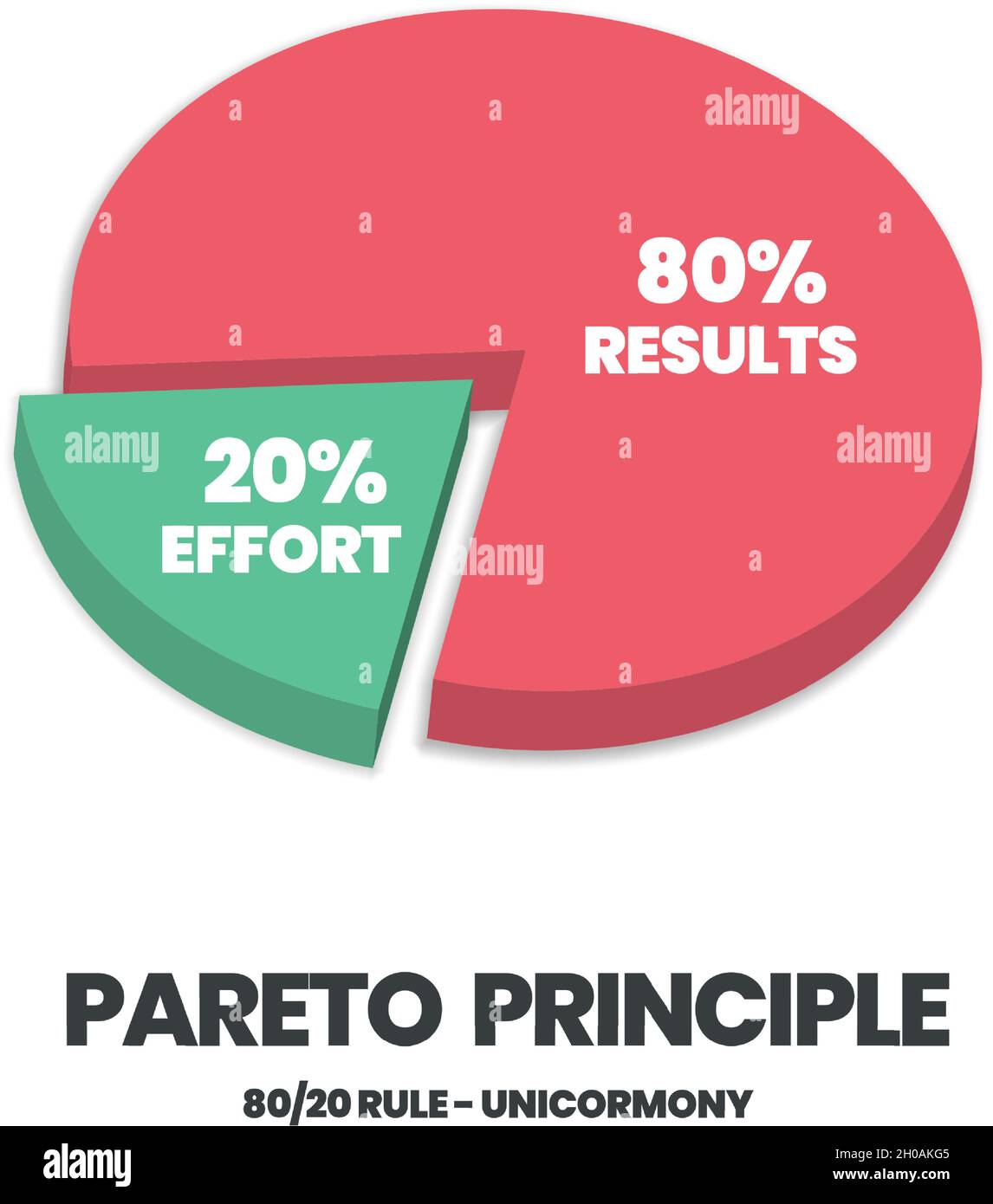
The Pareto chart, a hybrid chart combining a bar graph and a line graph, is a robust instrument for figuring out the "important few" from the "trivial many." It is based mostly on the Pareto precept, often known as the 80/20 rule, which means that 80% of results come from 20% of causes. The bar graph shows classes in descending order of frequency, whereas the road graph represents the cumulative share.
Strengths of Pareto Charts:
- Identifies Key Contributors: Pareto charts successfully spotlight probably the most vital contributors to an issue or final result. This permits for targeted efforts on addressing probably the most impactful elements.
- Prioritizes Downside Fixing: By visualizing the cumulative share, it helps prioritize areas for enchancment. Addressing the highest few classes typically yields probably the most vital outcomes.
- Combines Qualitative and Quantitative Information: It shows each categorical knowledge (the bars) and quantitative knowledge (the cumulative share).
- Reveals Patterns and Traits: The cumulative frequency line reveals tendencies and patterns within the knowledge, offering insights into the distribution of causes or results.
- Helps Determination Making: The visible illustration of the Pareto precept facilitates data-driven decision-making by focusing assets on high-impact areas.
Weaknesses of Pareto Charts:
- May be Deceptive with Few Classes: If the variety of classes is small, the Pareto precept won’t be obvious, diminishing the chart’s effectiveness.
- Requires Information Ordering: Classes have to be sorted in descending order of frequency, which could require knowledge manipulation.
- Complexity In comparison with Pie Charts: Pareto charts are barely extra complicated than pie charts, requiring a extra detailed understanding of their interpretation.
- Much less Appropriate for Easy Proportions: If the first purpose is solely to point out the proportions of various classes, a pie chart is likely to be a extra easy selection.
- Potential for Oversimplification: Whereas specializing in the "important few" is useful, it is essential to keep away from neglecting the opposite classes solely.
Selecting Between Pareto and Pie Charts:
The selection between a Pareto chart and a pie chart relies upon closely on the information and the insights you purpose to convey.
Use a Pie Chart when:
- You wish to present the relative proportions of a small variety of classes (usually lower than 6).
- A easy, simply understood visible illustration is adequate.
- The main target is solely on displaying the distribution of classes inside a complete.
- You want a fast overview of the information with out detailed evaluation.
Use a Pareto Chart when:
- You wish to determine probably the most vital contributors to an issue or final result.
- It is advisable to prioritize areas for enchancment based mostly on their impression.
- You wish to visualize the Pareto precept (80/20 rule).
- It is advisable to reveal patterns and tendencies within the knowledge.
- Information-driven determination making based mostly on impression is essential.
Instance Eventualities:
-
State of affairs 1: Buyer Satisfaction Survey: A survey reveals buyer suggestions categorized as "Glorious," "Good," "Honest," and "Poor." A pie chart would successfully visualize the proportion of every suggestions class.
-
State of affairs 2: Manufacturing Defects: A manufacturing unit identifies varied defect varieties and their frequencies. A Pareto chart could be extra appropriate to pinpoint probably the most frequent defect varieties and prioritize corrective actions.
-
State of affairs 3: Gross sales Efficiency by Product: Gross sales knowledge for various merchandise is offered. A pie chart might present the general gross sales distribution throughout merchandise. A Pareto chart could be higher to determine the top-selling merchandise and focus advertising and marketing efforts accordingly.
Conclusion:
Each Pareto and pie charts serve useful functions in knowledge visualization. Nonetheless, their purposes differ considerably. Pie charts excel at displaying easy proportions for a restricted variety of classes, whereas Pareto charts empower the identification of key contributors and prioritize problem-solving. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of every chart kind is important for choosing the simplest instrument to speak your knowledge insights precisely and effectively. Choosing the proper chart ensures clear communication and knowledgeable decision-making, in the end main to higher outcomes. The secret is to fastidiously think about your knowledge and the message you want to convey earlier than deciding which chart kind greatest serves your wants.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into pareto chart vs pie chart. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!