The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization
Associated Articles: The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization

Knowledge visualization is a strong instrument for speaking complicated info clearly and concisely. A well-designed chart can reveal tendencies, spotlight outliers, and inform a compelling story. Nonetheless, even essentially the most meticulously crafted knowledge will be rendered ineffective by a poorly chosen coloration palette. The colours we use in our charts will not be merely aesthetic decisions; they considerably influence the readability, understandability, and in the end, the persuasiveness of our visualizations. This text delves into the artwork and science of choosing efficient chart coloration palettes, exploring the rules of coloration idea, accessibility issues, and greatest practices for numerous chart varieties.
Understanding the Psychology of Shade:
Earlier than diving into particular palettes, it is essential to grasp the psychology of coloration and the way totally different hues evoke numerous feelings and associations. Shade psychology is a fancy discipline, however some normal rules are related to chart design:
-
Heat Colours (Reds, Oranges, Yellows): Typically related to power, pleasure, and urgency. They’ll draw consideration to particular knowledge factors or spotlight necessary tendencies. Nonetheless, overuse can result in visible fatigue or overwhelm.
-
Cool Colours (Blues, Greens, Purples): Sometimes related to calmness, tranquility, and belief. They’re typically used to symbolize impartial or background info. Overuse can result in a scarcity of visible curiosity.
-
Impartial Colours (Grays, Whites, Blacks): Present steadiness and readability. They’re helpful for making a clear and uncluttered look, significantly in charts with a considerable amount of knowledge. Nonetheless, relying solely on impartial colours could make the chart seem boring and unengaging.
-
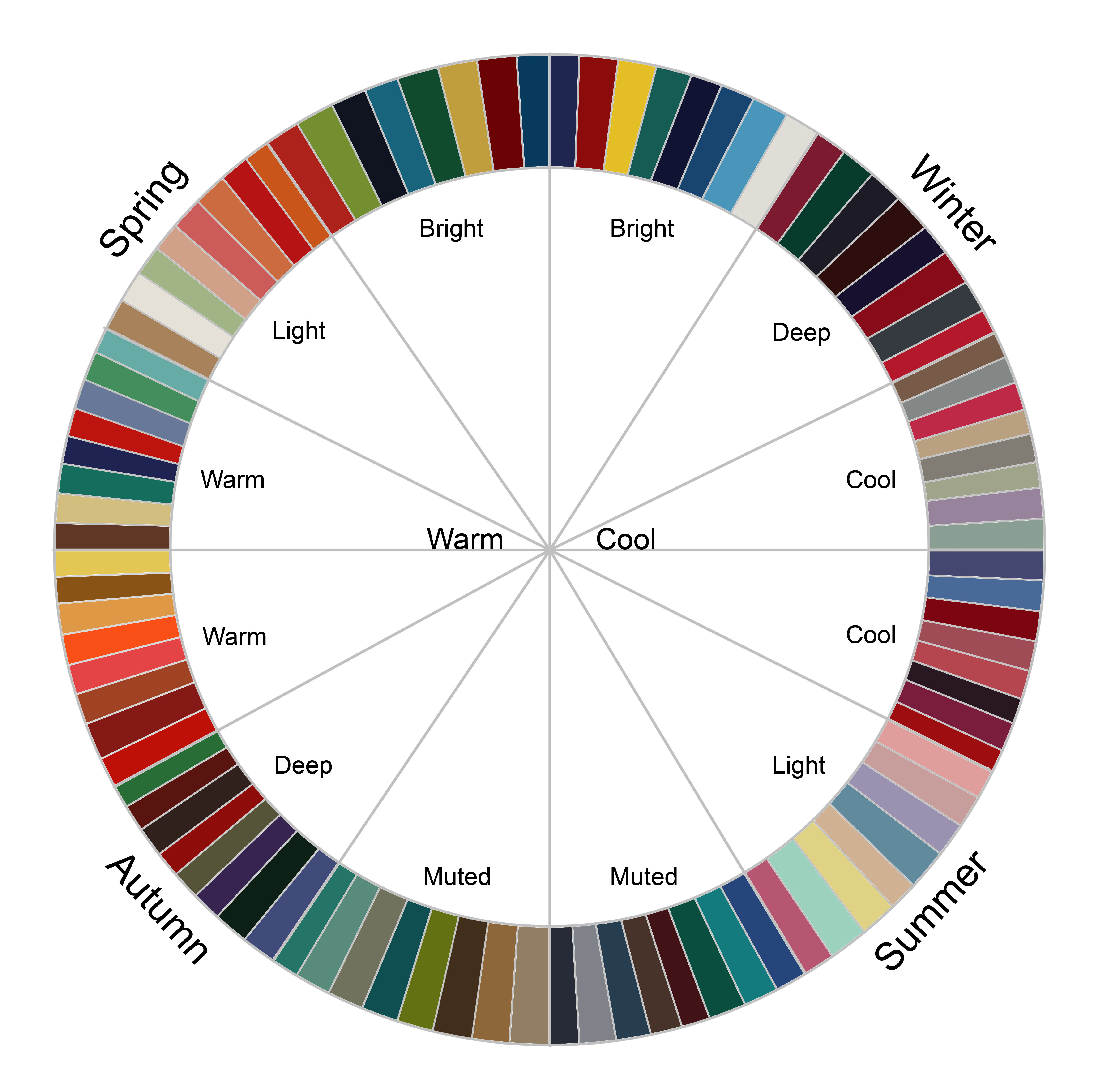
Complementary Colours: Colours reverse one another on the colour wheel (e.g., crimson and inexperienced, blue and orange). Used strategically, they’ll create a vibrant and visually putting distinction. Nonetheless, overuse will be jarring and tough to learn.
-
Analogous Colours: Colours adjoining to one another on the colour wheel (e.g., blue, blue-green, inexperienced). They create a harmonious and cohesive really feel, appropriate for charts emphasizing easy transitions or gradual modifications.
Shade Blindness and Accessibility:
A major issue typically missed is coloration blindness. Roughly 8% of males and 0.5% of girls expertise some type of coloration imaginative and prescient deficiency. Designing charts which are accessible to everybody, together with these with coloration blindness, is essential for making certain that your visualizations are inclusive and efficient.
The commonest sort of coloration blindness is red-green coloration blindness, making it important to keep away from relying solely on these colours to tell apart totally different knowledge sequence. As a substitute, think about using:
-
Distinct Hues: Select colours with considerably totally different hues, even when they’re comparable in saturation and brightness.
-
Form and Sample: Complement coloration with totally different shapes or patterns to distinguish knowledge sequence, particularly when utilizing a restricted coloration palette.
-
Knowledge Labels: All the time embrace clear knowledge labels to make sure that the knowledge is accessible to everybody, no matter their coloration notion.
-
Shade Distinction Checkers: Make the most of on-line instruments and software program that simulate coloration blindness to check the accessibility of your coloration palettes. These instruments might help determine potential points earlier than your chart is printed.
Selecting the Proper Palette for Completely different Chart Sorts:
The perfect coloration palette will fluctuate relying on the kind of chart getting used. Listed here are some suggestions for various chart varieties:
-
Bar Charts and Column Charts: These charts profit from a transparent and distinct palette, with every bar or column representing a singular class or knowledge level. Analogous or complementary coloration schemes will be efficient, however guarantee adequate distinction between colours.
-
Line Charts: Line charts typically present tendencies over time. Utilizing a restricted variety of colours, sometimes 2-4, is advisable to keep away from visible muddle. Think about using a sequential palette, the place colours step by step change in hue or saturation to symbolize a development or change in knowledge.
-
Pie Charts: Pie charts symbolize proportions of an entire. Restrict the variety of slices to keep away from visible confusion. Select colours which are simply distinguishable and make sure that crucial slices are visually distinguished. Keep away from utilizing too many comparable shades.
-
Scatter Plots: Scatter plots present the connection between two variables. Shade can be utilized to symbolize a 3rd variable or to group knowledge factors. A categorical coloration scheme is commonly applicable, with every class represented by a definite coloration.
-
Maps: Shade is essential in maps to symbolize geographical knowledge. Sequential palettes are sometimes used to indicate gradual modifications in a variable (e.g., inhabitants density). Categorical palettes can be utilized to symbolize totally different areas or administrative divisions. Think about using a colorblind-friendly palette for optimum accessibility.
Shade Palette Mills and Instruments:
Quite a few on-line instruments and software program packages can help in creating efficient coloration palettes. These instruments typically can help you specify the variety of colours wanted, the specified coloration scheme (e.g., sequential, categorical, diverging), and the extent of coloration blindness accessibility. Some widespread choices embrace:
-
Adobe Shade: A complete instrument for exploring and creating coloration palettes.
-
Coolors: A user-friendly instrument with a variety of pre-made palettes and customization choices.
-
Paletton: Means that you can create palettes based mostly on particular coloration harmonies and coloration blindness issues.
-
Shade Brewer: Focuses on creating coloration palettes particularly designed for cartography and knowledge visualization, emphasizing accessibility.
Greatest Practices for Efficient Chart Shade Palettes:
-
Maintain it Easy: Keep away from utilizing too many colours. A restricted palette is mostly simpler to learn and perceive.
-
Think about Context: The suitable coloration palette will rely on the info being offered and the general message you need to convey.
-
Preserve Consistency: Use the identical coloration scheme all through your visualization and throughout a number of charts if presenting associated knowledge.
-
Check and Iterate: Create a number of totally different palettes and check them to see which one is simplest. Collect suggestions from others, together with these with coloration blindness.
-
Prioritize Readability: The first purpose is to speak info clearly. Keep away from utilizing colours which are too comparable or that create visible muddle.
-
Use Knowledge Labels: All the time embrace knowledge labels to make sure that the knowledge is clearly conveyed, whatever the coloration palette used.
Conclusion:
The selection of coloration palette is a essential side of efficient knowledge visualization. By understanding the psychology of coloration, contemplating accessibility for coloration blindness, and using applicable instruments and strategies, you possibly can create charts that aren’t solely visually interesting but additionally clear, informative, and persuasive. Keep in mind that the purpose is to speak your knowledge successfully, and a well-chosen coloration palette is a strong instrument in attaining that purpose. By rigorously contemplating these rules and experimenting with totally different choices, you possibly can elevate your knowledge visualizations and guarantee your insights are readily understood and appreciated by your viewers.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into The Artwork and Science of Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!