The EPA Refrigerant Section-Out: A Complete Chart and Information to Understanding the Transition
Associated Articles: The EPA Refrigerant Section-Out: A Complete Chart and Information to Understanding the Transition
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to The EPA Refrigerant Section-Out: A Complete Chart and Information to Understanding the Transition. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The EPA Refrigerant Section-Out: A Complete Chart and Information to Understanding the Transition
The Environmental Safety Company (EPA) has carried out a phased method to eliminating the usage of ozone-depleting and excessive international warming potential (GWP) refrigerants. This strategic plan, detailed within the Clear Air Act, goals to mitigate local weather change and shield the stratospheric ozone layer. Understanding the EPA refrigerant phase-out schedule is essential for HVACR technicians, constructing homeowners, and anybody concerned within the refrigeration and air-con business. This text supplies a complete overview of the phase-out, presenting it in a digestible format alongside an in depth rationalization of the rules and their implications.
The Driving Drive Behind the Section-Out:
The first drivers behind the EPA’s refrigerant phase-out are:
-
Ozone Depletion: Sure refrigerants, significantly chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), have been discovered to severely deplete the ozone layer, which protects us from dangerous ultraviolet radiation. The Montreal Protocol, a global treaty, spurred international motion to section out these substances.
-
World Warming: Many refrigerants, even these circuitously damaging to the ozone layer, have excessive international warming potentials (GWPs). These refrigerants contribute considerably to local weather change by trapping warmth within the ambiance. The EPA’s rules concentrate on lowering the GWP of refrigerants utilized in new gear and phasing out high-GWP refrigerants altogether.
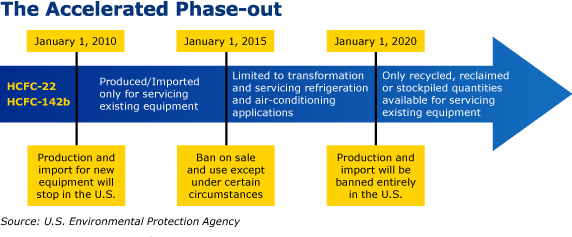
Understanding the EPA’s Strategy: A Phased Transition
The EPA’s method to refrigerant phase-out is not a single, abrupt change. As an alternative, it is a gradual course of involving a number of levels:
-
Manufacturing and Import Restrictions: The EPA restricts the manufacturing and import of sure refrigerants based mostly on their ozone-depleting potential and GWP. This restricts the supply of phased-out refrigerants, making their use more and more tough.
-
Gross sales Restrictions: Rules additionally limit the sale of sure refrigerants, additional limiting their availability for servicing current gear. This encourages the transition to lower-GWP options.
-
Tools Requirements: The EPA units requirements for brand spanking new gear, requiring producers to make use of refrigerants with decrease GWPs. This drives innovation and the event of extra environmentally pleasant applied sciences.
-
Recycling and Reclamation: The EPA emphasizes the significance of correct refrigerant dealing with, recycling, and reclamation to attenuate emissions and lengthen the lifespan of current refrigerants.
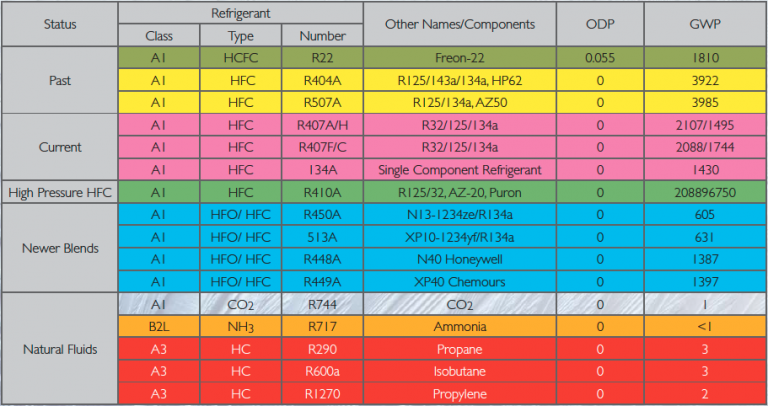
A Simplified Chart of the EPA Refrigerant Section-Out (Be aware: It is a simplified illustration and shouldn’t be thought-about an entire authorized doc. Consult with official EPA publications for exact particulars.)
| Refrigerant | Sort | Ozone Depleting Potential (ODP) | World Warming Potential (GWP) | Section-Out Standing (Approximate) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-11 (CFC-11) | CFC | 1.0 | 4750 | Phased out | Fully banned in most functions. |
| R-12 (CFC-12) | CFC | 1.0 | 10900 | Phased out | Fully banned in most functions. |
| R-22 (HCFC-22) | HCFC | 0.05 | 1760 | Phased out | Manufacturing and import banned, restricted use in servicing current gear. |
| R-134a (HFC-134a) | HFC | 0 | 1430 | Phased down | Use restricted in new gear, transitioning to lower-GWP options. |
| R-410A (HFC mix) | HFC | 0 | 2088 | Phased down | Use restricted in new gear, transitioning to lower-GWP options. |
| R-404A (HFC mix) | HFC | 0 | 3922 | Phased down | Use restricted in new gear, transitioning to lower-GWP options. |
| R-32 (HFC) | HFC | 0 | 675 | Steadily changing R-410A | Thought of a lower-GWP various. |
| R-1234yf (HFO) | HFO | 0 | 4 | Broadly adopted | Thought of a low-GWP various. |
| R-1234ze (HFO) | HFO | 0 | 7 | Broadly adopted | Thought of a low-GWP various. |
Necessary Concerns:
-
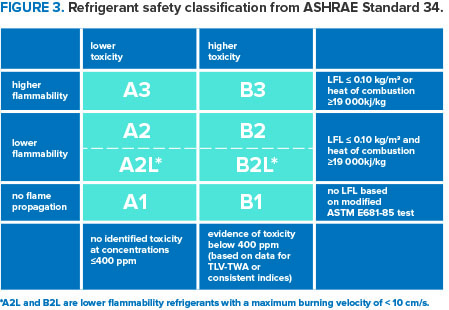
"Phased down" vs. "Phased out": "Phased out" means the manufacturing and import are fully banned, whereas "phased down" implies a gradual discount in manufacturing and use.
-
Servicing Present Tools: Whereas the manufacturing of some refrigerants is banned, servicing current gear utilizing these refrigerants should still be permitted beneath sure situations, often with recovered refrigerant. Nevertheless, that is topic to vary and rules ought to be checked frequently.
-
Refrigerant Reclaiming and Recycling: Correct dealing with, reclaiming, and recycling of refrigerants are essential to minimizing environmental affect and complying with EPA rules. Improper disposal can result in important fines.
-
Technological Developments: The business is continually creating new refrigerants with even decrease GWPs and improved effectivity. Staying up to date on these developments is significant for compliance and competitiveness.
-
Regional Variations: Whereas the EPA units nationwide requirements, some states or localities might need stricter rules. It is essential to test native rules along with federal pointers.
Implications for the HVACR Business:
The EPA refrigerant phase-out has important implications for the HVACR business:
-
Coaching and Certification: Technicians must be skilled on dealing with and utilizing new refrigerants and complying with up to date security rules.
-
Tools Upgrades: Companies have to spend money on new gear that makes use of low-GWP refrigerants.
-
Elevated Prices: The transition to new refrigerants and gear can contain larger upfront prices.
-
Innovation and Alternative: The phase-out drives innovation in refrigerant expertise and creates alternatives for companies that adapt shortly.
Conclusion:
The EPA’s refrigerant phase-out is a vital step in direction of defending the atmosphere and mitigating local weather change. Whereas it presents challenges for the HVACR business, it additionally fosters innovation and encourages the adoption of extra sustainable applied sciences. Staying knowledgeable in regards to the newest rules, investing in coaching and gear upgrades, and embracing sustainable practices are essential for compliance and success on this evolving panorama. Often consulting the EPA’s official web site and staying up to date on business publications are important to remaining compliant and knowledgeable in regards to the ongoing adjustments in refrigerant rules. Failure to conform can lead to important penalties, making proactive compliance a necessity for all stakeholders.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into The EPA Refrigerant Section-Out: A Complete Chart and Information to Understanding the Transition. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!