The Energy of Visible Comparability: A Complete Information to Charts for Information Evaluation
Associated Articles: The Energy of Visible Comparability: A Complete Information to Charts for Information Evaluation
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to The Energy of Visible Comparability: A Complete Information to Charts for Information Evaluation. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Energy of Visible Comparability: A Complete Information to Charts for Information Evaluation
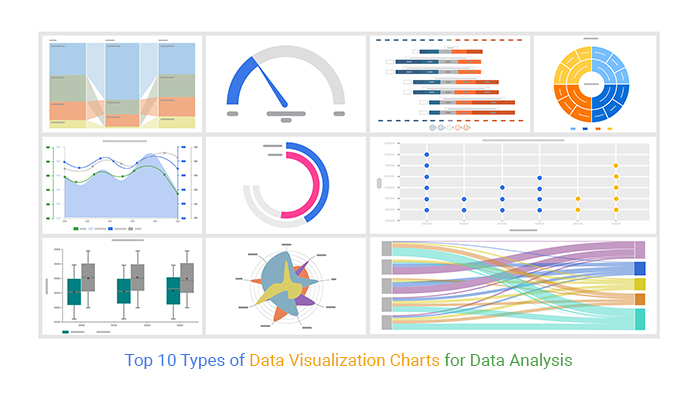
Charts are the unsung heroes of knowledge evaluation. They remodel complicated numerical info into simply digestible visible representations, facilitating understanding, figuring out tendencies, and making knowledgeable choices. This text delves into the various world of charts, exploring their purposes, strengths, weaknesses, and the way to decide on the correct chart for efficient comparability. We’ll focus significantly on charts designed for evaluating knowledge, highlighting their essential function in uncovering insights and speaking findings.
Understanding the Function of Comparability Charts:
Earlier than diving into particular chart varieties, it is important to grasp the aim of comparability. We evaluate knowledge to:
- Determine variations and similarities: Highlighting discrepancies and commonalities between knowledge units is key to understanding patterns and variations.
- Monitor progress and alter over time: Evaluating knowledge factors throughout totally different time intervals reveals tendencies, development, or decline.
- Benchmark efficiency: Evaluating efficiency towards business requirements or rivals permits for goal evaluation and strategic planning.
- Determine correlations and relationships: Evaluating knowledge from totally different variables can uncover hidden relationships and dependencies.
- Help decision-making: Visible comparability offers a transparent and concise overview, aiding in knowledgeable decision-making processes.
Varieties of Charts for Comparability:
A number of chart varieties excel at evaluating knowledge, every with its personal strengths and weaknesses. The optimum selection depends upon the kind of knowledge being in contrast and the message to be conveyed.
1. Bar Charts:
Bar charts are arguably essentially the most versatile and extensively used charts for comparability. They characterize knowledge utilizing rectangular bars, with the size of every bar proportional to the worth it represents.
- Strengths: Easy to grasp, efficient for evaluating discrete classes, simply accommodates giant datasets, readily exhibits variations in magnitude.
- Weaknesses: Can develop into cluttered with many classes, much less efficient for displaying steady knowledge or exact values.
- Variations: Clustered bar charts evaluate a number of classes inside every group, whereas stacked bar charts present the contribution of various parts to an entire. 100% stacked bar charts normalize the information to indicate proportions.
2. Column Charts:
Column charts are basically the vertical equal of bar charts. They’re equally efficient for evaluating discrete classes, providing a distinct visible perspective.
- Strengths: Much like bar charts by way of simplicity and effectiveness for evaluating discrete knowledge. The vertical orientation can generally be extra visually interesting, significantly when evaluating quite a few classes.
- Weaknesses: Comparable weaknesses to bar charts, turning into much less efficient with quite a few classes or steady knowledge.
3. Line Charts:
Line charts are perfect for evaluating knowledge over time or displaying tendencies. They join knowledge factors with traces, revealing patterns and modifications.
- Strengths: Successfully shows tendencies and modifications over time, permits for straightforward identification of peaks and troughs, appropriate for steady knowledge.
- Weaknesses: May be much less efficient for evaluating discrete classes, could develop into cluttered with a number of traces, requires evenly spaced knowledge factors for correct illustration.
- Variations: A number of traces on a single chart permit for comparability of various tendencies concurrently.
4. Space Charts:
Space charts are an extension of line charts, filling the world underneath the road to emphasise the magnitude of change over time.
- Strengths: Highlights the cumulative impact of modifications over time, efficient for displaying proportions and tendencies, visually interesting.
- Weaknesses: May be troublesome to interpret with a number of overlapping areas, much less efficient for evaluating exact values.
5. Scatter Plots:
Scatter plots are used to check two steady variables, revealing correlations and relationships between them.
- Strengths: Identifies correlations (constructive, adverse, or no correlation), exhibits the distribution of knowledge factors, useful for figuring out outliers.
- Weaknesses: Much less efficient for evaluating discrete classes, may be troublesome to interpret with giant datasets, would not straight present exact values.
6. Pie Charts:
Pie charts characterize proportions of an entire. Whereas helpful for displaying the relative contribution of various components, they’re typically much less efficient for evaluating a number of datasets straight.
- Strengths: Easy and intuitive for displaying proportions, efficient for highlighting the biggest parts.
- Weaknesses: Troublesome to check small proportions precisely, ineffective for evaluating a number of datasets, may be deceptive if too many segments are included.
7. Heatmaps:
Heatmaps use colour depth to characterize knowledge values, permitting for the comparability of a number of variables concurrently. They’re significantly helpful for visualizing giant datasets.
- Strengths: Efficient for visualizing giant datasets, simply identifies patterns and tendencies, permits for comparability throughout a number of variables.
- Weaknesses: May be troublesome to interpret with complicated datasets, requires cautious colour choice to keep away from misinterpretations.
8. Field Plots (Field and Whisker Plots):
Field plots are wonderful for evaluating the distribution of knowledge throughout totally different teams. They present the median, quartiles, and outliers, offering a abstract of the information’s unfold and central tendency.
- Strengths: Clearly exhibits the distribution of knowledge, identifies outliers, efficient for evaluating a number of teams, strong to outliers.
- Weaknesses: Would not present particular person knowledge factors, much less efficient for displaying exact values.
Selecting the Proper Chart for Comparability:
Choosing the suitable chart depends upon a number of elements:
- Sort of knowledge: Discrete or steady, categorical or numerical.
- Variety of knowledge factors: A big dataset may require a distinct chart than a small one.
- Message to be conveyed: What insights do you wish to spotlight?
- Viewers: Think about the viewers’s familiarity with totally different chart varieties.
Greatest Practices for Creating Efficient Comparability Charts:
- Clear and concise labels: Use clear and concise labels for axes, knowledge factors, and legends.
- Acceptable scaling: Select a scale that precisely represents the information with out distortion.
- Constant colour scheme: Use a constant colour scheme to keep away from confusion.
- Reduce litter: Keep away from pointless particulars that may distract from the principle message.
- Spotlight key findings: Use annotations or callouts to attract consideration to necessary tendencies or patterns.
- Think about accessibility: Make sure the chart is accessible to people with visible impairments.
Conclusion:
Charts are highly effective instruments for evaluating knowledge and extracting significant insights. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of various chart varieties and adhering to finest practices, you possibly can create efficient visualizations that facilitate understanding, inform choices, and talk findings successfully. The secret’s to decide on the chart that finest represents your knowledge and clearly communicates the comparisons you want to spotlight, making certain your message resonates together with your viewers. The choice course of needs to be pushed by the particular knowledge and the story you purpose to inform by way of your visible illustration. Do not forget that a well-designed chart is just not merely a show of knowledge; it is a highly effective device for communication and perception era.

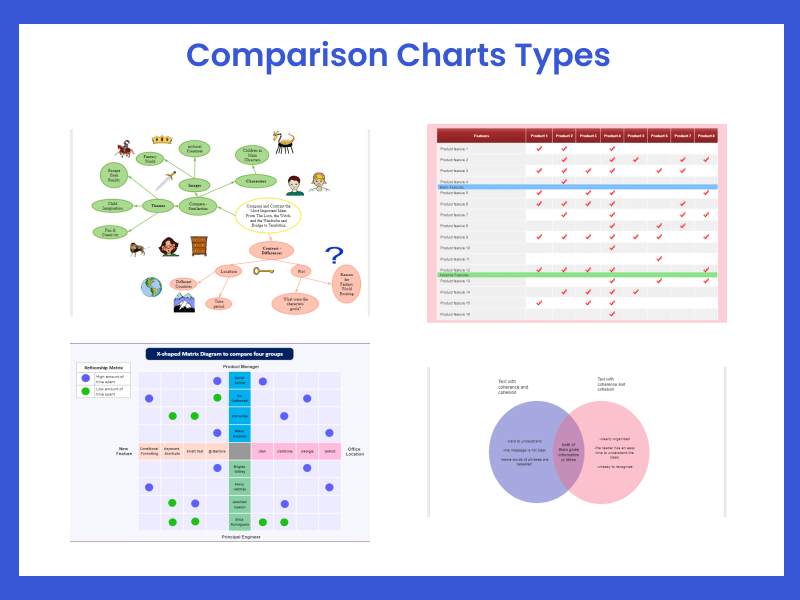
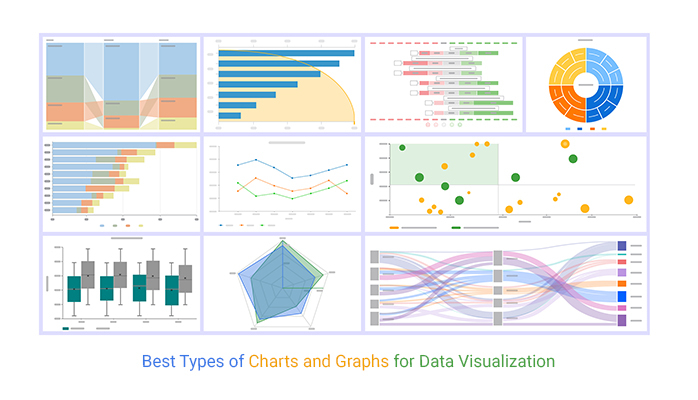




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into The Energy of Visible Comparability: A Complete Information to Charts for Information Evaluation. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!