Understanding and Making use of t-Charts and u-Charts for Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of t-Charts and u-Charts for Course of Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of t-Charts and u-Charts for Course of Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of t-Charts and u-Charts for Course of Management

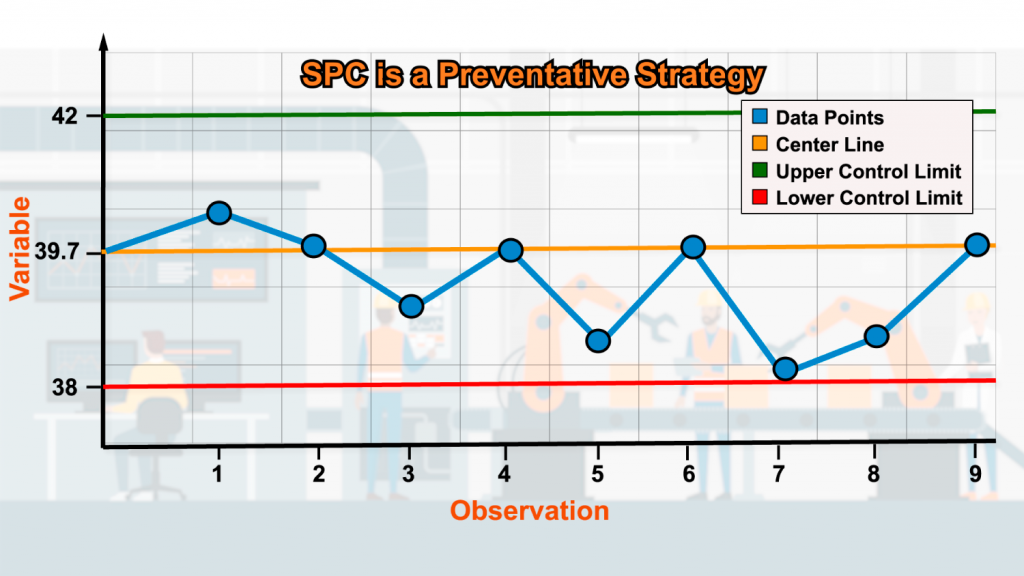
Management charts are elementary instruments in statistical course of management (SPC) used to observe and enhance the standard of processes. They supply a visible illustration of course of efficiency over time, permitting for the identification of tendencies, shifts, and particular causes of variation. Two generally used management charts for attribute information are the t-chart and the u-chart. Whereas each are designed for analyzing non-continuous information, they differ in how they deal with the pattern dimension. This text will delve into the small print of t-charts and u-charts, evaluating their functions, strengths, and limitations.
Understanding Attribute Knowledge
Earlier than diving into the specifics of t-charts and u-charts, it is essential to grasp the character of attribute information. In contrast to variable information (e.g., weight, size, temperature), which is measured on a steady scale, attribute information represents the presence or absence of a attribute. This attribute is usually a defect or nonconformity. Examples of attribute information embody:
- Variety of defects per unit: The variety of scratches on a painted automobile half.
- Variety of nonconforming models: The variety of defective circuit boards in a batch.
- Proportion of nonconforming models: The proportion of faulty mild bulbs in a cargo.
T-charts and u-charts are particularly designed to research attribute information, serving to us perceive the frequency of defects or nonconformities inside a course of.
The t-Chart: Management Chart for Defects per Unit
A t-chart, also called a c-chart per unit, is used to observe the variety of defects per unit (or merchandise). It is preferrred when the pattern dimension stays fixed for every subgroup. Every information level on the chart represents the rely of defects present in a single unit. The important thing assumption is that the variety of defects per unit follows a Poisson distribution, which is a likelihood distribution describing the probability of a given variety of occasions occurring in a hard and fast interval of time or area if these occasions happen with a identified common charge and independently of the time for the reason that final occasion.
Establishing a t-Chart:
-
Acquire Knowledge: Collect information on the variety of defects present in every unit inspected. Be certain that the pattern dimension (variety of models inspected) stays constant for every subgroup.
-
Calculate the Common Variety of Defects: Calculate the typical variety of defects per unit (t̄) by summing the entire variety of defects throughout all models and dividing by the entire variety of models inspected.
-
Calculate the Management Limits: The management limits are calculated utilizing the typical variety of defects (t̄). The formulation for the management limits are:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): t̄ + 3√t̄
- Central Line (CL): t̄
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): t̄ – 3√t̄ (Be aware: If LCL is unfavourable, it’s set to 0, as you can’t have a unfavourable variety of defects).
-
Plot the Knowledge: Plot the variety of defects for every unit on the chart, together with the central line and management limits.
-
Interpret the Chart: Factors falling outdoors the management limits point out potential particular trigger variation requiring investigation. Developments or patterns inside the management limits may additionally counsel the necessity for course of enchancment.
The u-Chart: Management Chart for Defects per Unit with Variable Pattern Sizes
In contrast to the t-chart, the u-chart is used when the pattern dimension (variety of models inspected) varies from subgroup to subgroup. It tracks the typical variety of defects per unit, making it appropriate for conditions the place the variety of models inspected modifications over time. The u-chart additionally assumes a Poisson distribution.
Establishing a u-Chart:
-
Acquire Knowledge: Collect information on the variety of defects and the variety of models inspected for every subgroup.
-
Calculate the Common Variety of Defects per Unit: Calculate the typical variety of defects per unit (ū) by summing the entire variety of defects throughout all subgroups and dividing by the entire variety of models inspected throughout all subgroups.
-
Calculate the Management Limits: The management limits for a u-chart are calculated utilizing the typical variety of defects per unit (ū). The formulation are:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): ū + 3√(ū/n̄)
- Central Line (CL): ū
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): ū – 3√(ū/n̄) (Once more, if LCL is unfavourable, it’s set to 0). The place n̄ is the typical pattern dimension.
-
Plot the Knowledge: Plot the typical variety of defects per unit for every subgroup on the chart, together with the central line and management limits.
-
Interpret the Chart: Much like the t-chart, factors outdoors the management limits or patterns inside the limits sign potential issues requiring investigation.
Evaluating t-Charts and u-Charts:
| Characteristic | t-Chart | u-Chart |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern Dimension | Fixed | Variable |
| Knowledge Measured | Variety of defects per unit | Common variety of defects per unit |
| Distribution | Poisson | Poisson |
| Software | Fixed pattern dimension conditions | Variable pattern dimension conditions |
| Management Limits | Primarily based on common defects per unit (t̄) | Primarily based on common defects per unit (ū) and common pattern dimension (n̄) |
| Complexity | Comparatively less complicated to assemble | Barely extra complicated to assemble |
Selecting Between t-Charts and u-Charts:
The selection between a t-chart and a u-chart relies upon totally on the character of your information assortment course of. If the variety of models inspected stays constant throughout all subgroups, a t-chart is acceptable. Nonetheless, if the pattern dimension varies, a u-chart is important to precisely replicate the method variation. Utilizing the mistaken chart can result in inaccurate interpretations and ineffective course of enchancment efforts.
Sensible Functions and Issues:
Each t-charts and u-charts discover intensive software in varied industries, together with manufacturing, healthcare, and providers. Examples embody:
- Manufacturing: Monitoring the variety of defects in manufactured items (e.g., scratches on automobile our bodies, flaws in textiles).
- Healthcare: Monitoring the variety of infections in a hospital ward.
- Service Trade: Monitoring buyer complaints or errors in service supply.
Nonetheless, it is essential to keep in mind that management charts are solely efficient when used appropriately. Components to contemplate embody:
- Knowledge Accuracy: Correct information assortment is crucial for dependable outcomes. Errors in information assortment can result in deceptive interpretations.
- Subgroup Choice: Subgroups ought to be consultant of the method and picked up in a constant method.
- Course of Stability: Management charts are handiest when the method is comparatively secure. Vital course of modifications ought to be investigated and addressed earlier than counting on management chart outcomes.
- Interpretation: Understanding the that means of factors outdoors the management limits and patterns inside the limits is essential for efficient course of enchancment. Merely figuring out out-of-control factors is inadequate; root trigger evaluation is crucial.
Conclusion:
T-charts and u-charts are highly effective instruments for monitoring and enhancing processes that generate attribute information. Understanding the variations between these charts and choosing the suitable chart primarily based on the pattern dimension is essential for acquiring correct and significant outcomes. By rigorously accumulating information, setting up the charts appropriately, and deciphering the outcomes successfully, organizations can leverage these instruments to establish and get rid of sources of variation, resulting in improved course of effectivity and product high quality. Do not forget that management charts are a part of a broader high quality enchancment technique and ought to be complemented by different methods equivalent to root trigger evaluation and course of enchancment methodologies.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Understanding and Making use of t-Charts and u-Charts for Course of Management. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!