Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart in High quality Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart in High quality Management
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart in High quality Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart in High quality Management

The pursuit of constant high quality is paramount throughout all industries. Sustaining excessive requirements requires efficient monitoring and management of processes, and statistical course of management (SPC) offers the instruments to attain this. Among the many numerous SPC charts, the p-chart holds a big place, significantly for monitoring the proportion of nonconforming items in a pattern. This text delves into the intricacies of the p-chart, explaining its software, interpretation, and limitations.
What’s a P-Chart?
A p-chart is a management chart utilized in statistical course of management to watch the proportion (or share) of faulty or nonconforming items in a pattern. In contrast to different management charts that observe steady variables like weight or size, the p-chart focuses on attributes – traits which are both current or absent, conforming or nonconforming. This makes it significantly helpful in conditions the place the end result is binary: go/fail, good/unhealthy, conforming/nonconforming.
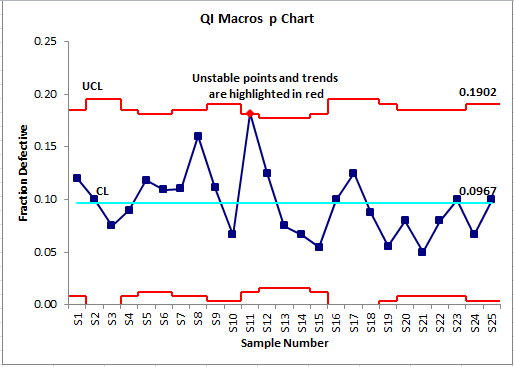
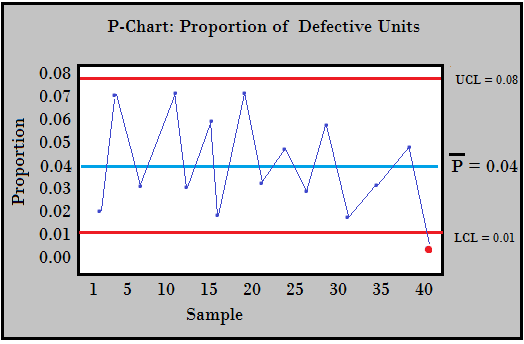
The chart plots the pattern proportion of nonconforming items in opposition to time or pattern quantity. Management limits are calculated based mostly on the historic information, offering a visible illustration of course of stability. Factors falling outdoors these limits sign potential issues requiring investigation and corrective motion.
When to Use a P-Chart
The p-chart is the suitable selection when:
-
The information are attribute information: The attribute being measured is categorical, leading to a binary final result. Examples embody the proportion of faulty gadgets in a batch of manufactured merchandise, the proportion of buyer complaints, the speed of errors in a knowledge entry course of, or the proportion of sufferers experiencing a selected aspect impact after therapy.
-
The pattern dimension is fixed: Whereas some variations are tolerable, constant pattern sizes are essential for correct management restrict calculation. Inconsistent pattern sizes necessitate changes to the management restrict formulation, which may complicate the evaluation. Nevertheless, strategies exist to deal with variable pattern sizes (mentioned later).
-
The information are unbiased: The end result of 1 pattern mustn’t affect the end result of one other. If there is a correlation between samples, the p-chart might not precisely replicate course of stability.
-
The method is secure (in-control) or anticipated to be secure: The p-chart is used to watch a course of, to not diagnose a constantly unstable course of. If the method is inherently unstable, a special method could be obligatory earlier than implementing a p-chart.
Establishing a P-Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Making a p-chart includes a number of steps:
-
Knowledge Assortment: Collect information on the variety of nonconforming items in a collection of samples of constant dimension (n). File the variety of nonconforming items (x) for every pattern. The variety of samples must be adequate to ascertain a dependable estimate of the method common. Usually, no less than 20-25 samples are really helpful.
-
Calculate the Pattern Proportions: For every pattern, calculate the pattern proportion (p) of nonconforming items utilizing the method: p = x/n
-
Calculate the Common Proportion: Calculate the common proportion of nonconforming items throughout all samples (p̄): p̄ = Σp / okay the place okay is the variety of samples.
-
Calculate the Customary Deviation: Calculate the usual deviation of the pattern proportions (σp): σp = √[p̄(1-p̄)/n]
-
Calculate the Management Limits: The management limits are calculated based mostly on the common proportion and commonplace deviation:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): UCL = p̄ + 3σp
- Central Line (CL): CL = p̄
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): LCL = p̄ – 3σp
Be aware: If the calculated LCL is destructive, it is usually set to 0, as a proportion can’t be destructive.
-
Plot the Knowledge: Plot the pattern proportions (p) on the y-axis in opposition to the pattern quantity or time on the x-axis. Draw the central line and higher and decrease management limits on the chart.
-
Interpret the Chart: Analyze the chart to determine any factors falling outdoors the management limits or patterns indicating instability. Factors outdoors the management limits counsel that the method is uncontrolled and requires investigation.
Deciphering the P-Chart: Figuring out Out-of-Management Alerts
A number of alerts point out that the method is uncontrolled and requires consideration:
-
Factors outdoors the management limits: Any level falling above the UCL or under the LCL suggests a big shift within the course of proportion of nonconforming items.
-
Runs: A collection of consecutive factors above or under the central line suggests a development or shift within the course of.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors round a selected degree signifies potential course of instability.
-
Cycles: Recurring patterns of factors oscillating above and under the central line counsel cyclical variations within the course of.
Figuring out these alerts prompts investigation into the underlying causes of the variation, permitting for corrective actions to revive course of stability.
Dealing with Variable Pattern Sizes
Whereas fixed pattern sizes are supreme, it is not all the time possible. When pattern sizes fluctuate, modifications to the management restrict calculations are obligatory. One widespread method is to make use of the common pattern dimension (ñ) in the usual deviation calculation: σp = √[p̄(1-p̄)/ñ]. Nevertheless, this methodology will be much less exact than utilizing fixed pattern sizes. Extra refined strategies, such because the variable pattern dimension p-chart (utilizing a weighted common), provide improved accuracy in these conditions.
Benefits of Utilizing a P-Chart
-
Simplicity and ease of understanding: The p-chart is comparatively easy to assemble and interpret, making it accessible to a variety of customers.
-
Visible illustration of course of stability: The chart offers a transparent visible illustration of the proportion of nonconforming items over time, facilitating simple identification of tendencies and out-of-control alerts.
-
Early detection of course of issues: By monitoring the method repeatedly, the p-chart permits for early detection of issues earlier than they result in important high quality points.
-
Efficient device for course of enchancment: The p-chart isn’t just a monitoring device; it additionally aids in figuring out areas for course of enchancment by pinpointing the sources of variation.
Limitations of the P-Chart
-
Requires fixed or almost fixed pattern dimension: Important variations in pattern dimension can have an effect on the accuracy of the management limits.
-
Assumes independence of samples: Correlated samples can result in inaccurate interpretations.
-
Will not be appropriate for all sorts of attribute information: The p-chart is handiest when coping with binary attributes. For extra advanced attribute information, different management charts could be extra acceptable.
-
Sensitivity to small pattern sizes: With small pattern sizes, the management limits could also be much less exact, doubtlessly resulting in false alarms.
Conclusion
The p-chart is a useful device in high quality management for monitoring the proportion of nonconforming items in a course of. Its simplicity, visible enchantment, and effectiveness in detecting course of instability make it a broadly used approach throughout numerous industries. Nevertheless, understanding its limitations and the assumptions underlying its use is essential for correct interpretation and efficient software. By fastidiously contemplating the info traits and deciding on the suitable management chart, organizations can successfully monitor and enhance their processes, finally resulting in larger high quality services. When coping with variable pattern sizes, using acceptable modifications or various strategies ensures the reliability of the evaluation. The constant software and correct interpretation of the p-chart contribute considerably to a proactive and data-driven method to high quality administration.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Understanding and Making use of the P-Chart in High quality Management. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!