Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management
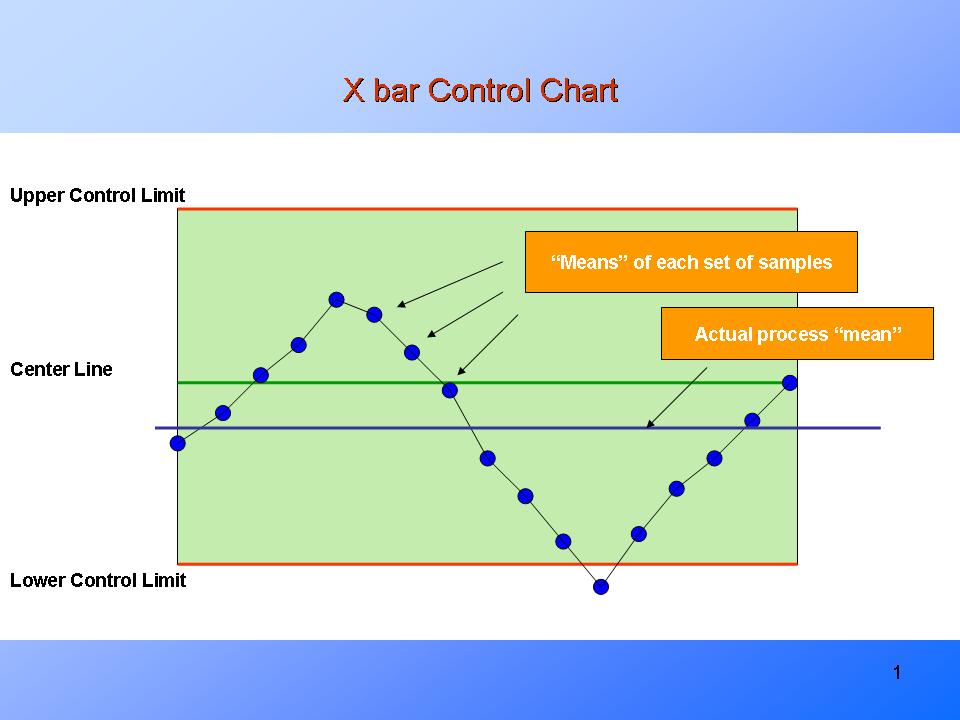
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a strong methodology used to observe and enhance the standard of processes. A cornerstone of SPC is the usage of management charts, graphical instruments that show information over time, permitting for the identification of traits and variations inside a course of. Among the many most generally used management charts are the X-bar and R charts, a strong duo designed for monitoring the central tendency (common) and dispersion (vary) of a course of. This text gives a complete overview of X-bar and R charts, protecting their development, interpretation, and purposes.
1. Introduction to X-bar and R Charts
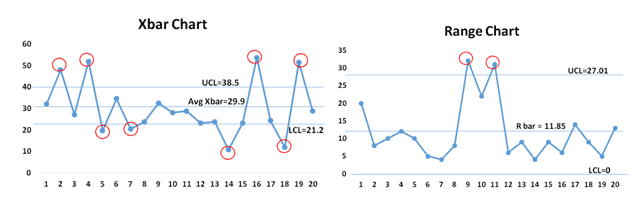
X-bar and R charts are used collectively to observe variables information, that means information that’s measured on a steady scale (e.g., weight, size, temperature). The X-bar chart tracks the common (imply) of a subgroup of information, whereas the R chart displays the vary (distinction between the most important and smallest values) inside every subgroup. By analyzing each the central tendency and the variability, these charts present a holistic view of course of efficiency. The mixed use permits for the detection of each shifts within the course of imply and modifications in course of variability, that are essential indicators of potential issues.
2. When to Use X-bar and R Charts
X-bar and R charts are notably efficient when:
- Information is steady: The information being monitored have to be measurable on a steady scale.
- Subgroups are rational: Information needs to be collected in rational subgroups, that means subgroups which might be homogeneous and symbolize a snapshot of the method at a selected time. The dimensions of those subgroups (sometimes 4-5 information factors) is essential for the accuracy of the charts. Bigger subgroups present extra exact estimates of the imply however could masks short-term variations. Smaller subgroups are extra delicate to short-term variations however could also be much less exact in estimating the imply.
- Course of stability is desired: The first purpose is to observe the method for stability and establish assignable causes of variation.
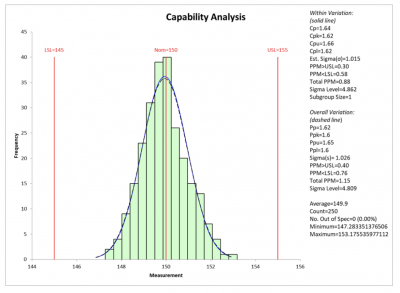
- Course of functionality is to be assessed: As soon as the method is deemed secure, X-bar and R charts can be utilized to evaluate the method functionality, i.e., its means to satisfy specs.
3. Developing X-bar and R Charts
The development of X-bar and R charts includes a number of steps:
-
Information Assortment: Acquire information in rational subgroups. The variety of subgroups and the subgroup measurement needs to be decided primarily based on the method and the specified sensitivity.
-
Calculate Subgroup Statistics: For every subgroup, calculate the imply (X-bar) and the vary (R).
-
Calculate General Statistics: Calculate the general common of the subgroup means (X-double bar) and the common vary (R-bar). These are used to determine the management limits.
-
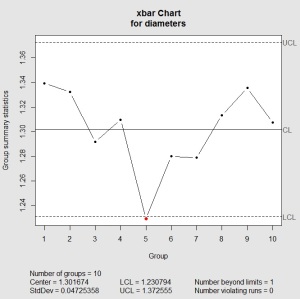
Decide Management Limits: Management limits are calculated utilizing management chart constants (A2, D3, D4) that are depending on the subgroup measurement. These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The formulation for the management limits are as follows:
-
X-bar chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL) = X-double bar + A2 * R-bar
- Heart Line (CL) = X-double bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL) = X-double bar – A2 * R-bar
-
R chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL) = D4 * R-bar
- Heart Line (CL) = R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL) = D3 * R-bar (Be aware: D3 is 0 for subgroup sizes lower than 7)
-
-
Plot the Information: Plot the X-bar and R values on their respective charts. The management limits are plotted as horizontal strains on every chart.
4. Decoding X-bar and R Charts
As soon as the charts are constructed, the method stability is assessed by in search of factors outdoors the management limits or patterns throughout the information. The next are widespread indicators of instability:
- Factors outdoors the management limits: Any level falling outdoors the higher or decrease management limits signifies a possible assignable reason for variation. This requires investigation to establish and remove the basis trigger.
- Tendencies: A constant upward or downward development suggests a scientific shift within the course of imply.
- Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low values point out cyclical variations that have to be investigated.
- Stratification: Clustering of factors round a selected worth suggests a scarcity of homogeneity throughout the subgroups.
- Runs: A sequence of consecutive factors above or under the middle line signifies a shift within the course of.
5. Addressing Out-of-Management Conditions
When an out-of-control situation is detected, a radical investigation is important to establish the assignable trigger. This sometimes includes:
- Reviewing the information assortment course of: Guarantee information was collected precisely and constantly.
- Investigating potential sources of variation: Study modifications in supplies, gear, personnel, or surroundings that may have influenced the method.
- Implementing corrective actions: As soon as the basis trigger is recognized, implement corrective actions to remove the variation.
- Re-establishing management: After corrective actions, acquire new information and re-construct the management charts to confirm that the method is again beneath management.
6. Benefits of Utilizing X-bar and R Charts
- Early detection of issues: The charts enable for the early detection of shifts within the course of imply or variability, stopping the manufacturing of faulty merchandise.
- Steady monitoring: The charts present a steady monitoring system, permitting for ongoing evaluation of course of efficiency.
- Improved course of functionality: By figuring out and eliminating sources of variation, the charts contribute to improved course of functionality.
- Lowered prices: Early detection of issues reduces waste, rework, and scrap, resulting in vital value financial savings.
- Information-driven resolution making: The charts present goal information for making knowledgeable choices about course of enchancment.
7. Limitations of X-bar and R Charts
- Assumption of normality: The charts assume that the information is generally distributed. If the information is considerably non-normal, different management chart strategies could also be extra acceptable.
- Subgroup measurement limitations: The effectiveness of the charts is influenced by the selection of subgroup measurement. Improper subgroup choice can result in inaccurate conclusions.
- Interpretation requires experience: Appropriate interpretation of the charts requires a great understanding of statistical ideas and management chart methodology.
- Not appropriate for all sorts of information: X-bar and R charts are particularly designed for variables information. For attribute information (e.g., rely of defects), different management charts (e.g., p-charts, c-charts) are extra acceptable.
8. Software program Functions for X-bar and R Charts
Quite a few software program packages can be found for establishing and analyzing X-bar and R charts, together with:
- Minitab: A extensively used statistical software program bundle with complete SPC capabilities.
- JMP: One other highly effective statistical software program bundle providing superior options for information evaluation and visualization.
- Excel: Whereas not as specialised as Minitab or JMP, Excel can be utilized to create primary X-bar and R charts utilizing add-ins or customized formulation.
9. Conclusion
X-bar and R charts are important instruments for monitoring and bettering course of efficiency. Their means to detect each shifts within the course of imply and modifications in variability makes them invaluable for sustaining constant high quality and lowering prices. Nevertheless, it is essential to know the underlying assumptions and limitations of those charts and to make use of them appropriately throughout the context of a well-defined course of. Correct implementation and interpretation, coupled with a scientific strategy to addressing out-of-control conditions, can considerably improve the effectiveness of X-bar and R charts in attaining course of enchancment targets. The mixed use of those charts empowers organizations to maneuver from reactive problem-solving to proactive course of management, resulting in greater high quality merchandise and elevated effectivity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Understanding and Making use of X-bar and R Charts: A Complete Information to Course of Management. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!