Understanding and Using T-Chart Accounts Payable: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Using T-Chart Accounts Payable: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Using T-Chart Accounts Payable: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Using T-Chart Accounts Payable: A Complete Information

Accounts payable (AP) is a vital facet of monetary accounting, representing an organization’s short-term liabilities – the cash owed to suppliers, distributors, and different collectors for items or providers obtained however not but paid for. Successfully managing accounts payable is important for sustaining wholesome money circulate, negotiating favorable fee phrases, and making certain correct monetary reporting. Whereas refined accounting software program handles the majority of AP administration at this time, understanding the elemental rules, significantly using a T-chart for visualizing AP transactions, stays essential for each learners and skilled professionals. This text offers a complete information to utilizing T-chart accounts payable, exploring its performance, purposes, and limitations.
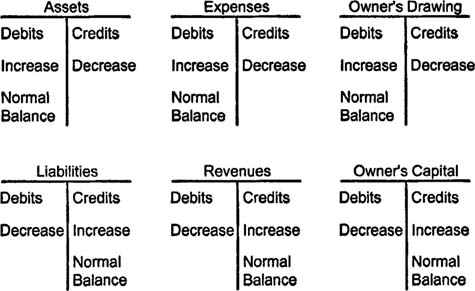
I. The T-Chart: A Visible Illustration of Accounting Equations
Earlier than diving into accounts payable particularly, let’s perceive the essential construction of a T-chart. The T-chart, named for its resemblance to the letter "T," is a straightforward but highly effective instrument for visualizing accounting transactions. It is based mostly on the elemental accounting equation:
Property = Liabilities + Fairness
The T-chart divides the equation into two sides:
- Debit (Left Facet): Represents will increase in belongings and reduces in liabilities and fairness.
- Credit score (Proper Facet): Represents will increase in liabilities and fairness and reduces in belongings.
Every transaction impacts a minimum of two accounts to keep up the steadiness of the equation. For instance, buying workplace provides with money would improve the "Workplace Provides" asset account (debit) and reduce the "Money" asset account (credit score).
II. Making use of the T-Chart to Accounts Payable
Accounts payable is a legal responsibility account. Because of this will increase in accounts payable are recorded as credit, whereas decreases are recorded as debits. Let’s illustrate this with examples:
A. Recording Purchases on Credit score:
Think about an organization, "ABC Corp," purchases $1,000 price of stock from "Provider X" on credit score. This transaction will increase ABC Corp’s accounts payable (a legal responsibility) and will increase its stock (an asset). The T-chart would appear to be this:
| Account Title | Debit | Credit score |
|---|---|---|
| Stock | $1,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $1,000 |
The debit to Stock displays the rise within the asset, whereas the credit score to Accounts Payable displays the rise within the legal responsibility. The equation stays balanced ($1,000 = $1,000).
B. Recording Funds on Accounts Payable:
When ABC Corp pays Provider X $500, it reduces its accounts payable legal responsibility and reduces its money asset. The T-chart would present:
| Account Title | Debit | Credit score |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable | $500 | |
| Money | $500 |
The debit to Accounts Payable decreases the legal responsibility, and the credit score to Money decreases the asset. Once more, the equation stays balanced.
C. Recording Buy Returns:
Suppose ABC Corp returns $100 price of faulty stock to Provider X. This reduces each the stock asset and the accounts payable legal responsibility. The T-chart entry could be:
| Account Title | Debit | Credit score |
|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable | $100 | |
| Stock | $100 |
The debit to Accounts Payable reduces the legal responsibility, and the credit score to Stock reduces the asset.
D. Recording Buy Reductions:
If ABC Corp takes benefit of a 2% low cost for early fee, the low cost obtained is recorded as a discount in the price of items offered (an expense) and a discount in accounts payable. Assuming a fee of $400 after the low cost:
| Account Title | Debit | Credit score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable | $400 | ||
| Buy Reductions | $8 | (2% of $400) | |
| Money | $408 |
The debit to Accounts Payable reduces the legal responsibility, the debit to Buy Reductions displays the discount in expense, and the credit score to Money reveals the fee made.
III. Limitations of the T-Chart for Accounts Payable Administration
Whereas the T-chart is a superb instrument for understanding the essential rules of accounts payable accounting, it has limitations when coping with a big quantity of transactions:
- Scalability: Manually sustaining a T-chart for a enterprise with tons of or hundreds of transactions turns into impractical and error-prone.
- Lack of Element: A T-chart would not present the extent of element wanted for complete AP administration, corresponding to bill numbers, due dates, and provider info.
- No Growing older Evaluation: The T-chart would not supply instruments for analyzing the getting old of accounts payable, which is essential for money circulate administration and figuring out overdue funds.
- Restricted Reporting Capabilities: Producing reviews summarizing AP balances, excellent invoices, and fee historical past shouldn’t be possible with a T-chart.
IV. Integration with Accounting Software program
Trendy accounting software program packages deal with the complexities of accounts payable administration successfully. These methods automate many duties, together with:
- Bill Processing: Automated bill entry and information seize.
- Fee Processing: Digital funds and automatic fee schedules.
- Growing older Reviews: Detailed reviews exhibiting the age of excellent invoices.
- Vendor Administration: Centralized database for managing vendor info.
- Monetary Reporting: Integration with normal ledger for correct monetary reporting.
V. Finest Practices for Accounts Payable Administration
Whatever the accounting instruments used, environment friendly accounts payable administration requires adhering to greatest practices:
- Set up Clear Procedures: Develop and doc clear procedures for bill processing, fee authorization, and reconciliation.
- Implement Inner Controls: Set up robust inside controls to stop fraud and errors. This contains segregation of duties and common audits.
- Negotiate Favorable Fee Phrases: Negotiate with suppliers to acquire favorable fee phrases, corresponding to reductions for early fee.
- Monitor Money Stream: Intently monitor money circulate to make sure adequate funds can be found to satisfy fee obligations.
- Make the most of Expertise: Leverage accounting software program and different applied sciences to streamline AP processes and enhance effectivity.
- Common Reconciliation: Usually reconcile accounts payable with vendor statements to establish discrepancies and stop errors.
VI. Conclusion
The T-chart offers a basic understanding of how accounts payable transactions are recorded utilizing the double-entry bookkeeping system. Whereas it is a priceless instrument for studying the essential rules, its limitations grow to be obvious when managing a big quantity of transactions. Trendy accounting software program gives the scalability, element, and reporting capabilities mandatory for environment friendly and efficient accounts payable administration in at this time’s enterprise atmosphere. Nonetheless, a strong grasp of the underlying accounting rules, as illustrated by the T-chart, stays important for anybody concerned in managing an organization’s monetary affairs. By combining the foundational information with the ability of recent expertise, companies can optimize their accounts payable processes, enhance money circulate, and preserve correct monetary data.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Understanding and Using T-Chart Accounts Payable: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!