Understanding the pH Chart and Its Implications for Mineral Availability in Soil and Water
Associated Articles: Understanding the pH Chart and Its Implications for Mineral Availability in Soil and Water
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to Understanding the pH Chart and Its Implications for Mineral Availability in Soil and Water. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding the pH Chart and Its Implications for Mineral Availability in Soil and Water

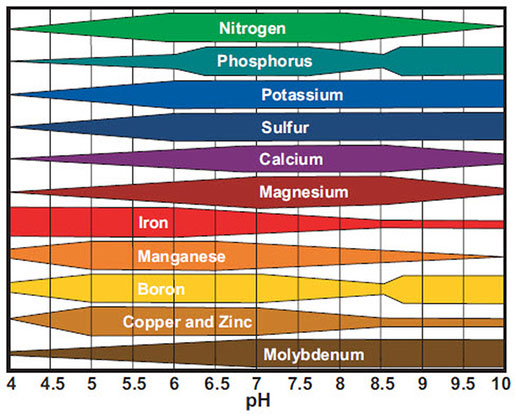
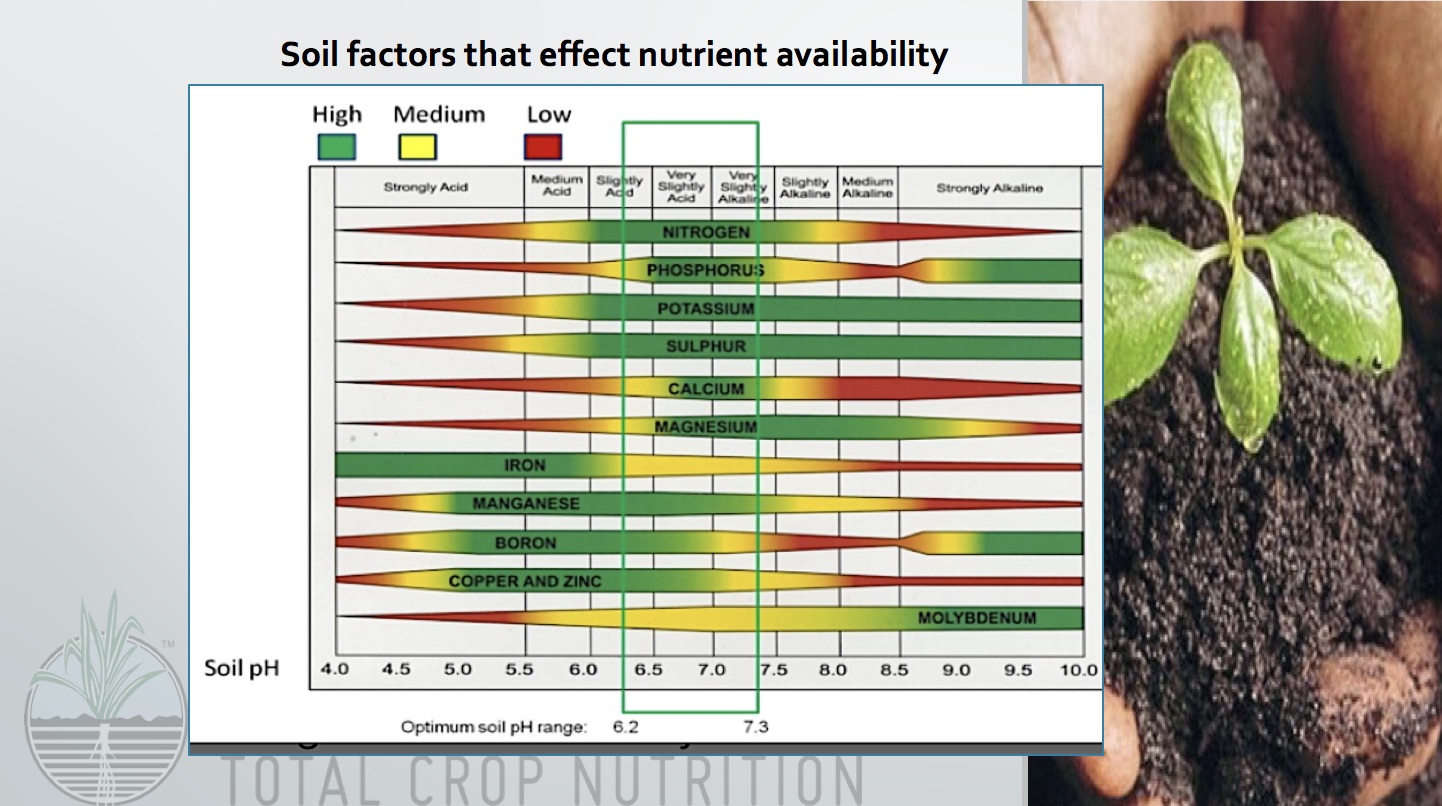
The pH scale, starting from 0 to 14, measures the acidity or alkalinity of an answer. A pH of seven is taken into account impartial, whereas values under 7 point out acidity and values above 7 point out alkalinity. This seemingly easy scale has profound implications for the provision and solubility of minerals in each soil and water, considerably impacting plant development, aquatic life, and even human well being. Understanding the connection between pH and mineral solubility, as depicted in a pH chart, is essential for numerous fields, from agriculture and horticulture to environmental science and water therapy.
The Chemistry Behind pH and Mineral Solubility:
The solubility of minerals is closely influenced by the hydrogen ion (H+) focus, which immediately pertains to pH. Many minerals are salts of weak acids or bases. Their solubility is ruled by equilibrium reactions which can be delicate to pH modifications. As an example, think about the solubility of phosphates. Phosphate minerals, essential for plant development, exist in numerous varieties, together with orthophosphates (H3PO4, H2PO4-, HPO42-, PO43-). The relative abundance of those varieties will depend on the pH. At low pH (acidic circumstances), extra H+ ions are current, resulting in the predominance of H2PO4- and H3PO4, that are extra soluble. As pH will increase (turns into extra alkaline), H+ ions are consumed, shifting the equilibrium in the direction of much less soluble varieties like HPO42- and PO43-. Because of this phosphate availability to vegetation is considerably increased in barely acidic to impartial circumstances.
Equally, the solubility of different important minerals like iron, manganese, copper, and zinc can be pH-dependent. These micronutrients are sometimes current as metallic oxides or hydroxides. In acidic circumstances, these compounds are usually extra soluble, making the minerals available to vegetation or organisms. Nevertheless, excessively acidic circumstances can result in toxicity because the excessive focus of soluble metals can grow to be dangerous. Conversely, at increased pH (alkaline circumstances), these metals are likely to precipitate out of answer, turning into much less out there. This explains why iron deficiency is widespread in alkaline soils, regardless of iron being ample within the soil itself. The iron is just unavailable to vegetation resulting from its low solubility.
Developing a pH Chart for Mineral Solubility:
A complete pH chart for mineral solubility would visually symbolize the solubility of assorted minerals throughout the pH vary. Such a chart would sometimes plot the solubility (usually expressed as focus in mg/L or ppm) on the y-axis and pH on the x-axis. Separate traces or curves could be plotted for every mineral, illustrating how its solubility modifications with various pH.
Whereas a universally relevant chart is troublesome to create resulting from variations in soil composition, water chemistry, and temperature, a normal illustration will be made. The chart would present:
-
Excessive solubility at low pH: Minerals like iron, manganese, zinc, and aluminum would exhibit excessive solubility at low pH values (under 6). This area usually represents acidic soils or waters.
-
Optimum pH vary: For many important vitamins, an optimum pH vary exists the place solubility is excessive sufficient for sufficient availability however not so excessive as to trigger toxicity. This vary sometimes falls between 6 and seven for a lot of important plant vitamins.
-
Decreased solubility at excessive pH: As pH will increase above 7, the solubility of many micronutrients decreases considerably. Iron, manganese, and zinc grow to be much less out there, resulting in deficiencies. Conversely, some components like molybdenum grow to be extra soluble at increased pH.
-
Precipitation and complexation: The chart might additionally point out the pH ranges the place precipitation of sure minerals happens, forming insoluble compounds. That is essential for understanding nutrient availability and potential environmental points like metallic contamination. Complexation with natural matter or different ligands can even have an effect on solubility, and this could possibly be integrated right into a extra refined chart.
Functions of the pH Chart:
Understanding the pH-dependent solubility of minerals has wide-ranging functions:
-
Agriculture and Horticulture: Soil pH is a vital consider plant vitamin. By analyzing soil pH and consulting a pH chart, farmers and gardeners can decide the provision of important vitamins and modify soil pH by way of liming (to extend pH) or the addition of acidifying brokers (to lower pH) to optimize plant development. This prevents nutrient deficiencies and ensures wholesome plant growth.
-
Aquatic Ecosystems: The pH of water considerably influences the well being of aquatic organisms. A pH chart may help perceive the provision of important minerals for aquatic life and predict potential toxicity from metals at completely different pH ranges. Water high quality administration methods usually contain pH changes to keep up optimum circumstances for aquatic ecosystems.
-
Environmental Science: Understanding mineral solubility helps assess the environmental affect of mining actions, industrial discharges, and agricultural runoff. A pH chart can be utilized to foretell the mobility and bioavailability of probably poisonous metals in contaminated websites, informing remediation methods.
-
Water Therapy: Water therapy vegetation usually modify the pH of water to optimize the removing of impurities. For instance, adjusting pH can affect the precipitation of metals or the effectivity of coagulation processes. A pH chart helps decide the optimum pH for environment friendly water therapy.
-
Human Well being: The pH of the human physique is tightly regulated. Mineral solubility performs a task in nutrient absorption and the potential toxicity of sure components. Understanding these relationships is essential in vitamin and toxicology.
Limitations of a Easy pH Chart:
It’s essential to acknowledge the restrictions of a simplistic pH chart. The solubility of a mineral shouldn’t be solely decided by pH. Different components considerably affect solubility, together with:
-
Temperature: Larger temperatures usually improve the solubility of most minerals.
-
Ionic Power: The presence of different ions within the answer can have an effect on mineral solubility by way of ionic interactions.
-
Natural Matter: Natural matter in soil can advanced with minerals, altering their solubility and availability.
-
Redox Potential: The oxidation-reduction potential (redox) of the answer influences the solubility of sure minerals, notably these involving transition metals.
-
Mineral Speciation: Minerals exist in numerous varieties (speciation) which have completely different solubilities. A easy chart can’t seize the complexity of all potential species.
Subsequently, whereas a pH chart gives a useful overview of the overall relationship between pH and mineral solubility, it must be used as a information relatively than a exact predictor. Extra refined fashions and analyses are sometimes mandatory for correct estimations of mineral availability in advanced programs.
Conclusion:
The pH chart serves as a basic instrument for understanding the advanced interaction between pH and mineral solubility. Its functions are far-reaching, impacting agriculture, environmental science, water therapy, and human well being. Whereas a easy chart gives a normal overview, it’s essential to recollect the restrictions and think about different components influencing mineral solubility for correct predictions and efficient administration methods. Additional analysis and growth of extra complete fashions are important to refine our understanding and enhance functions in numerous fields.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Understanding the pH Chart and Its Implications for Mineral Availability in Soil and Water. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!