Unveiling the Energy of Map Charts: Visualizing Geographic Information with Precision and Impression
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Energy of Map Charts: Visualizing Geographic Information with Precision and Impression
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to Unveiling the Energy of Map Charts: Visualizing Geographic Information with Precision and Impression. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Energy of Map Charts: Visualizing Geographic Information with Precision and Impression

Map charts, also called cartograms or thematic maps, are highly effective visualization instruments that overlay knowledge onto geographical maps. They transcend merely displaying places; they leverage the visible familiarity of maps to speak quantitative or qualitative details about particular geographic areas. This enables for a compelling and intuitive understanding of spatial patterns, developments, and relationships that might be tough to understand from tables or different static knowledge representations. This text delves into the intricacies of map charts, exploring their differing kinds, functions, design ideas, and the essential position they play in numerous fields.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Past Easy Location
A normal geographical map primarily serves to depict the bodily format of a area – displaying nations, states, cities, roads, and different geographical options. A map chart, nevertheless, takes this a step additional by integrating knowledge to disclose insights about these geographical areas. This knowledge may signify something from inhabitants density and revenue ranges to illness prevalence, election outcomes, or environmental components like air pollution ranges or deforestation charges. The visible illustration of this knowledge is often achieved via various colours, sizes, patterns, or symbols, instantly linked to the underlying knowledge values.
Varieties of Map Charts: A Various Toolkit for Information Visualization
The flexibility of map charts stems from the varied vary of strategies used to signify knowledge. Some widespread sorts embrace:
-
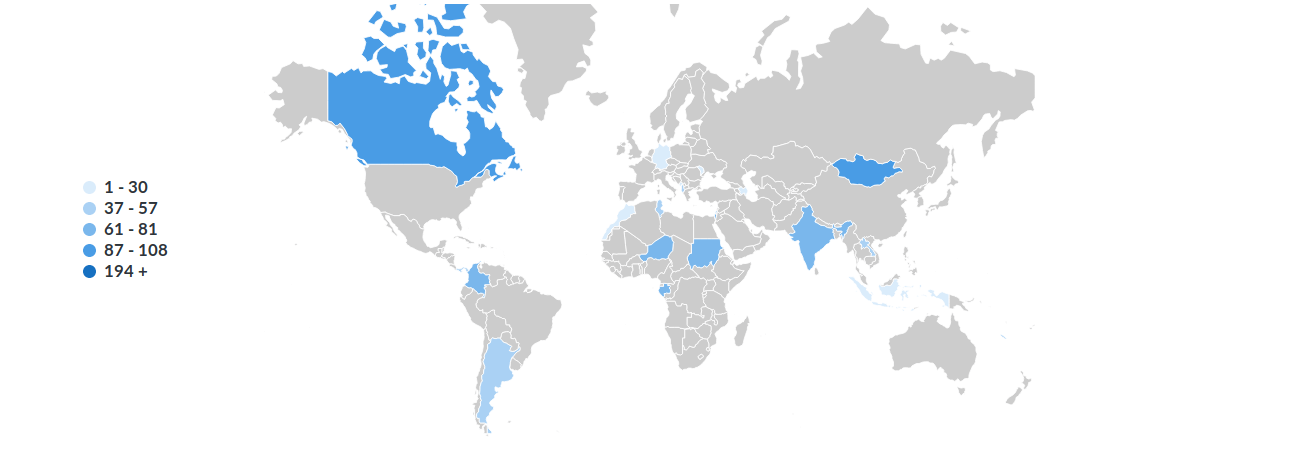
Choropleth Maps: These are arguably the most typical sort of map chart. They use shade shading or patterns to signify knowledge values throughout completely different geographical areas. Darker shades or particular patterns typically point out increased values, whereas lighter shades signify decrease values. Choropleth maps are wonderful for visualizing steady knowledge, equivalent to inhabitants density or revenue ranges, the place gradual modifications throughout areas are necessary. Nonetheless, they are often deceptive if the areas are drastically completely different in dimension; a small area with a excessive worth may seem disproportionately important in comparison with a big area with a decrease, but probably bigger general, worth.
-
Proportional Image Maps: These maps use symbols, usually circles or different shapes, whose dimension is proportional to the info worth for every area. Bigger symbols point out increased values, and smaller symbols signify decrease values. Any such map is efficient in displaying the magnitude of knowledge at particular places, making it appropriate for visualizing issues just like the variety of companies in a metropolis or the magnitude of an earthquake at its epicenter. Nonetheless, overcrowding can happen if many areas have excessive values, resulting in visible litter.
-
Dot Density Maps: As an alternative of utilizing symbols with various sizes, dot density maps use dots to signify particular person knowledge factors. The focus of dots in a specific space displays the info density in that area. Any such map is especially helpful for displaying the distribution of a discrete variable, equivalent to the situation of particular person homes or the unfold of a illness. Nonetheless, it might develop into visually overwhelming with massive datasets.
-
Isopleth Maps: Also called contour maps, isopleth maps use traces to attach factors of equal worth. These traces, referred to as isopleths, create zones of comparable knowledge values, serving to to visualise gradual modifications or gradients. Isopleth maps are generally used to signify steady knowledge like elevation, temperature, or precipitation.
-
Cartogram: Cartograms distort the geographical shapes of areas to emphasise the info values. The dimensions of a area is instantly proportional to the info worth, making it visually putting. This technique is useful for showcasing relative magnitudes, but it surely sacrifices geographical accuracy.
-
Movement Maps: These maps illustrate motion or move of knowledge between completely different places. That is achieved utilizing traces or arrows whose thickness or shade represents the magnitude of the move. Movement maps are generally used to indicate migration patterns, commerce routes, or transportation networks.
Design Ideas for Efficient Map Charts
Creating an efficient map chart includes extra than simply overlaying knowledge on a map. Cautious consideration of design ideas is essential to make sure readability, accuracy, and affect:
-
Selecting the Proper Map Kind: The choice of the map chart sort relies upon closely on the character of the info and the message to be conveyed. Understanding the strengths and limitations of every sort is crucial.
-
Colour Palette: A well-chosen shade palette enhances readability and emphasizes knowledge patterns. Utilizing a sequential shade scheme for steady knowledge (e.g., from gentle to darkish) is usually advisable. Diverging shade schemes can be utilized to spotlight deviations from a central worth. It’s essential to think about shade blindness and guarantee enough distinction.
-
Legend: A transparent and concise legend is crucial for deciphering the map. It ought to clearly outline the which means of colours, symbols, or patterns used.
-
Scale and Projection: The selection of map projection impacts the accuracy of distances and areas. Choosing an applicable projection based mostly on the geographical space and the kind of knowledge is important. The dimensions needs to be clearly indicated to keep away from misinterpretations.
-
Information Aggregation: For big datasets, knowledge aggregation could be essential to keep away from visible litter. Nonetheless, aggregation needs to be executed rigorously to keep away from shedding necessary particulars.
-
Labels and Annotations: Strategic labeling of areas or options can enhance understanding and spotlight key findings. Annotations can be utilized to supply further context or rationalization.
-
Context and Readability: The map chart needs to be introduced inside a bigger context, offering enough background data to facilitate interpretation. Keep away from pointless litter and deal with clear communication.
Purposes of Map Charts Throughout Various Fields
Map charts discover functions in a wide selection of fields, together with:
-
Public Well being: Visualizing illness outbreaks, healthcare useful resource distribution, and well being disparities.
-
Environmental Science: Mapping air pollution ranges, deforestation charges, local weather change impacts, and biodiversity hotspots.
-
Enterprise and Advertising: Analyzing market share, buyer demographics, and figuring out optimum places for companies.
-
City Planning: Mapping inhabitants density, infrastructure growth, and concrete sprawl.
-
Politics and Elections: Visualizing election outcomes, voter turnout, and political social gathering assist.
-
Economics and Finance: Mapping revenue inequality, poverty charges, and financial exercise.
-
Social Sciences: Mapping social phenomena equivalent to crime charges, schooling ranges, and migration patterns.
Limitations and Misinterpretations
Whereas map charts are highly effective instruments, in addition they have limitations:
-
Map Projection Distortions: All map projections inevitably distort geographical shapes and distances to some extent.
-
Information Aggregation Points: Aggregating knowledge can masks necessary native variations.
-
Deceptive Visualizations: Poorly designed map charts can result in misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions.
-
Information Bias: The information used to create the map chart might be biased, resulting in skewed interpretations.
Conclusion: A Highly effective Software for Speaking Geographic Information
Map charts are indispensable instruments for visualizing and speaking geographic knowledge. Their skill to combine spatial data with quantitative or qualitative knowledge makes them extremely efficient in revealing patterns, developments, and relationships that might in any other case be tough to discern. Nonetheless, it’s essential to grasp the strengths and limitations of various map chart sorts, adhere to sound design ideas, and concentrate on potential sources of bias and misinterpretation. When used successfully, map charts can present highly effective insights and contribute considerably to knowledgeable decision-making throughout a variety of disciplines. The cautious consideration of knowledge illustration, design aesthetics, and the suitable context ensures that these highly effective visualizations successfully talk advanced geographic data, resulting in a deeper and extra nuanced understanding of the world round us.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into Unveiling the Energy of Map Charts: Visualizing Geographic Information with Precision and Impression. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!